Research Area C - Publications 2009
13-Dec-2009
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article
Protein conformation is critically linked to function and often controlled by interactions with regulatory factors. Here we report the selection of camelid-derived single-domain antibodies (nanobodies) that modulate the conformation and spectral properties of the green fluorescent protein (GFP). One nanobody could reversibly reduce GFP fluorescence by a factor of ...
04-Dec-2009
Expression of the Escherichia coli tryptophanase operon depends on ribosome stalling during translation of the upstream TnaC leader peptide, a process for which interactions between the TnaC nascent chain and the ribosomal exit tunnel are critical. We determined a 5.8 angstrom–resolution cryo–electron microscopy and single-particle reconstruction of a ...
Structure of Monomeric Yeast and Mammalian Sec61 Complexes Interacting with the Translating Ribosome
04-Dec-2009
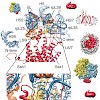
The trimeric Sec61/SecY complex is a protein-conducting channel (PCC) for secretory and membrane proteins. Although Sec complexes can form oligomers, it has been suggested that a single copy may serve as an active PCC. We determined subnanometer-resolution cryo–electron microscopy structures of eukaryotic ribosome-Sec61 complexes. In combination with biochemical ...
04-Dec-2009
Plastid-specific ribosomal proteins (PSRPs) have been proposed to play roles in the light-dependent regulation of chloroplast translation. Here we demonstrate that PSRP1 is not a bona fide ribosomal protein, but rather a functional homologue of the Escherichia coli cold-shock protein pY. Three-dimensional Cryo-electron microscopic (Cryo-EM) reconstructions reveal ...
01-Dec-2009
Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol., online article

Protein synthesis is one of the major targets in the cell for antibiotics. This review endeavors to provide a comprehensive “post-ribosome structure” A–Z of the huge diversity of antibiotics that target the bacterial translation apparatus, with an emphasis on correlating the vast wealth of biochemical data with more recently available ribosome structures, in ...
25-Nov-2009
Chem. Biol., online article
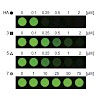
The antibacterial activity of hygromycin A (HA) arises from protein synthesis inhibition and is dependent upon a methylenedioxy bridged-aminocyclitol moiety. Selective gene deletions and chemical complementation in Streptomyces hygroscopicus NRRL 2388 showed that the hyg18 and hyg25 gene products, proposed to generate a myo-inositol intermediate, are dispensable ...
30-Oct-2009
Chem. Biol., online article
Most thiopeptide antibiotics target the translational machinery: thiostrepton (ThS) and nosiheptide (NoS) target the ribosome and inhibit translation factor function, whereas GE2270A/T binds to the elongation factor EF-Tu and prevents ternary complex formation. We have used several in vitro translational machinery assays to screen a library of thiopeptide ...
21-Oct-2009
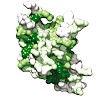
The PUR protein family is a distinct and highly conserved class that is characterized by its sequence-specific RNA- and DNA-binding. Its best-studied family member, Pur-α, acts as a transcriptional regulator, as host factor for viral replication, and as cofactor for mRNP localization in dendrites. Pur-α-deficient mice show severe neurologic defects and die after ...
10-Oct-2009
Biochem. Soc. Trans., online article

The RNA exosome is a multisubunit exonuclease involved in numerous RNA maturation and degradation processes. Exosomes are found in eukaryotes and archaea and are related to bacterial polynucleotide phosphorylates. Over the past years structural and biochemical analysis revealed that archaeal exosomes have a large processing chamber with three phosphorolytic ...
02-Oct-2009
Cell, 2009, 139(1), pp. 212 - 212.e1, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.08.009 published on 02.10.2009
Cell, online article
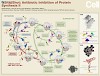
The translational apparatus is one of the major targets for antibiotics in the bacterial cell. Antibiotics predominantly interact with the functional centers of the ribosome, namely the messenger RNA (mRNA)-transfer RNA (tRNA) decoding region on the 30S subunit, the peptidyltransferase center on the 50S subunit, or the ribosomal exit tunnel through which the ...
02-Oct-2009
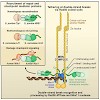
The Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 (MRN) complex senses DNA double-strand breaks and recruits different repair pathway and checkpoint proteins to break foci. Two new studies (Williams et al., 2009; Lloyd et al., 2009,Williams et al., 2009; Lloyd et al., 2009) identify Nbs1 as a key factor in this process and reveal how an N-terminal protein recruitment module in Nbs1 binds to ...
01-Oct-2009
GIT Laboratory Journal, online article

With over 47,000 citations, the sequence search method BLAST has been an essential tool in biological research since its development in 1990. By accounting for the influence of sequence context on the mutation probabilities of amino acids, context-specific BLAST (CS-BLAST) achieves two-fold higher sensitivity for distantly related protein sequences at the same ...
18-Sep-2009
Cell, online article
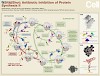
The translational apparatus is one of the major targets for antibiotics in the bacterial cell. Antibiotics predominantly interact with the functional centers of the ribosome, namely the messenger RNA (mRNA)-transfer RNA (tRNA) decoding region on the 30S subunit, the peptidyltransferase center on the 50S subunit, or the ribosomal exit tunnel through which the ...
17-Sep-2009
J. Biol. Chem., 2009, in press, doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.013847 published on 17.09.2009
J. Biol. Chem., online article

Termination of RNA polymerase (Pol) II transcription in vivo requires the 5’-RNA exonuclease Rat1. It was proposed that Rat1 degrades RNA from the 5’-end that is created by transcript cleavage, catches up with elongating Pol II, and acts like a torpedo that removes Pol II from DNA. Here we test the torpedo model in an in vitro system based on bead-coupled Pol II ...
16-Sep-2009
J. Biol. Chem., 2009, 284, 31658-31663, doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.022764 published on 16.09.2009
J. Biol. Chem., online article

Structure-function analysis has revealed the mechanism of yeast RNA polymerase II transcription at 8-oxoguanine (8-oxoG), the major DNA lesion resulting from oxidative stress. When polymerase II encounters 8-oxoG in the DNA template strand, it can misincorporate adenine, which forms a Hoogsteen bp with 8-oxoG at the active center. This requires rotation of the ...
12-Sep-2009
Antimicrob. Agents Ch., 2009, 53(12), 5163-5172, doi:10.1128/AAC.01069-09 published on 12.09.2009
Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, online article
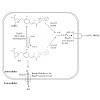
Hygromycin A (HA) is an aminocyclitol antibiotic produced and excreted by Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Deletion of hyg26 from the hygromycin A biosynthetic gene cluster has previously been shown to result in a mutant that produces 5''-dihydrohygromycin A (DHHA). We report herein on the purification and characterization of Hyg26 expressed in Escherichia coli. The ...
26-Aug-2009

In eukaryotic cells, dozens to hundreds of different mRNAs are localized by specialized motor-dependent transport complexes. One of the best-studied examples for directional mRNA transport is the localization of ASH1 mRNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. For transport, ASH1 mRNA is bound by the unusual RNA-binding protein She2p. Although previous results indicated ...
21-Aug-2009
EMBO reports, online article

Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is an abundant, dimeric ATPdependent molecular chaperone, and ATPase activity is essential for its in vivo functions. S-nitrosylation of a residue located in the carboxy-terminal domain has been shown to affect Hsp90 activity in vivo. To understand how variation of a specific amino acid far away from the amino-terminal ATP-binding ...
04-Aug-2009
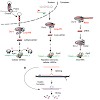
Transposons are mobile genetic elements found in the hereditary material of humans and other organisms. They can replicate and the new copies can insert at novel sites in the genome. Because this threatens the whole organism, molecular mechanisms have evolved which can repress transposon activity. CIPSM-Professor Klaus Förstemann of the Gene Center of ...
01-Aug-2009
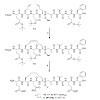
Cyclization of recently reported linear phosphino dipeptide isostere inhibitors of BACE1 via side chain olefin metathesis yielded macrocyclic BACE1 inhibitors. The most potent compound II-P1 (IC50 of 47 nM) and the corresponding linear analog I were tested for serum stability. The approach led to three times prolonged half life serum stability of 44 min for the ...
28-Jul-2009
Plant Cell, online article

Several factors regulate plant organ growth polarity. tortifolia2 (tor2), a right-handed helical growth mutant, has a conservative replacement of Arg-2 with Lys in the {alpha}-tubulin 4 protein. Based on a published high-resolution (2.89 Å) tubulin structure, we predict that Arg-2 of {alpha}-tubulin forms hydrogen bonds with the GTPase domain of {beta}-tubulin, ...
25-Jul-2009
Nuclear Transport, online article
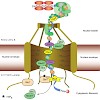
MRNA export is an indispensable step during the complex process of eukaryotic gene expression: the mRNA, created by RNA polymerase II in the nucleus, has to be transported to the cytoplasm, where the ribosomes are responsible for the synthesis of the encoded protein. This transport process is not restricted to the simple passage of the mRNA through the nuclear ...
20-Jul-2009
Nucl. Acids Res., 2009, 1-7, doi:10.1093/nar/gkp601 published on 20.07.2009
Nucl. Acids Res., online article
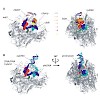
Crystallographic studies of the RNA polymerase II (Pol II) elongation complex (EC) revealed the locations of downstream DNA and the DNA-RNA hybrid, but not the course of the nontemplate DNA strand in the transcription bubble and the upstream DNA duplex. Here we used single-molecule Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (smFRET) experiments to locate nontemplate ...
13-Jul-2009
Angewandte Chemie, online article
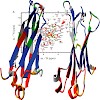
The formation of multicellular organisms requires concerted action by cells, which alter their adhesive and migratory behaviors. Cell adhesion and migration are tightly regulated by intra- and extracellular signals, which are conveyed through the cellular membrane by specialized receptors known as integrins.[1] Integrins are the starting point of a variety of ...
28-Jun-2009
Nature Genetics, online article

Congenital dyserythropoietic anemias (CDAs) are phenotypically and genotypically heterogeneous diseases. CDA type II (CDAII) is the most frequent CDA. It is characterized by ineffective erythropoiesis and by the presence of bi- and multinucleated erythroblasts in bone marrow, with nuclei of equal size and DNA content, suggesting a cytokinesis disturbance5. Other ...
26-Jun-2009
Mol. Cell, online article
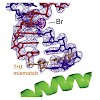
We show that RNA polymerase (Pol) II prevents erroneous transcription in vitro with different strategies that depend on the type of DNA⋅RNA base mismatch. Certain mismatches are efficiently formed but impair RNA extension. Other mismatches allow for RNA extension but are inefficiently formed and efficiently proofread by RNA cleavage. X-ray analysis reveals that a ...
25-Jun-2009
EMBO J., online article
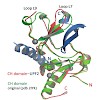
Nonsense-mediated decay (NMD) is a eukaryotic quality control mechanism that degrades mRNAs carrying premature stop codons. In mammalian cells, NMD is triggered when UPF2 bound to UPF3 on a downstream exon junction complex interacts with UPF1 bound to a stalled ribosome. We report structural studies on the interaction between the C-terminal region of UPF2 and ...
13-Jun-2009
Proteins, online article

Automated protein structure prediction is becoming a mainstream tool for biological research. This has been fueled by steady improvements of publicly available automated servers over the last decade, in particular their ability to build good homology models for an increasing number of targets by reliably detecting and aligning more and more remotely homologous ...
12-Jun-2009

A prerequisite for antibody secretion and function is their assembly into a defined quaternary structure, composed of two heavy and two light chains for IgG. Unassembled heavy chains are actively retained in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Here, we show that the CH1 domain of the heavy chain is intrinsically disordered invitro, which sets it apart from other ...
10-Jun-2009
Structure, 2009, 17(6), 781-783, doi:10.1016/j.str.2009.05.004 published on 10.06.2009
Structure, online article

The localization of mRNAs in subcellular compartments is an efficient way to spatially restrict gene expression. Crystal structures of raver1-vinculin reported by Izard and coworkers now suggest a possible mechanism for mRNA localization during the assembly of focal adhesions.
02-Jun-2009
Angewandte Chemie, 2009, 48, 24, 4436 - 40 published on 02.06.2009
Angewandte Chemie, online article
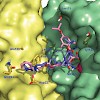
A suitable substitute: All integrin receptors bind their ligands, which contain an aspartate residue, in the metal-ion- dependent adhesion site (MIDAS). So far all attempts to replace the carboxyl group of aspartate with other, pharmacologically favorable isosteric groups have failed. Now it has been shown that a hydroxamic acid group can replace the carboxyl ...
02-Jun-2009
Accounts of Chemical Research online article
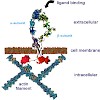
α5β1-integrins play a key role in angiogenesis, the formation of new vessels in tissues that lack them. By serving as receptors for a variety of extracellular matrix proteins containing an arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD) sequence, these integrins mediate migration of endothelial cells into the basement membrane and regulate their growth, survival, and ...
27-May-2009
Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 2009, 19(3), 294-299, doi:10.1016/j.sbi.2009.04.005 published on 27.05.2009
Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., online article
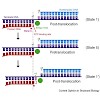
During gene transcription, RNA polymerase (Pol) passes through repetitive cycles of adding a nucleotide to the growing mRNA chain. Here we obtained a movie of the nucleotide addition cycle by combining structural information on different functional states of the Pol II elongation complex (EC). The movie illustrates the two-step loading of the nucleoside ...
26-May-2009
J. Mol. Biol., 2009, 389(1), 211-225, doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.04.016 published on 26.05.2009
J. Mol. Biol., online article

During transcription elongation through chromatin, the Ser2-phosphorylated C-terminal repeat domain of RNA polymerase II binds the C-terminal Src homology 2 (SH2) domain of the nucleosome re-assembly factor Spt6. This SH2 domain is unusual in its specificity to bind phosphoserine, rather than phosphotyrosine and because it is the only SH2 domain in the yeast ...
08-May-2009
Nucleic Acids Research, online article

Outer membrane proteins (OMPs) are the transmembrane proteins found in the outer membranes of Gram-negative bacteria, mitochondria and plastids. Most prediction methods have focused on analogous features, such as alternating hydrophobicity patterns. Here, we start from the observation that almost all β-barrel OMPs are related by common ancestry. We identify ...
24-Apr-2009
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2009, 48(42), 4056-4060, doi:10.1002/anie.200900939 published on 24.04.2009
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article

Translation of specific small peptides on the ribosome can confer resistance to macrolide antibiotics. To reveal the molecular details of this and related phenomena, stable RNA-peptide conjugates that mimic peptidyl-tRNA would be desirable, especially for ribosome structural biology. A flexible solid-phase synthesis strategy now allows efficient access to these ...
15-Apr-2009
Biophysical Chemistry, online article

We determine the binding mode of a macrocyclic radicicol-like oxime to yeast HSP90 by combining computer simulations and experimental measurements. We sample the macrocyclic scaffold of the unbound ligand by parallel tempering simulations and dock the most populated conformations to yeast HSP90. Docking poses are then evaluated by the use of binding free energy ...
01-Apr-2009
Biological Chemistry, online article

Molecular chaperones of the heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) family play a crucial role in the presentation of exogenous antigenic peptides by antigen-presenting cells (APCs). In a combined biochemical and immuno-logical approach, we characterize the biochemical interaction of tumor-associated peptides with human Hsp70 and show that the strength of this interaction ...
10-Mar-2009
PNAS, 2009, 106 no.10, 3770-5 published on 10.03.2009
PNAS, online article
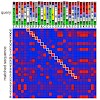
Sequence alignment and database searching are essential tools in biology because a protein’s function can often be inferred from homologous proteins. Standard sequence comparison methods use substitution matrices to find the alignment with the best sum of similarity scores between aligned residues. These similarity scores do not take the local sequence context ...
20-Feb-2009
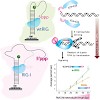
RIG-I is a cytosolic multi-domain protein that detects viral RNA and elicits an antiviral immune response. Two N-terminal caspase activation and recruitment domains (CARDs) transmit the signal and the regulatory domain prevents signaling in the absence of viral RNA. 5’-triphosphate and double stranded (ds) RNA are two molecular patterns that enable RIG-I to ...
14-Feb-2009
Journal of Molecular Biology, 2009, 387(4), 921-934, doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.02.018 published on 14.02.2009
Journal of Molecular Biology, online article
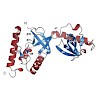
The Tudor-SN protein (p100, SND1) has been implicated in a variety of cellular processes, such as transcription, processing of edited double-stranded RNA, and splicing regulation. Molecular details of these functions are not yet understood. Tudor domains have previously been shown to bind methylated ligands, such as methylated lysines and arginines. It has been ...
10-Feb-2009
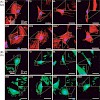
We herein present a novel platform of well-controlled ordered and disordered nanopatterns positioned with a cyclic peptide of arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD) on a bioinert poly(ethylene glycol) background, to study whether the nanoscopic order of spatial patterning of the integrin-specific ligands influences osteoblast adhesion. This is the first time that ...
10-Feb-2009
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
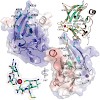
RIG-I and MDA5 sense cytoplasmic viral RNA and set-off a signal transduction cascade, leading to antiviral innate immune response. The third RIG-Ilike receptor, LGP2, differentially regulates RIG-Iand MDA5-dependent RNA sensing in an unknown manner. All three receptors possess a C-terminal regulatory domain (RD), which in the case of RIG-I senses the viral ...
05-Feb-2009
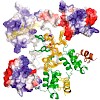
Protein import into peroxisomes depends on a complex and dynamic network of protein–protein interactions. Pex14 is a central component of the peroxisomal import machinery and binds the soluble receptors Pex5 and Pex19, which have important function in the assembly of peroxisome matrix and membrane, respectively. We show that the N-terminal domain of Pex14, ...
01-Feb-2009
Acta Chrystallogr. D, 2009, 65(2), 112-120, doi:10.1107/S0907444908039875 published on 01.02.2009
Acta Chrystallogr. D, online article

RNA polymerase II (Pol II) is the eukaryotic enzyme that is responsible for transcribing all protein-coding genes into messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA-transcription cycle can be divided into three stages: initiation, elongation and termination. During elongation, Pol II moves along a DNA template and synthesizes a complementary RNA chain in a processive manner. ...
30-Jan-2009
J. Mol. Biol., 2009, 385(4), 1179-1192, doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.11.042 published on 30.01.2009
J. Mol. Biol., online article
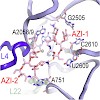
Azithromycin is a semisynthetic derivative of erythromycin that inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding within the peptide exit tunnel of the 50S ribosomal subunit. Nevertheless, there is still debate over what localization is primarily responsible for azithromycin binding and as to how many molecules of the drug actually bind per ribosome. In the present ...
30-Jan-2009
Mol. Cell, online article

In this issue of Molecular Cell, Kaberdina et al. (2009) show that prolonged exposure of ribosomes to the antibiotic kasugamycin triggers the spontaneous loss of small subunit proteins and produces a reduced ribosomal particle that exclusively translates leaderless mRNAs.
23-Jan-2009

Recent advances have led to insights into the structure of the bacterial ribosome, but little is knownabout the 3D organization of ribosomes in the context of translating polysomes. We employed cryoelectron tomography and a template-matching approach to map 70S ribosomes in vitrified bacterial translation extracts and in lysates of active E. coli spheroplasts. In ...
21-Jan-2009
Antimicrob. Agents Ch., 2009, 53(4), 1411-1419, doi:10.1128/AAC.01425-08 published on 21.01.2009
Antimicrob. Agents Ch., online article
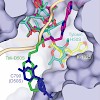
Ketolides represent the latest generation of macrolide antibiotics, displaying improved activities against some erythromycin resistant strains, while maintaining their activity against erythromycin susceptible ones. In this study we present a new ketolide K-1325 that carries an alkyl-aryl side chain at C-13 of the lactone ring. According to our genetic and ...
02-Jan-2009

Structural investigations are frequently hindered by difficulties in obtaining diffracting crystals of the target protein. Here, we report the crystallization and structure solution of the U2AF homology motif (UHM) domain of splicing factor Puf60 fused to Escherichia coli thioredoxin A. Both modules make extensive crystallographic contacts, contributing to a ...










