28-Dec-2015
Christian Schmidt, Thomas Becker, André Heuer, Katharina Braunger, Vivekanandan Shanmuganathan, Markus Pech, Otto Berninghausen, Daniel N. Wilson, Roland Beckmann
Nucl. Acids Res., doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1517
Nucl. Acids Res., online article
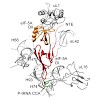
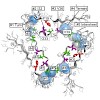
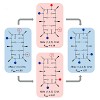
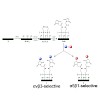
During protein synthesis, ribosomes become stalled on polyproline-containing sequences, unless they are rescued in archaea and eukaryotes by the initiation factor 5A (a/eIF-5A) and in bacteria by the homologous protein EF-P. While a structure of EF-P bound to the 70S ribosome exists, structural insight into eIF-5A on the 80S ribosome has been lacking. Here we ...
|READ MORE|
09-Dec-2015
Oleg V. Maltsev, Udaya Kiran Marelli, Tobias G. Kapp, Francesco Saverio Di Leva, Salvatore Di Maro, Markus Nieberler, Ute Reuning, Markus Schwaiger, Ettore Novellino, Luciana Marinelli, Horst Kessler
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Volume 55, Issue, Pages 1535–1539, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201508709
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online aticle
The αvβ6 integrin binds the RGD-containing peptide of the foot and mouth disease virus with high selectivity. In this study, the long binding helix of this ligand was downsized to an enzymatically stable cyclic peptide endowed with sub-nanomolar binding affinity toward the αvβ6 receptor and remarkable selectivity against other integrins. Computational studies ...
|READ MORE|
09-Dec-2015
Tobias G. Kapp, Maximilian Fottner, Oleg V. Maltsev, Horst Kessler
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Volume 55, Issue 4, Pages 1540–1543, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201508713
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article
Due to its unique role as a hydrogen-bond donor and its positive charge, the guanidine group is an important pharmacophoric group and often used in synthetic ligands. The chemical modification of the guanidine group is often considered to destroy its function. Herein, we show that the N-methylation, N-alkylation, or N-acylation of the guanidine group can be used ...
|READ MORE|
08-Dec-2015
Alain C. Jung, Anne-Marie Ray, Ludivine Ramolu, Christine Macabre, Florian Simon, Fanny Noulet, Anne-Florence Blandin, Guillaume Renner, Maxime Lehmann, Laurence Choulier, Horst Kessler, Joseph Abecassis, Monique Dontenwill, Sophie Martin
Oncotarget, 6(39):41884-901, doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6099
Oncotarget, online article
Distant metastases arise in 20-30% of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (HNSCC) in the 2 years following treatment. Therapeutic options are limited and the outcome of the patients is poor. The identification of predictive biomarkers of patient at risk for distant metastasis and therapies are urgently needed. We previously identified a ...
|READ MORE|
01-Dec-2015
Riddhiman Sarkar, Diana C. Rodriguez Camargo, Guido Pintacuda, Bernd Reif
J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 6 (24), pp 5040–5044, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b02467
J. Phys. Chem. Lett., online article
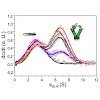
Spin-state-selective excitation (S3E) experiments allow the selection of individual transitions in a coupled two spin system. We show that in the solid state, the dipole–dipole interaction (DD) between 15N and 1H in a 1H–15N bond and the chemical shift anisotropy (CSA) of 15N in an amide moiety mutually cancel each other for a particular multiplet component at ...
|READ MORE|
26-Nov-2015
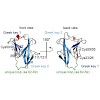
Charlotte Lässig, Sarah Matheisl, Konstantin MJ Sparrer, Carina C de Oliveira Mann, Manuela Moldt, Jenish R Patel, Marion Goldeck, Gunther Hartmann, Adolfo García-Sastre, Veit Hornung, Karl-Klaus Conzelmann, Roland Beckmann, Karl-Peter Hopfner
eLife, 4:e10859. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.10859
eLife, online article
The cytosolic antiviral innate immune sensor RIG-I distinguishes 5′ tri- or diphosphate containing viral double-stranded (ds) RNA from self-RNA by an incompletely understood mechanism that involves ATP hydrolysis by RIG-I's RNA translocase domain. Recently discovered mutations in ATPase motifs can lead to the multi-system disorder Singleton-Merten Syndrome (SMS) ...
|READ MORE|
16-Nov-2015
Annemarie Horn, Janosch Hennig, Yasar L. Ahmed, Gunter Stier, Klemens Wild, Michael Sattler, Irmgard Sinning
Nature Communications, 6, Article number: 8875, doi:10.1038/ncomms9875
Nature Communications, online article
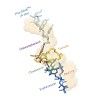
Canonical membrane protein biogenesis requires co-translational delivery of ribosome-associated proteins to the Sec translocase and depends on the signal recognition particle (SRP) and its receptor (SR). In contrast, high-throughput delivery of abundant light-harvesting chlorophyll a,b-binding proteins (LHCPs) in chloroplasts to the Alb3 insertase occurs ...
|READ MORE|
12-Nov-2015
Molecular Cell, 61,doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2015.10.019
Molecular Cell , online article
Protein synthesis is a major target within the bacterial cell for antibiotics. Investigations into ribosome-targeting antibiotics have provided much needed functional and structural insight into their mechanism of action. However, the increasing prevalence of multi-drug-resistant bacteria has limited the utility of our current arsenal of clinically relevant ...
|READ MORE|
12-Nov-2015
Molecular Cell, Volume 61, Issue 1, p3–14, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.10.019
Molecular Cell, online article
Protein synthesis is a major target within the bacterial cell for antibiotics. Investigations into ribosome-targeting antibiotics have provided much needed functional and structural insight into their mechanism of action. However, the increasing prevalence of multi-drug-resistant bacteria has limited the utility of our current arsenal of clinically relevant ...
|READ MORE|
06-Nov-2015
Cardine N. Nokwe, Manuel Hora, Martin Zacharias, Hisashi Yagi, Christine John, Bernd Reif , Yuji Goto, Johannes Buchner
Journal of Molecular Biology, Volume 427, Issue 22, Pages 3572–3586, doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2015.09.012
Journal of Molecular Biology, online article
The association of light chains (LCs) and heavy chains is the basis for functional antibodies that are essential for adaptive immune responses. However, in some cases, LCs and especially fragments consisting of the LC variable (VL) domain are pathologically deposited in fatal aggregation diseases. The two domains of the LC are connected by a highly conserved ...
|READ MORE|
05-Nov-2015
J. Rajan Prabu,Marisa Müller, Andreas W. Thomae, Steffen Schüssler, Fabien Bonneau, Peter B. Becker, Elena Conti
Molecular Cell, Volume 60, Issue 3, p487–499, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.10.011
Molecular Cell, online article
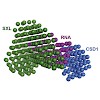
The MLE helicase remodels the roX lncRNAs, enabling the lncRNA-mediated assembly of the Drosophila dosage compensation complex. We identified a stable MLE core comprising the DExH helicase module and two auxiliary domains: a dsRBD and an OB-like fold. MLEcore is an unusual DExH helicase that can unwind blunt-ended RNA duplexes and has specificity for uridine ...
|READ MORE|
05-Nov-2015
Molecular Microbiology, DOI: 10.1111/mmi.13233
Molecular Microbiology, online article
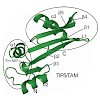
Synthesis of polyproline proteins leads to translation arrest. To overcome this ribosome stalling effect, bacteria depend on a specialized translation elongation factor P (EF-P), being orthologous and functionally identical to eukaryotic/archaeal elongation factor e/aIF-5A (recently renamed ‘EF5’). EF-P binds to the stalled ribosome between the peptidyl-tRNA ...
|READ MORE|
28-Oct-2015
Julia M. Eckl, Matthias J. Scherr, Lee Freiburger, Marina A. Daake, Michael Sattler, Klaus Richter
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 290, 30843-30854 , doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.693150
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, online article
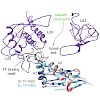
Protein kinases are the most prominent group of heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) clients and are recruited to the molecular chaperone by the kinase-specific cochaperone cell division cycle 37 (Cdc37). The interaction between Hsp90 and nematode Cdc37 is mediated by binding of the Hsp90 middle domain to an N-terminal region of Caenorhabditis elegans Cdc37 (CeCdc37). ...
|READ MORE|
27-Oct-2015
Sevim Ozgur, Jérôme Basquin, Anastasiia Kamenska, Witold Filipowicz, Nancy Standart, Elena Conti
Cell Reports, 13, 703–711, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.09.033
Cell Reports, online article
The DEAD-box protein DDX6 is a central component of translational repression mechanisms in maternal mRNA storage in oocytes and microRNA-mediated silencing in somatic cells. DDX6 interacts with the CCR4-NOT complex and functions in concert with several post-transcriptional regulators, including Edc3, Pat1, and 4E-T. We show that the conserved CUP-homology domain ...
|READ MORE|
24-Oct-2015
Calogero D’Alessandria, Karolin Pohle, Florian Rechenmacher, Stefanie Neubauer, Johannes Notni, Hans-Jürgen Wester, Markus Schwaiger, Horst Kessler, Ambros J. Beer
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, Volume 43, Issue 5, pp 953-963, DOI 10.1007/s00259-015-3218-z
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, online article
Purpose Integrins are transmembrane receptors responsible for cell–cell adhesion and cell–extracellular matrix binding and play an important role in angiogenesis and tumour metastasis. For this reason, integrins are increasingly used as targets for molecular imaging. Up to now interest has mostly been focused on the integrin subtype αvβ3. However, targeting of ...
|READ MORE|
20-Oct-2015
C. Herranz-Diez, Q. Li, C. Lamprecht, C. Mas-Moruno, S. Neubauer, H.Kessler, J.M. Manero, J. Guillem-Martí, C. Selhuber-Unkel
Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, Volume 136, Pages 704–711, doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.10.008
Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, online article
Implant materials require optimal biointegration, including strong and stable cell-material interactions from the early stages of implantation. Ti-based alloys with low elastic modulus are attracting a lot of interest for avoiding stress shielding, but their osseointegration potential is still very low. In this study, we report on how cell adhesion is influenced ...
|READ MORE|
16-Oct-2015
G Renner, H Janouskova, F Noulet, V Koenig, E Guerin, S Bär, J Nuesch, F Rechenmacher, S Neubauer, H Kessler, A-F Blandin, L Choulier, N Etienne-Selloum, M Lehmann, I Lelong-Rebel, S Martin, M Dontenwill
Cell Death & Differentiation, 23, 640-653, doi:10.1038/cdd.2015.131
Cell Death & Differentiation, online article
Integrin α5β1 expression is correlated with a worse prognosis in high-grade glioma. We previously unraveled a negative crosstalk between integrin α5β1 and p53 pathway, which was proposed to be part of the resistance of glioblastoma to chemotherapies. The restoration of p53 tumor-suppressor function is under intensive investigations for cancer therapy. However, ...
|READ MORE|
12-Oct-2015
Andi Mainz, Jirka Peschek, Maria Stavropoulou, Katrin C Back, Benjamin Bardiaux, Sam Asami, Elke Prade, Carsten Peters, Sevil Weinkauf, Johannes Buchner, Bernd Reif
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 22, 898–905, doi:10.1038/nsmb.3108
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article
Small heat-shock proteins, including αB-crystallin (αB), play an important part in protein homeostasis, because their ATP-independent chaperone activity inhibits uncontrolled protein aggregation. Mechanistic details of human αB, particularly in its client-bound state, have been elusive so far, owing to the high molecular weight and the heterogeneity of these ...
|READ MORE|
09-Oct-2015
Leonidas Emmanouilidis, Mohanraj Gopalswamy, Daniel M. Passonc, Matthias Wilmanns, Michael Sattler
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.09.034
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, online article
The peroxisomal proteins (peroxins) that mediate the import of peroxisomal matrix proteins have been identified. Recently, the purification of a functional peroxisomal translocon has been reported. However, the molecular details of the import pathways and the mechanisms by which the cargo is translocated into the lumen of the organelle are still poorly ...
|READ MORE|
03-Oct-2015
Evdokia-Anastasia Giannopoulou, Leonidas Emmanouilidis, Michael Sattler, Gabriele Dodt, Matthias Wilmanns
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.09.031
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, online article
The correct topogenesis of peroxisomal membrane proteins is a crucial step for the formation of functioning peroxisomes. Although this process has been widely studied, the exact mechanism with which it occurs has not yet been fully characterized. Nevertheless, it is generally accepted that peroxisomes employ three proteins – Pex3, Pex19 and Pex16 in mammals – for ...
|READ MORE|
28-Sep-2015
Elke Prade, Heiko J. Bittner, Riddhiman Sarkar, Juan Miguel Lopez del Amo, Gerhard Althoff-Ospelt, Gerd Multhaup, Peter W. Hildebrand, Bernd Reif
JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY, VOLUME 290, NUMBER 48, DOI 10.1074/jbc.M115.675215
JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY, online article
Alzheimer's disease is the most severe neurodegenerative disease worldwide. In the past years, a plethora of small molecules interfering with amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregation have been suggested. However, their mode of interaction with amyloid fibers is not understood. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are known γ-secretase modulators (GSMs). It has been ...
|READ MORE|
18-Sep-2015
Lili K. Doerfel, Ingo Wohlgemuth, Vladimir Kubyshkin, Agata L. Starosta, Daniel N. Wilson, Nediljko Budisa, Marina V. Rodnina
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 137 (40), pp 12997–13006, DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5b07427
J. Am. Chem. Soc., online article
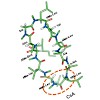
The peptide bond formation with the amino acid proline (Pro) on the ribosome is slow, resulting in translational stalling when several Pro have to be incorporated into the peptide. Stalling at poly-Pro motifs is alleviated by the elongation factor P (EF-P). Here we investigate why Pro is a poor substrate and how EF-P catalyzes the reaction. Linear free energy ...
|READ MORE|
07-Sep-2015
Bertrand Beckert, Alexej Kedrov, Daniel Sohmen, Georg Kempf, Klemens Wild, Irmgard Sinning, Henning Stahlberg, Daniel N Wilson, Roland Beckmann
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 22, 767–773, doi:10.1038/nsmb.3086
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article
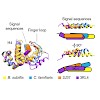
The signal recognition particle (SRP) recognizes signal sequences of nascent polypeptides and targets ribosome–nascent chain complexes to membrane translocation sites. In eukaryotes, translating ribosomes are slowed down by the Alu domain of SRP to allow efficient targeting. In prokaryotes, however, little is known about the structure and function of Alu ...
|READ MORE|
04-Sep-2015
Udaya Kiran Marelli, Oded Ovadia, Andreas Oliver Frank, Jayanta Chatterjee, Chaim Gilon, Amnon Hoffman, Horst Kessler
Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 15148 – 15152, DOI: 10.1002/chem.201501600
Chem. Eur. J.,online article
Recent structural studies on libraries of cyclic hexapeptides led to the identification of common backbone conformations that may be instrumental to the oral availability of peptides. Furthermore, the observation of differential Caco-2 permeabilities of enantiomeric pairs of some of these peptides strongly supports the concept of conformational specificity driven ...
|READ MORE|
30-Aug-2015
Lee Freiburger, Miriam Sonntag, Janosch Hennig, Jian Li, Peijian Zou, Michael Sattler
Journal of Biomolecular NMR, Volume 63, Issue 1, pp 1-8, DOI 10.1007/s10858-015-9981-0
J Biomol NMR, online article
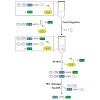
NMR studies of multi-domain protein complexes provide unique insight into their molecular interactions and dynamics in solution. For large proteins domain-selective isotope labeling is desired to reduce signal overlap, but available methods require extensive optimization and often give poor ligation yields. We present an optimized strategy for segmental labeling ...
|READ MORE|
10-Aug-2015
Agata Butryn, Jan M Schuller, Gabriele Stoehr, Petra Runge-Wollmann, Friedrich Förster, David T Auble, Karl-Peter Hopfner
eLife, 4, e07432, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.07432
eLife, online article
Swi2/Snf2 ATPases remodel substrates such as nucleosomes and transcription complexes to control a wide range of DNA-associated processes, but detailed structural information on the ATP-dependent remodeling reactions is largely absent. The single subunit remodeler Mot1 (modifier of transcription 1) dissociates TATA box-binding protein (TBP):DNA complexes, offering ...
|READ MORE|
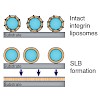
07-Aug-2015
Johannes P. Frohnmayer, Dorothea Brîggemann, Christian Eberhard, Stefanie Neubauer, Christine Mollenhauer, Heike Boehm, Horst Kessler, Benjamin Geiger, Joachim P. Spatz
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 12472 –12478, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201503184
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article
To shed light on cell-adhesion-related molecular pathways, synthetic cells offer the unique advantage of a well-controlled model system with reduced molecular complexity. Herein, we show that liposomes with the reconstituted platelet integrin αIIbβ3 as the adhesion-mediating transmembrane protein are a functional minimal cell model for studying cellular adhesion ...
|READ MORE|
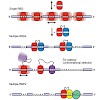
29-Jul-2015
Debora Lika Makino, Benjamin Schuch, Elisabeth Stegmann, Marc Baumgärtner, Claire Basquin, Elena Conti
Nature, 524, 54–58, doi:10.1038/nature14865
Nature, online article
The eukaryotic exosome is a conserved RNA-degrading complex that functions in RNA surveillance, turnover and processing. How the same machinery can either completely degrade or precisely trim RNA substrates has long remained unexplained. Here we report the crystal structures of a yeast nuclear exosome containing the 9-subunit core, the 3′–5′ RNases Rrp44 and ...
|READ MORE|
28-Jul-2015
Minying Cai, Udaya Kiran Marelli, Jennifer Bao, Johannes G. Beck, Florian Opperer, Florian Rechenmacher, Kaitlyn R. McLeod, Morgan R. Zingsheim, Lucas Doedens, Horst Kessler, Victor J. Hruby
J. Med. Chem., 2015, 58 (16), pp 6359–6367, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00102
J. Med. Chem., online article
Human melanocortin receptors (hMCRs) have been challenging targets to develop ligands that are explicitly selective for each of their subtypes. To modulate the conformational preferences of the melanocortin ligands and improve the biofunctional agonist/antagonist activities and selectivities, we have applied a backbone N-methylation approach on ...
|READ MORE|
23-Jul-2015
Martina Müller, Tobias Deimling, Karl-Peter Hopfner, Gregor Witte
Biochemical Journal, 469 (3) 367-374, DOI: 10.1042/BJ20150373
Biochemical Journal, online article
The identification of the essential bacterial second messenger cyclic-di-AMP (c-di-AMP) synthesized by the DNA-integrity scanning protein A (DisA) has opened up a new and emerging field in bacterial signalling. To further analyse the diadenylate cyclase (DAC) reaction catalysed by the DAC domains of DisA, we crystallized Thermotoga maritima DisA in the presence ...
|READ MORE|
14-Jul-2015
Katharina Nakel, Fabien Bonneau, Christian R. Eckmann, Elena Conti
PNAS, vol. 112 no. 28, 8614–8619, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1504648112
PNAS, online article
The Caenorhabditis elegans germ-line development defective (GLD)-2–GLD-3 complex up-regulates the expression of genes required for meiotic progression. GLD-2–GLD-3 acts by extending the short poly(A) tail of germ-line–specific mRNAs, switching them from a dormant state into a translationally active state. GLD-2 is a cytoplasmic noncanonical poly(A) polymerase ...
|READ MORE|
10-Jul-2015
N. Helge Meyer, Hubert Mayerhofer, Konstantinos Tripsianes, Silke Blindow, Daniela Barths, Astrid Mewes, Thomas Weimar, Thies Köhli, Steffen Bade, Tobias Madl, Andreas Frey, Helmut Haas, Jochen Mueller-Dieckmann, Michael Sattler, Gabriele Schramm
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, VOL. 290, NO. 36, pp. 22111–22126, doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.675066
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, online article
The IL-4-inducing principle from Schistosoma mansoni eggs (IPSE/α-1), the major secretory product of eggs from the parasitic worm S. mansoni, efficiently triggers basophils to release the immunomodulatory key cytokine interleukin-4. Activation by IPSE/α-1 requires the presence of IgE on the basophils, but the detailed molecular mechanism underlying activation is ...
|READ MORE|
07-Jul-2015
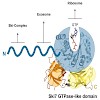
Eva Kowalinski, Anthony Schuller, Rachel Green, Elena Conti
Structure, Volume 23, Issue 7, p1336–1343, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2015.04.018
Structure, online article
Ski7 is a cofactor of the cytoplasmic exosome in budding yeast, functioning in both mRNA turnover and non-stop decay (NSD), a surveillance pathway that degrades faulty mRNAs lacking a stop codon. The C-terminal region of Ski7 (Ski7C) shares overall sequence similarity with the translational GTPase (trGTPase) Hbs1, but whether Ski7 has retained the properties of a ...
|READ MORE|
08-Jun-2015
Florian Ulrich Seifert, Katja Lammens,
Karl-Peter Hopfner Acta Cryst.,
2015,
http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X15007566, F71, 752-757 published on 08.06.2015
Acta Cryst., online article
Together with the Rad50 ATPase, the Mre11 nuclease forms an evolutionarily conserved protein complex that plays a central role in the repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). Mre11-Rad50 detects and processes DNA ends, and has functions in the tethering as well as the signalling of DSBs. The Mre11 dimer can bind one or two DNA ends or hairpins, and processes ...
|READ MORE|
08-Jun-2015
Janosch Hennig,
Michael Sattler Bioessays,
2015,
DOI: 10.1002/bies.201500033, published on 08.06.2015
Bioessays,
online article
RNA binding proteins (RBPs) are key factors for the regulation of gene expression by binding to cis elements, i.e. short sequence motifs in RNAs. Recent studies demonstrate that cooperative binding of multiple RBPs is important for the sequence-specific recognition of RNA and thereby enables the regulation of diverse biological activities by a limited set of ...
|READ MORE|
04-Jun-2015
Yury S. Polikanov, Agata L. Starosta, Manuel F. Juette, Roger B. Altman, Daniel S. Terry, Wanli Lu, Benjamin J. Burnett, George Dinos, Kevin A. Reynolds, Scott C. Blanchard, Thomas A. Steitz,
Daniel N Wilson Molecular Cell,
2015,
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.04.014, Volume 58, Issue 5, p832–844 published on 04.06.2015
Molecular Cell,
online article
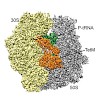
The increase in multi-drug-resistant bacteria is limiting the effectiveness of currently approved antibiotics, leading to a renewed interest in antibiotics with distinct chemical scaffolds. We have solved the structures of the Thermus thermophilus 70S ribosome with A-, P-, and E-site tRNAs bound and in complex with either the aminocyclitol-containing antibiotic ...
|READ MORE|
01-Jun-2015
Veronika Haslbeck, Adrian Drazic, Julia M. Eckl, Ferdinand Alte, Martin Helmuth, Grzegorz Popowicz, Werner Schmidt, Frank Braun, Matthias Weiwad, Gunter Fischer, Gerd Gemmecker, Michael Sattler, Frank Striggow, Michael Groll, Klaus Richter
Bioscience Reports,
2015,
DOI: 10.1042/BSR20150042, 35 (3) e00210 published on 01.06.2015
Bioscience Reports, online article
Protein phosphatase 5 (PP5) is an evolutionary conserved serine/threonine phosphatase. Its dephosphorylation activity modulates a diverse set of cellular factors including protein kinases and the microtubule-associated tau protein involved in neurodegenerative disorders. It is auto-regulated by its heat-shock protein (Hsp90)-interacting tetratricopeptide repeat ...
|READ MORE|
29-May-2015
Anders Friberg, Sybille Thumann, Janosch Hennig, Peijian Zou, Elfriede Nössner, Paul D. Ling,
Michael Sattler, Bettina Kempkes
PLOS Pathogens,
2015,
DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004910, published on 29.05.2015
PLOS Pathogens,
online article
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a γ-herpesvirus that may cause infectious mononucleosis in young adults. In addition, epidemiological and molecular evidence links EBV to the pathogenesis of lymphoid and epithelial malignancies. EBV has the unique ability to transform resting B cells into permanently proliferating, latently infected lymphoblastoid cell lines. ...
|READ MORE|
15-May-2015
Judith Guasch, Bert Conings, Stefanie Neubauer, Florian Rechenmacher, Karen Ende, Claudio G. Rolli, Christian Kappel ,Viktoria Schaufler , Alexandre Micoulet, Horst Kessler, Hans-Gerd Boyen, Elisabetta Ada Cavalcanti-Adam, Joachim P. Spatz
Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3737–3747, DOI: 10.1002/adma.201500900
Adv. Mater.,online article
Orthogonally functionalized binary micropatterned substrates are produced using a novel protocol. The use of adequate peptido-mimetics enables an unprecedented segregation of purified αvβ3 and α5β1 integrins in adjacent microislands and evidences the preference of U2OS cells to colocalize such receptors. Moreover, this tendency can be altered by varying the ...
|READ MORE|
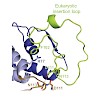
12-May-2015
Sophie Buchner, Andreas Schlundt, Jürgen Lassak,
Michael Sattler,
Kirsten Jung Journal of Molecular Biology,
2015,
doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2015.05.001, published on 12.05.2015
Journal of Molecular Biology,
online article
The pH-responsive one-component signaling system CadC in Escherichia coli belongs to the family of ToxR-like proteins, whose members share a conserved modular structure, with an N-terminal cytoplasmic winged helix–turn–helix DNA-binding domain being followed by a single transmembrane helix and a C-terminal periplasmic pH-sensing domain. In E. coli CadC, a ...
|READ MORE|
05-May-2015
Varun Bhaskar, Jérôme Basquin, Elena Conti
Structure, Volume 23, Issue 5, p921–928, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2015.03.011
Structure, online article
The Ccr4-Not complex regulates eukaryotic gene expression at multiple levels, including mRNA turnover, translational repression, and transcription. We have studied the ubiquitylation module of the yeast Ccr4-Not complex and addressed how E3 ligase binds cognate E2 and how it is tethered to the complex. The 2.8-Å resolution crystal structure of the N-terminal RING ...
|READ MORE|
27-Apr-2015
Udaya Kiran Marelli, Jacqueline Bezençon, Eduard Puig, Beat Ernst,
Horst Kessler Chemistry - A European Journal,
2015,
DOI: 10.1002/chem.201501270, Volume 21, Issue 22, pages 8023–8027, published on 27.04.2015
Chemistry - A European Journal,
online article
Recently, oral absorption of cyclic hexapeptides was improved by N-methylation of their backbone amides. However, the number and position of N-methylations or of solvent exposed NHs did not correlate to intestinal permeability, measured in a Caco-2 model. In this study, we investigate enantiomeric pairs of three polar and two lipophilic peptides to demonstrate ...
|READ MORE|
27-Apr-2015
Irina Anosova, Svitlana Melnik, Konstantinos Tripsianes, Fatiha Kateb, Ingrid Grummt,
Michael Sattler Nucl. Acids Res.,
2015,
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv365, Vol. 43, No. 10, 5208–5220 published on 27.04.2015
Nucl. Acids Res.,
online article
The chromatin remodeling complex NoRC, comprising the subunits SNF2h and TIP5/BAZ2A, mediates heterochromatin formation at major clusters of repetitive elements, including rRNA genes, centromeres and telomeres. Association with chromatin requires the interaction of the TAM (TIP5/ARBP/MBD) domain of TIP5 with noncoding RNA, which targets NoRC to specific genomic ...
|READ MORE|
23-Apr-2015
Daniel Sohmen, Shinobu Chiba, Naomi Shimokawa-Chiba, C. Axel Innis, Otto Berninghausen,
Roland Beckmann,, Koreaki Ito,
Daniel N Wilson Nature Communications,
2015,
doi:10.1038/ncomms7941, 6, Article number: 6941 published on 23.04.2015
Nature Communications,
online aricle
Ribosomal stalling is used to regulate gene expression and can occur in a species-specific manner. Stalling during translation of the MifM leader peptide regulates expression of the downstream membrane protein biogenesis factor YidC2 (YqjG) in Bacillus subtilis, but not in Escherichia coli. In the absence of structures of Gram-positive bacterial ribosomes, a ...
|READ MORE|
21-Apr-2015
Bernd K. Gilsbach, Ana C. Messias, Genta Ito,
Michael Sattler, Dario R. Alessi, Alfred Wittinghofer, Arjan Kortholt
J. Med. Chem.,
2015,
DOI: 10.1021/jm5018779, 58 (9), pp 3751–3756 published on 21.04.2015
J. Med. Chem.,
online article
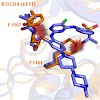
Kinase inhibition is considered to be an important therapeutic target for LRRK2 mediated Parkinson’s disease (PD). Many LRRK2 kinase inhibitors have been reported but have yet to be optimized in order to qualify as drug candidates for the treatment of the disease. In order to start a structure–function analysis of such inhibitors, we mutated the active site of ...
|READ MORE|
13-Apr-2015
Stefan Arenz, Fabian Nguyen,
Roland Beckmann,
Daniel N Wilson PNAS,
2015,
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1501775112, vol. 112 no. 17 5401-5406 published on 13.04.2015
PNAS,
online article
Ribosome protection proteins (RPPs) confer resistance to tetracycline by binding to the ribosome and chasing the drug from its binding site. Current models for RPP action are derived from 7.2- to 16-Å resolution structures of RPPs bound to vacant or nontranslating ribosomes. Here we present a cryo-electron microscopy reconstruction of the RPP TetM in complex with ...
|READ MORE|
09-Apr-2015
Oliver Baron
2015, published on 09.04.2015
R. Bruce Merrifield Award
We are happy that two prestigious distinctions from the fields of peptide chemistry have been awarded to our CIPSM researcher Horst Kessler. The R. Bruce Merrifield Award is the most prestigious award of the American Peptide Society. Presented at the biennial symposia of the American Peptide Society, it recognizes the lifetime achievement of a peptide scientist ...
|READ MORE|
08-Apr-2015
Alina Röhl, Daniela Wengler, Tobias Madl, Stephan Lagleder, Franziska Tippel, Monika Herrmann, Jelle Hendrix, Klaus Richter, Gordon Hack, Andreas B. Schmid, Horst Kessler, Don C. Lamb, Johannes Buchner
Nature Communications, 2015, doi:10.1038/ncomms7655, 6, Article number: 6655 published on 08.04.2015
Nature Communications, online article
The cochaperone Sti1/Hop physically links Hsp70 and Hsp90. The protein exhibits one binding site for Hsp90 (TPR2A) and two binding sites for Hsp70 (TPR1 and TPR2B). How these sites are used remained enigmatic. Here we show that Sti1 is a dynamic, elongated protein that consists of a flexible N-terminal module, a long linker and a rigid C-terminal module. Binding ...
|READ MORE|
01-Apr-2015
Roberta Fraioli Florian Rechenmacher, Stefanie Neubauer, José M. Manero, Javier Gila,,
Horst Kessler, Carlos Mas-Moruno
Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces,
2015,
doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.12.057, Volume 128, Pages 191–200 published on 01.04.2015
Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces,
online article
lInteraction between the surface of implants and biological tissues is a key aspect of biomaterials research. Apart from fulfilling the non-toxicity and structural requirements, synthetic materials are asked to direct cell response, offering engineered cues that provide specific instructions to cells. This work explores the functionalization of titanium with ...
|READ MORE|
26-Mar-2015
Janosch Hennig, Lisa R. Warner, Bernd Simon, Arie Geerlof, Cameron D. Mackereth,
Michael Sattler Methods in Enzymology,
2015,
doi:10.1016/bs.mie.2015.02.006, Volume 558, Pages 333–362 published on 26.03.2015
Methods in Enzymology,
online article
Biological activity in the cell is predominantly mediated by large multiprotein and protein–nucleic acid complexes that act together to ensure functional fidelity. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is the only method that can provide information for high-resolution three-dimensional structures and the conformational dynamics of these complexes in ...
|READ MORE|
22-Mar-2015
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society,
2015,
doi: 10.1261/rna.050971.115, 21: 727-728 published on 22.03.2015
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society,
online article
My research entered the RNA world when I joined the EMBL Heidelberg. During my doctoral and postdoctoral research I had focused on developing and applying solution NMR methods and studied protein structure and dynamics of the Bcl family proteins, which are important regulators of apoptosis. When I set up my own group at EMBL in 1997 I became quickly interested in ...
|READ MORE|
03-Mar-2015
Kristina Lakomek, Gabriele Stoehr, Alessandro Tosi, Monika Schmailzl, Karl-Peter Hopfner
Structure, 2015, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2014.12.015, Volume 23, Issue 3, p483–495 published on 03.03.2015
Structure, online article
As building blocks of diverse macromolecular complexes, the AAA+ ATPases Rvb1 and Rvb2 are crucial for many cellular activities including cancer-related processes. Their oligomeric structure and function remain unclear. We report the crystal structures of full-length heteromeric Rvb1·Rvb2 complexes in distinct nucleotide binding states. Chaetomium thermophilum ...
|READ MORE|
01-Mar-2015
Hans Jürgen Wester, Ulrich Keller, Margret Schottelius, Ambros Beer, Kathrin Philipp-Abbrederis, Frauke Hoffmann, Jakub Šimeček, Carlos Gerngross, Michael Lassmann, Ken Herrmann, Natalia Pellegata, Martina Rudelius,
Horst Kessler, Markus Schwaiger
Theranostics,
2015,
doi:10.7150/thno.11251, 5(6):618-630 published on 01.03.2015
Theranostics,
online article
Chemokine ligand-receptor interactions play a pivotal role in cell attraction and cellular trafficking, both in normal tissue homeostasis and in disease. In cancer, chemokine receptor-4 (CXCR4) expression is an adverse prognostic factor. Early clinical studies suggest that targeting CXCR4 with suitable high-affinity antagonists might be a novel means for therapy. ...
|READ MORE|
16-Feb-2015
Carolin Seefeldt, Fabian Nguyen, Stéphanie Antunes, Natacha Pérébaskine, Michael Graf, Stefan Arenz, K Kishore Inampudi, Céline Douat, Gilles Guichard,
Daniel N Wilson, C Axel Innis
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology,
2015,
doi:10.1038/nsmb.3034, 22, 470–475 published on 16.02.2015
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology,
online article
The increasing prevalence of multidrug-resistant pathogenic bacteria is making current antibiotics obsolete. Proline-rich antimicrobial peptides (PrAMPs) display potent activity against Gram-negative bacteria and thus represent an avenue for antibiotic development. PrAMPs from the oncocin family interact with the ribosome to inhibit translation, but their mode of ...
|READ MORE|
16-Feb-2015
Jürgen Lassak, Eva Keilhauer, Maximilian Fürst, Kristin Wuichet, Julia Gödeke, Agata L Starosta, Jhong-Min Chen, Lotte Søgaard-Andersen, Jürgen Rohr,
Daniel N Wilson, Susanne Häussler,
Matthias Mann,
Kirsten Jung Nature Chemical Biology,
2015,
doi:10.1038/nchembio.1751, published on 16.02.2015
Nature Chemical Biology,
online article
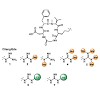
Ribosome stalling at polyproline stretches is common and fundamental. In bacteria, translation elongation factor P (EF-P) rescues such stalled ribosomes, but only when it is post-translationally activated. In Escherichia coli, activation of EF-P is achieved by (R)-β-lysinylation and hydroxylation of a conserved lysine. Here we have unveiled a markedly ...
|READ MORE|
15-Feb-2015
Diana C. Rodriguez Camargo, Konstantinos Tripsianes, Tobias G. Kapp, Joaquim Mendes, Jasmin Schubert , Burghard Cordes,
Bernd Reif Protein Expression and Purification,
2015,
doi:10.1016/j.pep.2014.10.012, Volume 106, Pages 49–56 published on 15.02.2015
Protein Expression and Purification,
online article
Type II diabetes is characterized by deposition of the hormone human Islet Amyloid Polypeptide (hIAPP). Formation of hIAPP amyloid fibrils and aggregates is considered to be responsible for pancreatic β-cell losses. Therefore, insight into the structure of hIAPP in the solid-state and in solution is of fundamental importance in order to better understand the ...
|READ MORE|
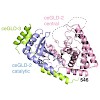
09-Feb-2015
Mathias Riebold, Christian Kozany, Lee Freiburger,
Michael Sattler, Michael Buchfelder, Felix Hausch, Günter K Stalla, Marcelo Paez-Pereda
Nature Medicine,
2015,
doi:10.1038/nm.3776, 21, 276–280 published on 09.02.2015
Nature Medicine,
online article
One function of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) in corticotroph cells is to suppress the transcription of the gene encoding proopiomelanocortin (POMC), the precursor of the stress hormone adrenocorticotropin (ACTH). Cushing disease is a neuroendocrine condition caused by partially glucocorticoid-resistant corticotroph adenomas that excessively secrete ACTH, ...
|READ MORE|
05-Feb-2015
Emeline Barbet-Massin, Chih-Ting Huang, Venita Daebel, Shang-Te Danny Hsu,
Bernd Reif Angewandte Chemie International Edition,
2015,
DOI: 10.1002/anie.201409393, Volume 54, Issue 14, pages 4367–4369 published on 05.02.2015
Angewandte Chemie International Edition,
online article
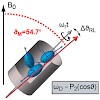
Co-translational protein folding is not yet well understood despite the availability of high-resolution ribosome crystal structures. We present first solid-state NMR data on non-mobile regions of a prokaryotic ribosomal complex. Localized chemical shift perturbations and line broadening are observed for the backbone amide resonances corresponding to the regions ...
|READ MORE|
30-Jan-2015
Veniamin Chevelkov, ShengQi Xiang, Karin Giller, Stefan Becker, Adam Lange,
Bernd Reif Journal of Biomolecular NMR,
2015,
DOI 10.1007/s10858-015-9902-2, Volume 61, Issue 2, pp 151-160 published on 30.01.2015
Journal of Biomolecular NMR,
online article
In this work, we show how the water flip-back approach that is widely employed in solution-state NMR can be adapted to proton-detected MAS solid-state NMR of highly deuterated proteins. The scheme allows to enhance the sensitivity of the experiment by decreasing the recovery time of the proton longitudinal magnetization. The method relies on polarization transfer ...
|READ MORE|
22-Jan-2015
Andreas O. Frank, J. Christoph Freudenberger, Alexey K. Shaytan,
Horst Kessler, Burkhard Luy
Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry,
2015,
DOI: 10.1002/mrc.4181, Volume 53, Issue 3, pages 213–217 published on 22.01.2015
Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry,
online article
Residual dipolar couplings are highly useful NMR parameters for calculating and refining molecular structures, dynamics, and interactions. For some applications, however, it is inevitable that the preferred orientation of a molecule in an alignment medium is calculated a priori. Several methods have been developed to predict molecular orientations and residual ...
|READ MORE|
07-Jan-2015
Sam Asami, Justin R. Porter, Oliver F. Lange,
Bernd Reif J. Am. Chem. Soc.,
2015,
DOI: 10.1021/ja509367q, 137 (3), pp 1094–1100 published on 07.01.2015
J. Am. Chem. Soc.,
online article
We introduce a labeling scheme for magic angle spinning (MAS) solid-state NMR that is based on deuteration in combination with dilution of the carbon spin system. The labeling strategy achieves spectral editing by simplification of the HαCα and aliphatic side chain spectral region. A reduction in both proton and carbon spin density in combination with fast ...
|READ MORE|