Research Area C - Publications 2014
31-Dec-2014
Cell Cycle, online article

Recognition of mRNA transcripts by RNA binding proteins plays essential roles at various steps of gene expression, including splicing, translation, stability and general mRNA metabolism. Also the biogenesis and activity of non-coding RNAs (miRNAs, siRNAs, lncRNAs) and other regulatory RNA molecules depends on protein interactions. Cis elements, i.e. short RNA ...
20-Dec-2014
FEBS Letters, online article
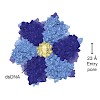
DNA double-strand breaks can be repaired by homologous recombination, during which the DNA ends are long-range resected by helicase–nuclease systems to generate 3′ single strand tails. In archaea, this requires the Mre11–Rad50 complex and the ATP-dependent helicase–nuclease complex HerA–NurA. We report the cryo-EM structure of Sulfolobus solfataricus HerA–NurA at ...
19-Dec-2014
Molecular Systems Biology ,10: 768, DOI 10.15252/msb.20145654
Molecular Systems Biology, online article
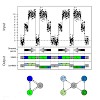
DNA replication, transcription and repair involve the recruitment of protein complexes that change their composition as they progress along the genome in a directed or strand‐specific manner. Chromatin immunoprecipitation in conjunction with hidden Markov models (HMMs) has been instrumental in understanding these processes, as they segment the genome into ...
12-Dec-2014
Nucleic Acid Chemistry, online article
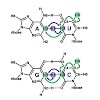
NMR spectroscopy is a powerful tool to study the structure and dynamics of nucleic acids. In this unit, we give an overview of important experiments to determine and characterize hydrogen bonds in nucleic acids and provide detailed instructions for setting up recently developed sensitivity-improved NMR pulse sequences, i.e., BEST selective long-range HNN-COSY, ...
26-Nov-2014
J. Exp. Bot., online article

Despite the importance of superoxide dismutases (SODs) in the plant antioxidant defence system little is known about their regulation by post-translational modifications. Here, we investigated the in vitro effects of nitric oxide derivatives on the seven SOD isoforms of Arabidopsis thaliana. S-nitrosoglutathione, which causes S-nitrosylation of cysteine residues, ...
27-Oct-2014
The EMBO Journal, online article

The Mre11–Rad50 nuclease–ATPase is an evolutionarily conserved multifunctional DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair factor. Mre11–Rad50's mechanism in the processing, tethering, and signaling of DSBs is unclear, in part because we lack a structural framework for its interaction with DNA in different functional states. We determined the crystal structure of ...
09-Oct-2014
Cell Reports, online artticle
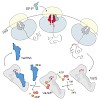
Bacterial ribosomes stall on polyproline stretches and require the elongation factor P (EF-P) to relieve the arrest. Yet it remains unclear why evolution has favored the development of EF-P rather than selecting against the occurrence of polyproline stretches in proteins. We have discovered that only a single polyproline stretch is invariant across all domains of ...
08-Oct-2014
Molecular Cell, 2014, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.09.014, 56, 1–7, published on 08.10.2014
Molecular Cell, online article

During protein synthesis, nascent polypeptide chains within the ribosomal tunnel can act in cis to induce ribosome stalling and regulate expression of downstream genes. The Staphylococcus aureus ErmCL leader peptide induces stalling in the presence of clinically important macrolide antibiotics, such as erythromycin, leading to the induction of the downstream ...
26-Sep-2014
FEMS Microbiology Review, online article
Throughout their life, bacteria need to sense and respond to environmental stress. Thus, such stress responses can require dramatic cellular reprogramming, both at the transcriptional as well as the translational level. This review focuses on the protein factors that interact with the bacterial translational apparatus to respond to and cope with different types ...
22-Sep-2014
Chemistry - A European Journal, 2014, DOI: 10.1002/chem.201403839, Volume 20, Issue 44, pages 14201–14206, published on 22.09.2014
Chemistry - A European Journal, online article
The X-ray crystal and NMR spectroscopic structures of the peptide drug candidate Cilengitide (cyclo(RGDf(NMe)Val)) in various solvents are obtained and compared in addition to the integrin receptor bound conformation. The NMR-based solution structures exhibit conformations closely resembling the X-ray structure of Cilengitide bound to the head group of integrin ...
22-Sep-2014
Angewandte Chemie International Edition, online article
The molecular chaperone Hsp90 undergoes an ATP-driven cycle of conformational changes in which large structural rearrangements precede ATP hydrolysis. Well-established small-molecule inhibitors of Hsp90 compete with ATP-binding. We wondered whether compounds exist that can accelerate the conformational cycle. In a FRET-based screen reporting on conformational ...
11-Sep-2014
BioEssays, online article
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are one of the most deleterious forms of DNA damage and can result in cell inviability or chromosomal aberrations. The Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 (MRN) ATPase-nuclease complex is a central player in the cellular response to DSBs and is implicated in the sensing and nucleolytic processing of DSBs, as well as in DSB signaling by activating the ...
07-Sep-2014
Genetic equality between males and females is established by chromosome-wide dosage-compensation mechanisms. In the fruitfly Drosophila melanogaster, the dosage-compensation complex promotes twofold hypertranscription of the single male X-chromosome and is silenced in females by inhibition of the translation of msl2, which codes for the limiting component of the ...
04-Sep-2014
Cell, online article

Biogenesis of eukaryotic messenger ribonucleoprotein complexes (mRNPs) involves the synthesis, splicing, and 3′ processing of pre-mRNA, and the assembly of mature mRNPs for nuclear export. We mapped 23 mRNP biogenesis factors onto the yeast transcriptome, providing 104–106 high-confidence RNA interaction sites per factor. The data reveal how mRNP biogenesis ...
26-Aug-2014
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, online article

The retention and splicing (RES) complex is a conserved spliceosome-associated module that was shown to enhance splicing of a subset of transcripts and promote the nuclear retention of unspliced pre-mRNAs in yeast. The heterotrimeric RES complex is organized around the Snu17p protein that binds to both the Bud13p and Pml1p subunits. Snu17p exhibits an RRM domain ...
20-Aug-2014
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
The polymerization of amino acids into proteins occurs on ribosomes, with the rate influenced by the amino acids being polymerized. The imino acid proline is a poor donor and acceptor for peptide-bond formation, such that translational stalling occurs when three or more consecutive prolines (PPP) are encountered by the ribosome. In bacteria, stalling at PPP ...
07-Aug-2014
Molecular Cell, online article
The Nrd1-Nab3-Sen1 (NNS) complex is essential for controlling pervasive transcription and generating sn/snoRNAs in S. cerevisiae. The NNS complex terminates transcription of noncoding RNA genes and promotes exosome-dependent processing/degradation of the released transcripts. The Trf4-Air2-Mtr4 (TRAMP) complex polyadenylates NNS target RNAs and favors their ...
05-Aug-2014
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2014, doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.582247, 289, 26829-26846, published on 05.08.2014
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, online article
Variable (V) domains of antibodies are essential for antigen recognition by our adaptive immune system. However, some variants of the light chain V domains (VL) form pathogenic amyloid fibrils in patients. It is so far unclear which residues play a key role in governing these processes. Here, we show that the conserved residue 2 of VL domains is crucial for ...
31-Jul-2014
Perspect Biol., online article
DNA double-strand breaks are repaired by two major pathways, homologous recombination or nonhomologous end joining. The commitment to one or the other pathway proceeds via different steps of resection of the DNA ends, which is controlled and executed by a set of DNA double-strand break sensors, endo- and exonucleases, helicases, and DNA damage response factors. ...
23-Jul-2014
Oncotarget, online article
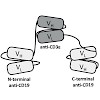
Triplebody 19-3-19, an antibody-derived protein, carries three single chain fragment variable domains in tandem in a single polypeptide chain. 19-3-19 binds CD19-bearing lymphoid cells via its two distal domains and primary T cells via its CD3-targeting central domain in an antigen-specific manner. Here, malignant B-lymphoid cell lines and primary cells from ...
18-Jul-2014
Nature Reviews Immunology, online article
Recent discoveries in the field of innate immunity have highlighted the existence of a family of nucleic acid-sensing proteins that have similar structural and functional properties. These include the well-known oligoadenylate synthase (OAS) family proteins and the recently identified OAS homologue cyclic GMP–AMP (cGAMP) synthase (cGAS). The OAS proteins and cGAS ...
18-Jul-2014
Cell, online article
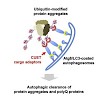
Selective ubiquitin-dependent autophagy plays a pivotal role in the elimination of protein aggregates, assemblies, or organelles and counteracts the cytotoxicity of proteins linked to neurodegenerative diseases. Following substrate ubiquitylation, the cargo is delivered to autophagosomes involving adaptors like human p62 that bind ubiquitin and the autophagosomal ...
13-Jul-2014
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article
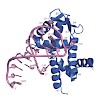
Roquin function in T cells is essential for the prevention of autoimmune disease. Roquin interacts with the 3′ untranslated regions (UTRs) of co-stimulatory receptors and controls T-cell activation and differentiation. Here we show that the N-terminal ROQ domain from mouse roquin adopts an extended winged-helix (WH) fold, which is sufficient for binding to the ...
08-Jul-2014
Structure, online article
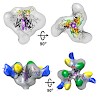
Repeat proteins consisting of helical segments seem to fold by a matrix-assisted mechanism in which folded segments induce structure in intrinsically disordered parts of the protein, as shown by Watson and colleagues in this issue of Structure for an Armadillo repeat protein and previously by the Balbach group for an Ankyrin repeat protein.
07-Jul-2014
Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, online article

NMR spectroscopy is a key method for studying the structure and dynamics of (large) multidomain proteins and complexes in solution. It plays a unique role in integrated structural biology approaches as especially information about conformational dynamics can be readily obtained at residue resolution. Here, we review NMR techniques for such studies focusing on ...
06-Jul-2014

Idiopathic achalasia is characterized by a failure of the lower esophageal sphincter to relax due to a loss of neurons in the myenteric plexu. This ultimately leads to massive dilatation and an irreversibly impaired megaesophagus. We performed a genetic association study in 1,068 achalasia cases and 4,242 controls and fine-mapped a strong MHC association signal ...
03-Jul-2014
J Biomol NMR, online article
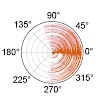
Relaxation parameters such as longitudinal relaxation are susceptible to artifacts such as spin diffusion, and can be affected by paramagnetic impurities as e.g. oxygen, which make a quantitative interpretation difficult. We present here the site-specific measurement of [1H]13C and [1H]15N heteronuclear rates in an immobilized protein. For methyls, a strong ...
03-Jul-2014
Cell, online article
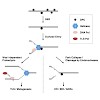
Toxic DNA-protein crosslinks (DPCs) arise by ionizing irradiation and UV light, are particularly caused by endogenously produced reactive compounds such as formaldehyde, and also occur during compromised topoisomerase action. Although nucleotide excision repair and homologous recombination contribute to cell survival upon DPCs, hardly anything is known about ...
02-Jul-2014
ChemMedChem, online article
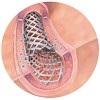
The use of highly active and selective integrin ligands in combination with stent implantation is emerging as a promising alternative to the release of classical immunosuppressive drugs by current drug-eluting stents (DES), which has been associated with delayed vascular healing and late stent thrombosis. Herein we present the development and biological ...
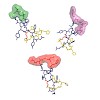
24-Jun-2014
PLOS ONE, online article
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and proteins containing antibody domains are the most prevalent class of biotherapeutics in diverse indication areas. Today, established techniques such as immunization or phage display allow for an efficient generation of new mAbs. Besides functional properties, the stability of future therapeutic mAbs is a key selection criterion ...
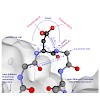
20-Jun-2014
J. Med. Chem., online article
Integrins moderate diverse important functions in the human body and are promising targets in cancer therapy. Hence, the selective inhibition of specific integrins is of great medicinal interest. Here, we report the optimization of a grafted lasso peptide, yielding MccJ25(RGDF), which is a highly potent and selective αvβ3 integrin inhibitor. Furthermore, its NMR ...
The structural analysis of shark IgNAR antibodies reveals evolutionary principles of immunoglobulins
03-Jun-2014
PNAS, online article
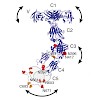
Sharks and other cartilaginous fish are the phylogenetically oldest living organisms that rely on antibodies as part of their adaptive immune system. They produce the immunoglobulin new antigen receptor (IgNAR), a homodimeric heavy chain-only antibody, as a major part of their humoral adaptive immune response. Here, we report the atomic resolution structure of ...
21-May-2014
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, online article
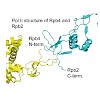
RNA polymerase II (Pol II) is the central enzyme that carries out eukaryotic mRNA transcription and consists of a 10-subunit catalytic core and a subcomplex of subunits Rpb4 and Rpb7 (Rpb4/7). Rpb4/7 has been proposed to dissociate from Pol II, enter the cytoplasm, and function there in mRNA translation and degradation. Here we provide evidence that Rpb4 mainly ...
28-Apr-2014

Double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) in the cytoplasm triggers the production of interleukin 1β (IL-1β) as an antiviral host response, and deregulation of the pathways involved can promote inflammatory disease. Here we report a direct cytosolic interaction between the DNA-damage sensor Rad50 and the innate immune system adaptor CARD9. Transfection of dendritic cells with ...
25-Apr-2014
Molecular Systems Biology, online article
During the cell cycle, the levels of hundreds of mRNAs change in a periodic manner, but how this is achieved by alterations in the rates of mRNA synthesis and degradation has not been studied systematically. Here, we used metabolic RNA labeling and comparative dynamic transcriptome analysis (cDTA) to derive mRNA synthesis and degradation rates every 5 min during ...
17-Apr-2014
PLOS Pathogens, online article
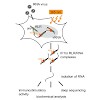
RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs: RIG-I, MDA5 and LGP2) play a major role in the innate immune response against viral infections and detect patterns on viral RNA molecules that are typically absent from host RNA. Upon RNA binding, RLRs trigger a complex downstream signaling cascade resulting in the expression of type I interferons and proinflammatory cytokines. In the ...
17-Apr-2014
Protein Science, online article
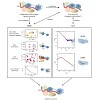
Structural biology provides essential information for elucidating molecular mechanisms that underlie biological function. Advances in hardware, sample preparation, experimental methods, and computational approaches now enable structural analysis of protein complexes with increasing complexity that more closely represent biologically entities in the cellular ...
17-Apr-2014
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
Instead of a classical single-stranded deoxyribonuleic acid (DNA)-binding protein (SSB), some hyperthermophilic crenarchaea harbor a non-canonical SSB termed ThermoDBP. Two related but poorly characterized groups of proteins, which share the ThermoDBP N-terminal DNA-binding domain, have a broader phylogenetic distribution and co-exist with ThermoDBPs and/or other ...
16-Apr-2014
J. Am. Chem. Soc., online article
Multidomain proteins containing intrinsically disordered linkers exhibit large-scale dynamic modes that play key roles in a multitude of molecular recognition and signaling processes. Here, we determine the conformational space sampled by the multidomain splicing factor U2AF65 using complementary nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and small-angle scattering ...
15-Apr-2014
PNAS, online article

The 26S proteasome is a 2.5 MDa molecular machine that executes the degradation of substrates of the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. The molecular architecture of the 26S proteasome was recently established by cryo-EM approaches. For a detailed understanding of the sequence of events from the initial binding of polyubiquitylated substrates to the translocation into ...
31-Mar-2014
Molecular and Cellular Biology, online article
Mutations in the leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 gene (LRRK2) are associated with familial and sporadic Parkinson's disease (PD). LRRK2 is a complex protein that consists of multiple domains, including predicted C-terminal WD40 repeats. In this study, we analyzed functional and molecular features conferred by the WD40 domain. Electron microscopic analysis of the ...
26-Mar-2014
Mol. Pharmaceutics, online article
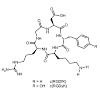
The αvβ3-integrin addressing cyclic pentapeptide cyclo(RGDfK) was conjugated to NOPO, 1,4,7-triazacyclononane 1,4-bis[methylene(hydroxymethyl)phosphinic acid]-7-[methylene(2-carboxyethyl)phosphinic acid], a bifunctional chelator with exceptional gallium-68 labeling properties. NOPO–c(RGDfK) and its Ga(III) and Cu(II) complexes showed high affinity to αvβ3 ...
25-Mar-2014
Nucl. Acids Res., 2014, doi: 10.1093/nar/gku193, 42 (9): 5949-5966 published on 25.03.2014
Nucleic Acids Research, online article

Alternative pre-messenger ribonucleic acid (pre-mRNA) splicing is an essential process in eukaryotic gene regulation. The T-cell intracellular antigen-1 (TIA-1) is an apoptosis-promoting factor that modulates alternative splicing of transcripts, including the pre-mRNA encoding the membrane receptor Fas. TIA-1 is a multi-domain ribonucleic acid (RNA) binding ...
24-Mar-2014
Nature Communications, online article
In bacteria, ribosome stalling during translation of ErmBL leader peptide occurs in the presence of the antibiotic erythromycin and leads to induction of expression of the downstream macrolide resistance methyltransferase ErmB. The lack of structures of drug-dependent stalled ribosome complexes (SRCs) has limited our mechanistic understanding of this regulatory ...
Pharmacophoric Modifications Lead to Superpotent αvβ3 Integrin Ligands with Suppressed α5β1 Activity
23-Mar-2014
J. Med. Chem., online article
The selective targeting of the αvβ3 integrin subtype without affecting the structurally closely related receptor α5β1 is crucial for understanding the details of their biological and pathological functions and thus of great relevance for diagnostic and therapeutic approaches in cancer treatment. Here, we present the synthesis of highly active RGD peptidomimetics ...
20-Mar-2014
Molecular Cell, online article
Hsp90 is the most abundant molecular chaperone in the eukaryotic cell. One of the most stringent clients is the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), whose in vivo function strictly depends on the interaction with the Hsp90 machinery. However, the molecular mechanism of this interaction has been elusive. Here we have reconstituted the interaction of Hsp90 with ...
12-Mar-2014
Angewandte Chemie International Edition, online article

Ultra-high-field NMR spectroscopy requires an increased bandwidth for heteronuclear decoupling, especially in biomolecular NMR applications. Composite pulse decoupling cannot provide sufficient bandwidth at practical power levels, and adiabatic pulse decoupling with sufficient bandwidth is compromised by sideband artifacts. A novel low-power, broadband ...
05-Mar-2014
Journal of Biomolecular NMR, online article

Aggregates formed by amyloidogenic peptides and proteins and reconstituted membrane protein preparations differ significantly in terms of the spectral quality that they display in solid-state NMR experiments. Structural heterogeneity and dynamics can both in principle account for that observation. This perspectives article aims to point out challenges and ...
27-Feb-2014
Cell, online article

In eukaryotes, Dom34 is involved in the rescue of ribosomes that stall on mRNAs during protein synthesis. Using ribosome profiling, Guydosh and Green reveal that, in addition to rescue of ribosomes stalled on truncated mRNAs, Dom34 also recycles ribosomes that are unexpectedly found in the 3′ untranslated regions of many cellular mRNAs.
25-Feb-2014
PNAS, online article
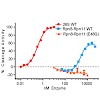
The ATP-dependent degradation of polyubiquitylated proteins by the 26S proteasome is essential for the maintenance of proteome stability and the regulation of a plethora of cellular processes. Degradation of substrates is preceded by the removal of polyubiquitin moieties through the isopeptidase activity of the subunit Rpn11. Here we describe three crystal ...
12-Feb-2014
Cell Host & Microbe, online article
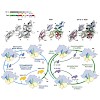
Robust immune responses are essential for eliminating pathogens but must be metered to avoid prolonged immune activation and potential host damage. Upon recognition of microbial DNA, the cytosolic DNA sensor cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) synthetase (cGAS) produces the second messenger cGAMP to initiate the stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway and subsequent ...
10-Feb-2014
Current Opinion in Structural Biology, online article

A system for naming ribosomal proteins is described that the authors intend to use in the future. They urge others to adopt it. The objective is to eliminate the confusion caused by the assignment of identical names to ribosomal proteins from different species that are unrelated in structure and function. In the system proposed here, homologous ribosomal proteins ...
06-Feb-2014
Interface Focus, online article
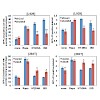
Multi-potent adult mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from bone marrow have therapeutic potential for bone diseases and regenerative medicine. However, an intrinsic heterogeneity in their phenotype, which in turn results in various differentiation potentials, makes it difficult to predict the response of these cells. The aim of this study is to investigate ...
05-Feb-2014
Biological Chemistry, online article
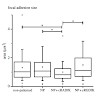
The ribosome and protein synthesis are major targets within the cell for inhibition by antibiotics, such as the tetracyclines. The tetracycline family of antibiotics represent a large and diverse group of compounds, ranging from the naturally produced chlortetracycline, introduced into medical usage in the 1940s, to second and third generation semi-synthetic ...
12-Jan-2014
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article
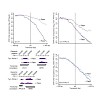
At the 3′ ends of protein-coding genes, RNA polymerase (Pol) II is dephosphorylated at tyrosine residues (Tyr1) of its C-terminal domain (CTD). In addition, the associated cleavage-and-polyadenylation factor (CPF) cleaves the transcript and adds a poly(a) tail. Whether these events are coordinated and how they lead to transcription termination remains poorly ...
10-Jan-2014
Nature Reviews Microbiology, online article
The ribosome is one of the main antibiotic targets in the bacterial cell. Crystal structures of naturally produced antibiotics and their semi-synthetic derivatives bound to ribosomal particles have provided unparalleled insight into their mechanisms of action, and they are also facilitating the design of more effective antibiotics for targeting ...
06-Jan-2014
Nucl. Acids Res., online article
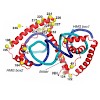
The mitochondrial genome is transcribed by a single-subunit T7 phage-like RNA polymerase (mtRNAP), structurally unrelated to cellular RNAPs. In higher eukaryotes, mtRNAP requires two transcription factors for efficient initiation—TFAM, a major nucleoid protein, and TFB2M, a transient component of mtRNAP catalytic site. The mechanisms behind assembly of the ...
02-Jan-2014
ChemBioChem, online article

Peptides have the specificity and size required to target the protein–protein interactions involved in many diseases. Some cyclic peptides have been utilised as scaffolds for peptide drugs because of their stability; however, other cyclic peptide scaffolds remain to be explored. θ-Defensins are cyclic peptides from mammals; they are characterised by a cyclic ...










