Research Area C - Publications 2007
27-Dec-2007

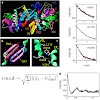
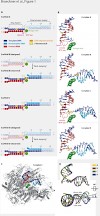
Synthesis of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) by RNA polymerase (Pol) I is the first step in ribosome biogenesis and a regulatory switch in eukaryotic cell growth. Here we report the 12 A° cryoelectron microscopic structure for the complete 14-subunit yeast Pol I, a homology model for the core enzyme, and the crystal structure of the subcomplex A14/43. In the resulting ...
16-Dec-2007
Molecular Microbiology, online article
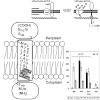
In an acidic (pH 5.8) and lysine-rich environment Escherichia coli induces expression of the cadBA operon which encodes CadA, catalysing the decarboxylation of lysine to cadaverine, and CadB, the lysine/cadaverine antiporter. cadBA expression is dependent on CadC, a membrane-integrated transcriptional activator which belongs to the ToxR-like protein family and ...
15-Dec-2007
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
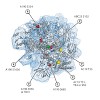
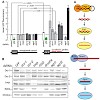
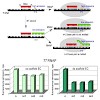
All nuclear RNA polymerases are phosphoprotein complexes. Yeast RNA polymerase I (Pol I) contains approximately 15 phosphate groups, distributed to 5 of the 14 subunits. Information about the function of the single phosphosites and their position in the primary, secondary and tertiary structure is lacking. We used a rapid and efficient way to purify yeast RNA Pol ...
07-Dec-2007
www.dfg.de
The Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation, DFG) announced yesterday the winners of its 2008 Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Prize. At its meeting on December 6th 2007, the DFG Joint Committee named CIPSM researcher Dr. Elena Conti as recipient of Germany's most highly endowed research award. Elena will receive 1.25 million euros flexibly over a ...
04-Dec-2007
PNAS, 2007, vol. 104, no. 49, 19315–20 published on 04.12.2007
www.pnas.org, online article
Protein synthesis in the chloroplast is carried out by chloroplast ribosomes (chloro-ribosome) and regulated in a light-dependent manner. Chloroplast or plastid ribosomal proteins (PRPs) generally are larger than their bacterial counterparts, and chloro-ribosomes contain additional plastid-specific ribosomal proteins (PSRPs); however, it is unclear to what extent ...
15-Nov-2007
Nature, 2007, 450, 445-49 published on 15.11.2007
Nature, online article
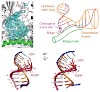
RNA polymerase (Pol) II catalyses DNA-dependent RNA synthesis during gene tran- scription. There is, however, evidence that Pol II also possesses RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) activity. Pol II can use a homopolymeric RNA template, can extend RNA by several nucleotides in the absence of DNA, and has been implicated in the replication of the RNA genomes of ...
15-Nov-2007

"There's great excitement here" “If the show is over in five years, then it was but a flash in the pan”
12-Nov-2007
Chemical & Engineering News, online article

CISPLATIN HAS BEEN USED to treat cancer for decades. But the drug's detailed molecular interactions with the enzymes it aims to interrupts have remained obscure. In two separate papers, researchers are now reporting the first crystal structures of cisplatin complexed with two key enzymes. "For the first time, we are getting deep insight on what goes on at the ...
11-Nov-2007
www.nature.com/nsmb, online article

The anticancer drug cisplatin forms 1,2-d(GpG) DNA intrastrand cross-links (cisplatin lesions) that stall RNA polymerase II (Pol II) and trigger transcription-coupled DNA repair. Here we present a structure-function analysis of Pol II stalling at a cisplatin lesion in the DNA template. Pol II stalling results from a translocation barrier that prevents delivery of ...
09-Nov-2007
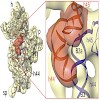
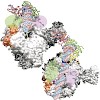
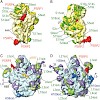
Ribosome binding factor A (RbfA) is a bacterial cold shock response protein, required for an efficient processing of the 5' end of the 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) during assembly of the small (30S) ribosomal subunit. Here we present a crystal structure of Thermus thermophilus (Tth) RbfA and a three-dimensional cryo-electron microscopic (EM) map of the Tth 30S.RbfA ...
09-Nov-2007
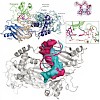
DNA polymerase eta (Pol eta) is a eukaryotic lesion bypass polymerase that helps organisms to survive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, and tumor cells to gain resistance against cisplatin-based chemotherapy. It allows cells to replicate across cross-link lesions such as 1,2-d(GpG) cisplatin adducts (Pt-GG) and UVinduced cis–syn thymine dimers. We present ...
01-Nov-2007
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, online article
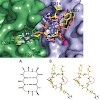
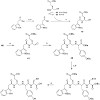
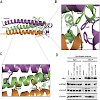
An unselective cyclic peptide integrin ligand was sequentially N-methylated by a designed approach, where only the externally oriented (solvent exposed) amide bonds were N-methylated. The N-methylation resulted in tremendous enhancement in selectivity among the different integrin receptor subtypes (alpha5beta1, alphavbeta3, and alphaIIbbeta3). Conformational and ...