News 2013
29-Dec-2013

Inhibitors of dipeptidylpeptidase IV (DPP-IV) represent a novel class of frequently used anti-diabetic drugs. In addition to its function in metabolic regulation, DPP-IV also plays a role in the immune system. Whether the DPP-IV inhibitors sitagliptin, vildagliptin or saxagliptin impair immune responses is, however, currently unknown. Here, we investigated the ...
24-Dec-2013
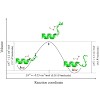
Volume changes associated with protein folding reactions contain valuable information about the folding mechanism and the nature of the transition state. However, meaningful interpretation of such data requires that overall volume changes be deconvoluted into individual contributions from different structural components. Here we focus on one type of structural ...
20-Dec-2013
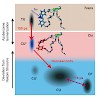
Conformational changes in proteins and peptides can be initiated by diverse processes. This raises the question how the variation of initiation mechanisms is connected to differences in folding or unfolding processes. In this work structural dynamics of a photoswitchable β-hairpin model peptide were initiated by two different mechanisms: temperature jump (T-jump) ...
19-Dec-2013

Wir wünschen allen ein frohes und gesegnetes Weihnachtsfest, und einen guten Start in das neue Jahr!
17-Dec-2013
The structural sensitivity of NMR chemical shifts as computed by quantum chemical methods is compared to a variety of empirical approaches for the example of a prototypical peptide, the 38-residue kaliotoxin KTX comprising 573 atoms. Despite the simplicity of empirical chemical shift prediction programs, the agreement with experimental results is rather good, ...
12-Dec-2013

The macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF)-homologue D- dopachrome tautomerase (D-DT) recently has been described to have similar functions as MIF. However, the role of D-DT, as opposed to MIF, in tumor biology remains unknown. We hypothesized that D-DT could represent a target for therapeutic interventions in cancer. We analyzed the production of D-DT in ...
09-Dec-2013

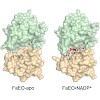
We report on the preparation of a new type of immunotoxin via in vitro ligation of the αHer2 antigen binding fragment (Fab) of the clinically-validated antibody trastuzumab to the plant toxin gelonin, employing catalysis by the bacterial enzyme sortase A (SrtA). The αHer2 Fab was fused with the extended SrtA recognition motif LPET↓GLEH6 at the C-terminus of its ...
05-Dec-2013

Nucleosomes confer a barrier to processes that require access to the eukaryotic genome such as transcription, DNA replication and repair. A variety of ATP-dependent nucleosome remodeling machines and ATP-independent histone chaperones facilitate nucleosome dynamics by depositing or evicting histones and unwrapping the DNA. It is clear that remodeling machines can ...
03-Dec-2013
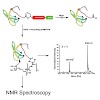
Many cellular processes are regulated by posttranslational modifications that are recognized by specific domains in protein binding partners. These interactions are often weak, thus allowing a highly dynamic and combinatorial regulatory network of protein–protein interactions. We report an efficient strategy that overcomes challenges in structural analysis of ...
02-Dec-2013
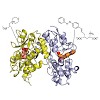
Incorporation of the azobenzene derivative gluazo, a synthetic photochromic ligand, into a kainate receptor allows for the optical control of neuronal activity. The crystal structure of gluazo bound to a dimeric GluK2 ligand-binding domain reveals one monomer in a closed conformation, occupied by gluazo, and the other in an open conformation, with a bound buffer ...
21-Nov-2013

Bacterial pathogenesis is triggered by complex molecular mechanisms that sense bacterial density within an infected host and induce the expression of toxins for overriding the immune response. Virulence is controlled by a set of transcriptional regulators that directly bind to DNA promoter regions of toxin-encoding genes. Here, we identified an ...
21-Nov-2013
Pervasive transcription of eukaryotic genomes stems to a large extent from bidirectional promoters that synthesize mRNA and divergent noncoding RNA (ncRNA). Here, we show that ncRNA transcription in the yeast S. cerevisiae is globally restricted by early termination that relies on the essential RNA-binding factor Nrd1. Depletion of Nrd1 from the nucleus results ...
14-Nov-2013

Messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis and export are tightly linked, but the molecular mechanisms of this coupling are largely unknown. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the conserved TREX complex couples transcription to mRNA export and mediates mRNP formation. Here, we show that TREX is recruited to the transcription machinery by direct interaction of its subcomplex THO ...
14-Nov-2013

Speciation involves the reproductive isolation of natural populations due to the sterility or lethality of their hybrids. However, the molecular basis of hybrid lethality and the evolutionary driving forces that provoke it remain largely elusive. The hybrid male rescue (Hmr) and the lethal hybrid rescue (Lhr) genes serve as a model to study speciation in ...
14-Nov-2013
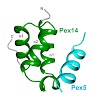
Protein import into peroxisomes relies on the import receptor Pex5, which recognizes proteins with a peroxisomal targeting signal 1 (PTS1) in the cytosol and directs them to a docking complex at the peroxisomal membrane. Receptor-cargo docking occurs at the membrane-associated protein Pex14. In human cells, this interaction is mediated by seven conserved ...
11-Nov-2013

Sinus node dysfunction (SND) is a major clinically relevant disease which is associated with sudden cardiac death and requires surgical implantation of electrical pacemaker devices. Frequently, SND occurs in heart failure and hypertension, conditions that lead to electrical instability of the heart. While the pathologies of acquired SND have been extensively ...
06-Nov-2013
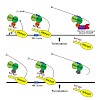
The RNA polymerase II (RNApII) C-terminal domain (CTD)-interacting domain (CID) proteins are involved in two distinct RNApII termination pathways and recognize different phosphorylated forms of CTD. To investigate the role of differential CTD-CID interactions in the choice of termination pathway, we altered the CTD-binding specificity of Nrd1 by domain swapping. ...
04-Nov-2013

Three for two: By using a Methanosarcina mazei PylRS triple mutant (Y306G, Y384F, I405R) the incorporation of two new exo-norbornene-containing pyrrolysine analogues was achieved. X-ray crystallographic analysis led to the identification of the crucial structural elements involved in substrate recognition by the evolved synthetase.
04-Nov-2013
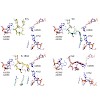
Ketolides, the third generation of expanded-spectrum macrolides, have in the last years become a successful weapon in the endless war against macrolide-resistant pathogens. Ketolides are semisynthetic derivatives of the naturally produced macrolide erythromycin, displaying not only improved activity against some erythromycin-resistant strains but also increased ...
31-Oct-2013
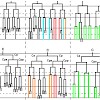
The coordination of cell proliferation and cell fate determination is critical during development but the mechanisms through which this is accomplished are unclear. We present evidence that the Snail-related transcription factor CES-1 of Caenorhabditis elegans coordinates these processes in a specific cell lineage. CES-1 can cause loss of cell polarity in the NSM ...
31-Oct-2013
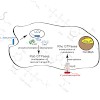
Pathogenic bacteria have developed a variety of mechanisms with which to manipulate the functions of proteins in important cellular pathways of host organisms. Because of their pivotal role in the regulation of cell physiology, members of the family of G-proteins and cytoskeletal proteins are frequent targets for pathogens.
30-Oct-2013
β-Sultams are potent electrophiles that modify nucleophilic residues in selected enzyme active sites. We here identify and characterize some of the specific bacterial targets and show a unique inhibition of the azoreductase family.
26-Oct-2013

Mutations in CACNA1F encoding the α1-subunit of the retinal Cav1.4 L-type calcium channel have been linked to Cav1.4 channelopathies including incomplete congenital stationary night blindness type 2A (CSNB2), Åland Island eye disease (AIED) and cone-rod dystrophy type 3 (CORDX3). Since CACNA1F is located on the X chromosome, Cav1.4 channelopathies are typically ...
25-Oct-2013

Copper-catalysed alkyne–azide 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition (CuAAC) is the predominantly used bioconjugation method in the field of activity-based protein profiling (ABPP). Several limitations, however, including conversion efficiency, protein denaturation and buffer compatibility, restrict the scope of established procedures. We introduce an ABPP customised click ...
25-Oct-2013

Epigenetic regulation of gene expression involves, besides DNA and histone modifications, the relative positioning of DNA sequences within the nucleus. To trace specific DNA sequences in living cells, we used programmable sequence-specific DNA binding of designer transcription activator-like effectors (dTALEs). We designed a recombinant dTALE (msTALE) with ...
24-Oct-2013
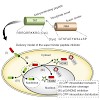
Protein–protein interactions are the basis of all processes in living cells, but most studies of these interactions rely on biochemical in vitro assays. Here we present a simple and versatile fluorescent-three-hybrid (F3H) strategy to visualize and target protein–protein interactions. A high-affinity nanobody anchors a GFP-fusion protein of interest at a defined ...
23-Oct-2013

Transcription of ribosomal RNA by RNA polymerase (Pol) I initiates ribosome biogenesis and regulates eukaryotic cell growth. The crystal structure of Pol I from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae at 2.8 Å resolution reveals all 14 subunits of the 590-kilodalton enzyme, and shows differences to Pol II. An ‘expander’ element occupies the DNA template site and ...
22-Oct-2013
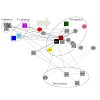
After transcription initiation, RNA polymerase (Pol) II escapes from the promoter and recruits elongation factors. The molecular basis for the initiation-elongation factor exchange during this transition remains poorly understood. Here, we used chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to elucidate the initiation-elongation transition of Pol II in the budding yeast ...
18-Oct-2013
The three tetratricopeptide repeat domain-containing docking proteins Toc64, OM64, and AtTPR7 reside in the chloroplast, mitochondrion, and endoplasmic reticulum of Arabidopsis thaliana, respectively. They are suggested to act during post-translational protein import by association with chaperone-bound preprotein complexes. Here, we performed a detailed ...
16-Oct-2013
The interaction of specific surface receptors of the integrin family with different extracellular matrix-based ligands is of utmost importance for the cellular adhesion process. A ligand consists of an integrin-binding group, here cyclic RGDfX, a spacer molecule that lifts the integrin-binding group from the surface and a surface anchoring group. c(-RGDfX-) ...
15-Oct-2013

Integrins are heterodimeric cell surface receptors, which enable adhesion, proliferation, and migration of cells by recognizing binding motifs in extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins. As transmembrane linkers between the cytoskeleton and the ECM, they are able to recruit a huge variety of proteins and to influence signaling pathways bidirectionally, thereby ...
11-Oct-2013

The backbone dynamics of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) transmembrane helix was compared to those of other transmembrane domains. In contrast to expectation, no above-average backbone dynamics was found for the APP transmembrane helix; the dynamics thus appears not to be optimized for cleavage.
11-Oct-2013
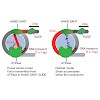
Nucleosome remodelling enzymes of the ISWI family reposition nucleosomes in eukaryotes. ISWI contains an ATPase and a HAND-SANT-SLIDE (HSS) domain. Conformational changes between these domains have been proposed to be critical for nucleosome repositioning by pulling flanking DNA into the nucleosome. We inserted flexible linkers at strategic sites in ISWI to ...
Global Analysis of Eukaryotic mRNA Degradation Reveals Xrn1-Dependent Buffering of Transcript Levels
10-Oct-2013

The rates of mRNA synthesis and degradation determine cellular mRNA levels and can be monitored by comparative dynamic transcriptome analysis (cDTA) that uses nonperturbing metabolic RNA labeling. Here we present cDTA data for 46 yeast strains lacking genes involved in mRNA degradation and metabolism. In these strains, changes in mRNA degradation rates are ...
09-Oct-2013
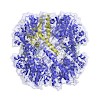
Over 100 protease inhibitors are currently used in the clinics, and most of them use blockage of the active site for their mode of inhibition. Among the protease drug targets are several enzymes for which the correct multimeric assembly is crucial to their activity, such as the proteasome and the HIV protease. Here, we present a novel mechanism of protease ...
06-Oct-2013

Here we report the crystal structure of the human mitochondrial RNA polymerase (mtRNAP) transcription elongation complex, determined at 2.65-Å resolution. The structure reveals a 9-bp hybrid formed between the DNA template and the RNA transcript and one turn of DNA both upstream and downstream of the hybrid. Comparisons with the distantly related RNA polymerase ...
04-Oct-2013
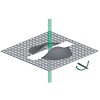
Cryo-electron tomography (CET) is ideally suited for bridging the resolution gap between molecular and cellular structural studies. However, CET is limited to a sample thickness under 500 nm, which is thinner than most cells. Here, we review a method for preparing cells for CET using focused-ion-beam milling, a technique commonly used in materials science. ...
03-Oct-2013
Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) infects and transforms human primary B cells inducing indefinite proliferation. To investigate the potential participation of chromatin mechanisms during the EBV-mediated transformation of resting B cells we performed an analysis of global changes in histone modifications. We observed a remarkable decrease and redistribution of ...
03-Oct-2013
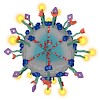
Nanosized mesoporous silica particles with high colloidal stability attract growing attention as drug delivery systems for targeted cancer treatment and as bioimaging devices. This Perspective describes recent breakthroughs in mesoporous silica nanoparticle design to demonstrate their high potential as multifunctional drug delivery nanocarriers. These types of ...
03-Oct-2013

Chromatin organization and gene activity are responsive to developmental and environmental cues. Although many genes are transcribed throughout development and across cell types, much of gene regulation is highly cell-type specific. To readily track chromatin features at the resolution of cell types within complex tissues, we developed and validated chromatin ...
01-Oct-2013
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging mass spectrometry (MALDI IMS) is a powerful tool for the visualization of proteins in tissues and has demonstrated considerable diagnostic and prognostic value. One main challenge is that the molecular identity of such potential biomarkers mostly remains unknown. We introduce a generic method that removes this ...
01-Oct-2013
High concentrations (> 100 µM) of the ribonucleoside analog 4-thiouridine (4sU) is widely used in methods for RNA analysis like photoactivatable-ribonucleoside-enhanced crosslinking and immunoprecipitation (PAR-CLIP) and nascent messenger (m)RNA labeling (4sU-tagging). Here, we show that 4sU-tagging at low concentrations ≤ 10 µM can be used to measure production ...
01-Oct-2013
The small heat shock protein αB-crystallin is an oligomeric molecular chaperone that binds aggregation-prone proteins. As a component of the proteostasis system, it is associated with cataract, neurodegenerative diseases, and myopathies. The structural determinants for the regulation of its chaperone function are still largely elusive. Combining different ...
27-Sep-2013

Significant differences in the reactivity of norbornene derivatives in the inverse electron-demand Diels–Alder reaction with tetrazines were revealed by kinetic studies. Substantial rate enhancement for the exo norbornene isomers was observed (see scheme). Quantum-chemical calculations were used to rationalize and support the observed experimental data.
26-Sep-2013
The knowledge that many pathogens rely on cell-to-cell communication mechanisms known as quorum sensing, opens a new disease control strategy: quorum quenching. Here we report on one of the rare examples where Gram-positive bacteria, the ‘Staphylococcus intermedius group’ of zoonotic pathogens, excrete two compounds in millimolar concentrations that suppress the ...
26-Sep-2013

Small G-proteins of the Ras superfamily control the temporal and spatial coordination of intracellular signaling networks by acting as molecular on/off switches. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) regulate the activation of these G-proteins through catalytic replacement of GDP by GTP. During nucleotide exchange, three distinct substrate·enzyme complexes ...
20-Sep-2013

For the two angiogenic relevant integrins α5β1 and αvβ3, functionalized derivatives of the selective antagonists 1 and 2 could target and discriminate between tumor cells in vivo based on their different integrin patterns and also delay tumor growth in vivo. In addition, the first α5β1-selective integrin antagonist that enables specific molecular imaging by ...
19-Sep-2013
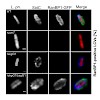
The causative agent of Legionnaires' disease, Legionella pneumophila, uses the Icm/Dot type IV secretion system (T4SS) to form in phagocytes a distinct “Legionella-containing vacuole” (LCV), which intercepts endosomal and secretory vesicle trafficking. Proteomics revealed the presence of the small GTPase Ran and its effector RanBP1 on purified LCVs. Here we ...
19-Sep-2013

On July 18th CIPSM researchers took part in the 2013 Munich B2run project. We thank them for participating so neonish!
19-Sep-2013

The Scientific Oktoberfest will be this years meeting point for some of the internationally most distinguished researchers in the field of Chemistry & Chemical Biology. The CIPSM Scientific Oktoberfest will be held from the 19th to the 20th of September in the Department of Chemistry of the Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität (LMU) München. At the two-day conference, ...
17-Sep-2013

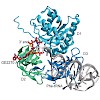
Bypass of Ess1 (Bye1) is a nuclear protein with a domain resembling the central domain in the transcription elongation factor TFIIS. Here we show that Bye1 binds with its TFIIS-like domain (TLD) to RNA polymerase (Pol) II, and report crystal structures of the Bye1 TLD bound to Pol II and three different Pol II–nucleic acid complexes. Like TFIIS, Bye1 binds with ...
17-Sep-2013
Three analogues of amythiamicin D, which differ in the substitution pattern at the methine group adjacent to C2 of the thiazole ring C, were prepared by de novo total synthesis. In amythiamicin D, this carbon atom is (S)-isopropyl substituted. Two of the new analogues carry a hydroxymethyl in place of the isopropyl group, one at an S- (compound 3 a) and the other ...
13-Sep-2013
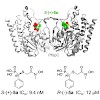
The emergence and spread of multidrug-resistant pathogens are widely believed to endanger human health. New drug targets and lead compounds exempt from cross-resistance with existing drugs are urgently needed. We report on the synthesis and properties of “reverse” thia analogs of fosmidomycin, which inhibit the first committed enzyme of a metabolic pathway that ...
12-Sep-2013
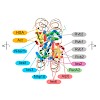
INO80/SWR1 family chromatin remodelers are complexes composed of >15 subunits and molecular masses exceeding 1 MDa. Their important role in transcription and genome maintenance is exchanging the histone variants H2A and H2A.Z. We report the architecture of S. cerevisiae INO80 using an integrative approach of electron microscopy, crosslinking and mass ...
11-Sep-2013
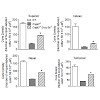
Photoreceptor cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) channels regulate Ca2+ influx in rod and cone photoreceptors. cGMP, the native ligand of the photoreceptor CNG channels, has been associated with cytotoxicity when its levels rise above normal due to defects in photoreceptor phosphodiesterase (PDE6) or regulation of retinal guanylyl cyclase (retGC). We found a massive ...
10-Sep-2013

The CH3 homodimer at the C-terminal end of the antibody heavy chain is the key noncovalent interaction stabilizing antibody proteins. Here, we use single-molecule force spectroscopy to investigate the dissociation mechanics of CH3 as a proxy for antibody mechanical stability. We find the CH3 homodimer to be a highly stable complex, and its dissociation force of ...
06-Sep-2013
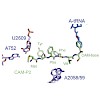
The ribosomal exit tunnel had recently become the centre of many functional and structural studies. Accumulated evidence indicates that the tunnel is not simply a passive conduit for the nascent chain, but a rather functionally important compartment where nascent peptide sequences can interact with the ribosome to signal translation to slow down or even stop. To ...
05-Sep-2013
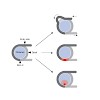
Nucleosomes, the basic organizational units of chromatin, package and regulate eukaryotic genomes. ATP-dependent nucleosome-remodeling factors endow chromatin with structural flexibility by promoting assembly or disruption of nucleosomes and the exchange of histone variants. Furthermore, most remodeling factors induce nucleosome movements through sliding of ...
05-Sep-2013
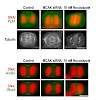
During animal cell cytokinesis, the spindle directs contractile ring assembly by activating RhoA in a narrow equatorial zone. Rapid GTPase activating protein (GAP)-mediated inactivation (RhoA flux) is proposed to limit RhoA zone dimensions. Testing the significance of RhoA flux has been hampered by the fact that the GAP targeting RhoA is not known. Here, we ...
05-Sep-2013
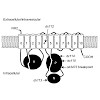
In previous work, we found that gain-of-function mutations that hyperactivate GEM-1 (an SLC16A transporter protein) can bypass the requirement for GON-2 (a TRPM channel protein) during the initiation of gonadogenesis in C. elegans. Consequently, we proposed that GEM-1 might function as part of a Mg2+ uptake pathway that functions in parallel to GON-2. In this ...
03-Sep-2013
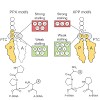
Ribosomes are the protein synthesizing factories of the cell, polymerizing polypeptide chains from their constituent amino acids. However, distinct combinations of amino acids, such as polyproline stretches, cannot be efficiently polymerized by ribosomes, leading to translational stalling. The stalled ribosomes are rescued by the translational elongation factor P ...
03-Sep-2013

The 26S proteasome is a 2.5 MDa molecular machine for the degradation of substrates of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway with a key role in cellular proteostasis. Until recently, only the structure of its core particle, the 20S proteasome, could be studied in detail, whereas the 19S regulatory particle or the holocomplex remained elusive. Novel integrative ...
31-Aug-2013
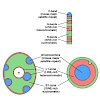
To improve light propagation through the retina, the rod nuclei of nocturnal mammals are uniquely changed compared to the nuclei of other cells. In particular, the main classes of chromatin are segregated in them and form regular concentric shells in order; inverted in comparison to conventional nuclei. A broad study of the epigenetic landscape of the inverted ...
30-Aug-2013

Selective and targeted delivery of drugs to tumors is a major challenge for an effective cancer therapy and also to overcome the side-effects associated with current treatments. Overexpression of various receptors on tumor cells is a characteristic structural and biochemical aspect of tumors and distinguishes them from physiologically normal cells. This abnormal ...
27-Aug-2013
Three new cytosine derived DNA modifications, 5-hydroxymethyl-2′-deoxycytidine (hmdC), 5-formyl-2′-deoxycytidine (fdC) and 5-carboxy-2′-deoxycytidine (cadC) were recently discovered in mammalian DNA, particularly in stem cell DNA. Their function is currently not clear, but it is assumed that in stem cells they might be intermediates of an active demethylation ...
26-Aug-2013
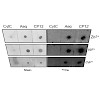
Calcium plays an important role in the regulation of several chloroplast processes. However, very little is still understood about the calcium fluxes or calcium-binding proteins present in plastids. Indeed, classical EF-hand containing calcium-binding proteins appears to be mostly absent from plastids. In the present study we analyzed the stroma fraction of ...
25-Aug-2013

We report that low percentages of dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) in liquid chromatography solvents lead to a strong enhancement of electrospray ionization of peptides, improving the sensitivity of protein identification in bottom-up proteomics by up to tenfold. The method can be easily implemented on any LC-MS/MS system without modification to hardware or software and ...
23-Aug-2013
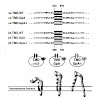
Integrin heterodimeric cell adhesion and signaling receptors bind ligands of the extracellular matrix and relay signals bidirectionally across cell membranes. Thereby, integrins adopt multiple conformational and functional states that control ligand binding affinity and linkage to cytosolic/cytoskeletal proteins. Here, we designed an integrin chimera encompassing ...
23-Aug-2013
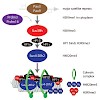
The proper regulation and spatial organization of heterochromatin is crucial for a broad range of cellular processes, ranging from gene silencing to maintenance of genomic integrity and cell division. The most prominent heterochromatin domains are formed across repetitive sequences (major satellite repeats) around the centromere regions. Those pericentric ...
22-Aug-2013
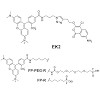
Rhomboids are intramembrane serine proteases that play diverse biological roles, including some that are of potential therapeutical relevance. Up to date, rhomboid inhibitor assays are based on protein substrate cleavage. Although rhomboids have an overlapping substrate specificity, substrates cannot be used universally. To overcome the need for substrates, we ...
16-Aug-2013
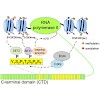
The smallest viable unit of life is the cell. From bacteria to mammals, all cells use the same nucleic acid-based universal code for the maintenance and inheritance of genetic information. All life on earth probably started with a common ancestral cell1 approximately 4 billion years ago. Today, a huge diversity of organisms live on Earth, many of them still at ...
14-Aug-2013
Matrix enzymes are imported into peroxisomes and glyoxysomes, a subclass of peroxisomes involved in lipid mobilization. Two peroxisomal targeting signals (PTS), the C-terminal PTS1 and the N-terminal PTS2, mediate the translocation of proteins into the organelle. PTS2 processing upon import is conserved in higher eukaryotes, and in watermelon the glyoxysomal ...
13-Aug-2013
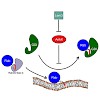
Membrane trafficking is regulated by small Ras-like GDP/GTP binding proteins of the Rab subfamily (Rab GTPases) that cycle between membranes and cytosol depending on their nucleotide state. The GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI) solubilizes prenylated Rab GTPases from and shuttles them between membranes in the form of a soluble cytosolic complex. We use attenuated ...
13-Aug-2013
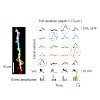
Layer 5 pyramidal neurons process information from multiple cortical layers to provide a major output of cortex. Because of technical limitations it has remained unclear how these cells integrate widespread synaptic inputs located in distantly separated basal and tuft dendrites. Here, we obtained in vivo two-photon calcium imaging recordings from the entire ...
12-Aug-2013
Dynamic Nuclear Polarization solid-state NMR holds the potential to enable a dramatic increase in sensitivity by exploiting the large magnetic moment of the electron. However, applications to biological solids are hampered in uniformly isotopically enriched biomacromolecules due to line broadening which yields a limited spectral resolution at cryogenic ...
11-Aug-2013
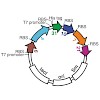
The essential core of the transcription coactivator Mediator consists of two conserved multiprotein modules, the head and middle modules. Whereas the structure of the head module is known, the structure of the middle module is lacking. Here we report a 3D model of a 6-subunit Mediator middle module. The model was obtained by arranging crystal structures and ...
08-Aug-2013

The NCI-60 cell line collection is a very widely used panel for the study of cellular mechanisms of cancer in general and in vitro drug action in particular. It is a model system for the tissue types and genetic diversity of human cancers and has been extensively molecularly characterized. Here, we present a quantitative proteome and kinome profile of the NCI-60 ...
06-Aug-2013
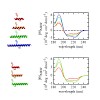
The dynamics of peptide α-helices have been studied extensively for many years, and the kinetic mechanism of the helix–coil dynamics has been discussed controversially. Recent experimental results have suggested that equilibrium helix–coil dynamics are governed by movement of the helix/coil boundary along the peptide chain, which leads to slower unfolding ...
05-Aug-2013

The pathogenic bacterium Legionella pneumophila interacts intimately with signaling molecules during the infection of eukaryotic host cells. Among a diverse set of regulatory molecules, host small GTPases appear to be prominent and significant targets. Small GTPases are molecular switches that regulate cellular signaling via their respective nucleotide-bound ...
05-Aug-2013

Electron microscopy played a key role in establishing cell biology as a discipline, by producing fundamental insights into cellular organization and ultrastructure. Many seminal discoveries were made possible by the development of new sample preparation methods and imaging modalities. Recent technical advances include sample vitrification that faithfully ...
01-Aug-2013
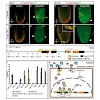
Several signalling cascades are implicated in the formation and patterning of the three principal germ layers, but their precise temporal-spatial mode of action in progenitor populations remains undefined. We have used conditional gene deletion of mouse β-catenin in Sox17-positive embryonic and extra-embryonic endoderm as well as vascular endothelial progenitors ...
01-Aug-2013
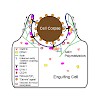
The engulfment and subsequent degradation of apoptotic cells by phagocytes is an evolutionarily conserved process that efficiently removes dying cells from animal bodies during development. Here, we report that clathrin heavy chain (CHC-1), a membrane coat protein well known for its role in receptor-mediated endocytosis, and its adaptor epsin (EPN-1) play crucial ...
31-Jul-2013
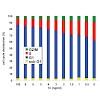
The proto-oncogene c-myc encodes a basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper transcription factor (c-Myc). c-Myc plays a crucial role in cell growth and proliferation. Here, we examined how expression of c-Myc target genes and cell proliferation depend on variation of c-Myc protein levels. We show that proliferation rates, the number of cells in S-phase, and cell ...
31-Jul-2013
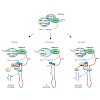
Post-translational modifications of the carboxy-terminal domain of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII CTD) provide recognition marks to coordinate recruitment of numerous nuclear factors controlling transcription, cotranscriptional RNA processing, chromatin remodeling, and RNA export. Compared with the progress in yeast and mammals, deciphering the ...
30-Jul-2013
The field of proteomics continues to be driven by improvements in analytical technology, notably in peptide separation, quantitative MS, and informatics. In this study, we have characterized a hybrid linear ion trap high field Orbitrap mass spectrometer (Orbitrap Elite) for proteomic applications. The very high resolution available on this instrument allows 95% ...
25-Jul-2013

Dosage compensation in Drosophila involves a global activation of genes on the male X chromosome. The activating complex (MSL-DCC) consists of male-specific-lethal (MSL) proteins and two long, noncoding roX RNAs. The roX RNAs are essential for X-chromosomal targeting, but their contributions to MSL-DCC structure and function are enigmatic. Conceivably, the RNA ...
22-Jul-2013
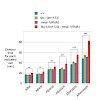
Mitochondrial morphology changes in response to various stimuli but the significance of this is unclear. In a screen for mutants with abnormal mitochondrial morphology, we identified MMA-1, the Caenorhabditis elegans homolog of the French Canadian Leigh Syndrome protein LRPPRC (leucine-rich pentatricopeptide repeat containing). We demonstrate that reducing mma-1 ...
19-Jul-2013
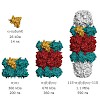
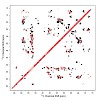
Solution-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is a very successful method to characterize the structure and dynamics of biomolecules in solution.[1, 2] However, resonance lines broaden significantly with increasing molecular weight, simultaneously affecting sensitivity and resolution. This broadening is due to long rotational tumbling correlation ...
17-Jul-2013
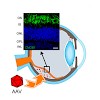
Visual phototransduction relies on the function of cyclic nucleotide-gated channels in the rod and cone photoreceptor outer segment plasma membranes. The role of these ion channels is to translate light-triggered changes in the second messenger cyclic guanosine 3′–5′-monophosphate levels into an electrical signal that is further processed within the retinal ...
09-Jul-2013

Caseinolytic proteases (ClpPs) are large oligomeric protein complexes that contribute to cell homeostasis as well as virulence regulation in bacteria. Although most organisms possess a single ClpP protein, some organisms encode two or more ClpP isoforms. Here, we elucidated the crystal structures of ClpP1 and ClpP2 from pathogenic Listeria monocytogenes and ...
08-Jul-2013
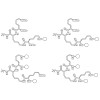
We present a click chemistry-based molecular toolkit for the biofunctionalization of materials to selectively control integrin-mediated cell adhesion. To this end, α5β1-selective RGD peptidomimetics were covalently immobilized on Ti-based materials, and the capacity to promote the selective binding of α5β1 was evaluated using a solid-phase integrin binding assay. ...
03-Jul-2013
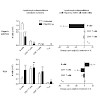
Early in the course of infection, detection of pathogen-associated molecular patterns by innate immune receptors can shape the subsequent adaptive immune response. Here we investigate the influence of virus-associated innate immune activation on lymphocyte distribution in secondary lymphoid organs. We show for the first time that virus infection of mice induces ...
02-Jul-2013
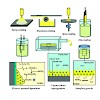
In this article, we discuss how fluorescence microscopy techniques are used to investigate important characteristics of porous silica materials. We start with a discussion of the synthesis, formation mechanism and functionalization of these materials. We then give an introduction to single molecule microscopy and show how this technique can be used to gain deeper ...
01-Jul-2013

Duocarmycin-derived seco-cyclopropabenzindole (CBI) drugs have been shown to bind DNA and an aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH1A1) in lung cancer cells. The removal of the DNA-binding indole moiety results in a CBI compound that does not bind to DNA in whole cells but still exhibits remarkable cytotoxicity. This CBI compound has an increased affinity for ALDH1A1. ...
01-Jul-2013
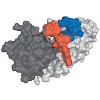
The final step in the biosynthesis of the 22nd genetically encoded amino acid, pyrrolysine, is catalyzed by PylD, a structurally and mechanistically unique dehydrogenase. This catalyzed reaction includes an induced-fit mechanism achieved by major structural rearrangements of the N-terminal helix upon substrate binding. Different steps of the reaction trajectory ...
01-Jul-2013
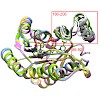
The NADP+-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase from Ralstonia sp. (RasADH) belongs to the protein superfamily of short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (SDRs). As an enzyme that accepts different types of substrates—including bulky–bulky as well as small–bulky secondary alcohols or ketones—with high stereoselectivity, it offers potential as a biocatalyst for industrial ...
30-Jun-2013
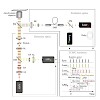
Pulsed interleaved excitation (PIE) is the methodology of interleaved or alternating excitation of different fluorophores on the nanosecond timescale, which allows quasi-simultaneous, yet independent measurements to be performed. PIE simplifies quantification of several fluorescence techniques such as FCCS and FRET experiments. Foremost, it allows to specifically ...
30-Jun-2013
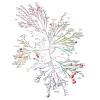
The Hsp70-interacting protein, Hip, cooperates with the chaperone Hsp70 in protein folding and prevention of aggregation. Hsp70 interacts with non-native protein substrates in an ATP-dependent reaction cycle regulated by J-domain proteins and nucleotide exchange factors (NEFs). Hip is thought to delay substrate release by slowing ADP dissociation from Hsp70. Here ...
27-Jun-2013
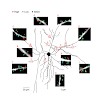
In the mammalian brain, calcium signals in dendritic spines are involved in many neuronal functions, particularly in the induction of synaptic plasticity. Recent studies have identified sensory stimulation-evoked spine calcium signals in cortical neurons in vivo. However, spine signaling during ongoing cortical activity in the absence of sensory input, which is ...
27-Jun-2013

We are happy that Nature notes: „One goal of the Excellence Initiative is to create research clusters that integrate university laboratories more closely with local non-university institutes such as Max Planck and Helmholtz centres. The clusters are also intended to form a conduit between academia and business, a sector which funds and conducts two-thirds of ...
25-Jun-2013
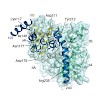
Protein kinases are key regulators of cellular processes, and aberrant function is often associated with human disease. Consequently, kinases represent an important class of therapeutic targets and about 20 kinase inhibitors (KIs) are in clinical use today. Detailed knowledge about the selectivity of KIs is important for the correct interpretation of their ...
21-Jun-2013
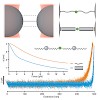
Single molecule mechanical techniques like AFM or optical tweezers provide insight into the conformational dynamics of macromolecules and allow reconstructing details of the free energy landscapes that direct such processes.1 Single-molecule mechanical assays have been successfully applied to analyze large conformational changes like the ones that occur in ...
18-Jun-2013
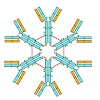
IgM is the first antibody produced during the humoral immune response. Despite its fundamental role in the immune system, IgM is structurally only poorly described. In this work we used X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy to determine the atomic structures of the constant IgM Fc domains (Cµ2, Cµ3, and Cµ4) and to address their roles in IgM oligomerization. ...
17-Jun-2013

Isobaric mass tagging (e.g., TMT and iTRAQ) is a precise and sensitive multiplexed peptide/protein quantification technique in mass spectrometry. However, accurate quantification of complex proteomic samples is impaired by cofragmentation of peptides, leading to systematic underestimation of quantitative ratios. Label-free quantification strategies do not suffer ...
13-Jun-2013

Beyond their role in post-transcriptional gene silencing, Dicer and Argonaute, two components of the RNA interference (RNAi) machinery, were shown to be involved in epigenetic regulation of centromeric heterochromatin and transcriptional gene silencing. In particular, RNAi mechanisms appear to play a role in repeat induced silencing and some aspects of ...
12-Jun-2013
Transcriptional enhancement of X-linked genes to compensate for the sex chromosome monosomy in Drosophila males is brought about by a ribonucleoprotein assembly called Male-Specific-Lethal or Dosage Compensation Complex (MSL-DCC). This machinery is formed in male flies and specifically associates with active genes on the X chromosome. After assembly at dedicated ...
10-Jun-2013
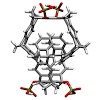
Selective binding of the phosphate-substituted molecular tweezer 1a to protein lysine residues was suggested to explain the inhibition of certain enzymes and the aberrant aggregation of amyloid petide Aβ42 or α-synuclein, which are assumed to be responsible for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, respectively. In this work we systematically investigated the ...
10-Jun-2013

A major limitation of biopharmaceutical proteins is their fast clearance from circulation via kidney filtration, which strongly hampers efficacy both in animal studies and in human therapy. We have developed conformationally disordered polypeptide chains with expanded hydrodynamic volume comprising the small residues Pro, Ala and Ser (PAS). PAS sequences are ...
07-Jun-2013

When applied to biomolecules, solid-state NMR suffers from low sensitivity and resolution. The major obstacle to applying proton detection in the solid state is the proton dipolar network, and deuteration can help avoid this problem. In the past, researchers had primarily focused on the investigation of exchangeable protons in these systems. In this Account, we ...
07-Jun-2013
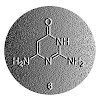
Queuosine is one of the most strongly modified nucleosides found in transferRNA (tRNA) of almost all species. Queuosine is found exclusively in the wooble position of the anticodon loop of several tRNA, where it is involved in tRNAAsp, tRNAAsn tRNAHis, and tRNATyr. The biosynthesis of queuosine is performed by prokaryotes, and eukaryotes are fully dependent on ...
07-Jun-2013
Evolutionarily young genes that serve essential functions represent a paradox; they must perform a function that either was not required until after their birth or was redundant with another gene. How young genes rapidly acquire essential function is largely unknown. We traced the evolutionary steps by which the Drosophila gene Umbrea acquired an essential role ...
06-Jun-2013

Drosophila cryptochrome (dCRY) is a FAD-dependent circadian photoreceptor, whereas mammalian cryptochromes (CRY1/2) are integral clock components that repress mCLOCK/mBMAL1-dependent transcription. We report crystal structures of full-length dCRY, a dCRY loop deletion construct, and the photolyase homology region of mouse CRY1 (mCRY1). Our dCRY structures depict ...
06-Jun-2013

Ribosome biogenesis is a process required for cellular growth and proliferation. Processing of ribosomal (r)RNA is highly sensitive to flavopiridol, a specific inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (Cdk9). Cdk9 has been characterised as the catalytic subunit of the positive transcription elongation factor-b (P-TEFb) of RNA polymerase (RNAP)II. Here we studied ...
04-Jun-2013
The interactions and coordination of biomolecules are crucial for most cellular functions. The observation of protein interactions in live cells may provide a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms. After fluorescent labeling of the interacting partners and live-cell microscopy, the colocalization is generally analyzed by quantitative global methods. ...
03-Jun-2013

The trigger loop (TL) forms a conserved element in the RNA polymerase active centre that functions in the elongation phase of transcription. Here, we show that the TL also functions in transcription initiation and termination. Using recombinant variants of RNA polymerase from Pyrococcus furiosus and a reconstituted transcription system, we demonstrate that the TL ...
29-May-2013

Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) is an autosomal dominant myopathy with a strong epigenetic component. It is associated with deletion of a macrosatellite repeat leading to over-expression of the nearby genes. Among them, we focused on FSHD region gene 1 (FRG1) since its over-expression in mice, Xenopus laevis and Caenorhabditis elegans, leads to ...
26-May-2013
Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation is involved in the regulation of a variety of cellular pathways, including, but not limited to, transcription, chromatin, DNA damage and other stress signalling. Similar to other tightly regulated post-translational modifications, poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation employs ‘writers’, ‘readers’ and ‘erasers’ to confer regulatory functions. The ...
25-May-2013
Diurnality, associated with enhanced visual acuity and color vision, is typical of most modern Primates. However, it remains a matter of debate when and how many times primates re-acquired diurnality or returned to nocturnality. We analyzed the features specific to nocturnal and diurnal vision that were recently found in the nuclei of mammalian rod photoreceptor ...
22-May-2013
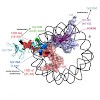
Facilitates chromatin transcription (FACT) is a conserved histone chaperone that reorganizes nucleosomes and ensures chromatin integrity during DNA transcription, replication and repair. Key to the broad functions of FACT is its recognition of histones H2A–H2B (ref. 2). However, the structural basis for how histones H2A–H2B are recognized and how this integrates ...
21-May-2013
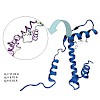
Here we report that chromatin, the complex and dynamic eukaryotic DNA packaging structure, is able to sense cellular redox changes. Histone H3, the only nucleosomal protein that possesses cysteine(s), can be modified by glutathione (GSH).
19-May-2013
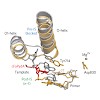
8-Oxopurines (8-oxodG and 8-oxodA) and formamidopyrimidines (FaPydG and FaPydA) are major oxidative DNA lesions involved in cancer development and aging. Their mutagenicity is believed to result from a conformational shift of the N9-C1′ glycosidic bonds from anti to syn, which allows the lesions to form noncanonical Hoogsteen-type base pairs with incoming ...
19-May-2013
We present a peptide library and data resource of >100,000 synthetic, unmodified peptides and their phosphorylated counterparts with known sequences and phosphorylation sites. Analysis of the library by mass spectrometry yielded a data set that we used to evaluate the merits of different search engines (Mascot and Andromeda) and fragmentation methods (beam-type ...
17-May-2013
In this study, it is shown that the cytotoxic response of cells as well as the uptake kinetics of nanoparticles (NPs) is cell type dependent. We use silica NPs with a diameter of 310 nm labeled with perylene dye and 304 nm unlabeled particles to evaluate cell type-dependent uptake and cytotoxicity on human vascular endothelial cells (HUVEC) and cancer cells ...
13-May-2013
Pigment cells and neuronal cells both are derived from the neural crest. Here, we describe the Pit-Oct-Unc (POU) domain transcription factor Brn3a, normally involved in neuronal development, to be frequently expressed in melanoma, but not in melanocytes and nevi. RNAi-mediated silencing of Brn3a strongly reduced the viability of melanoma cell lines and decreased ...
Targeted Drug Delivery in Cancer Cells with Red-Light Photoactivated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
13-May-2013
Mesoporous nanoparticles for drug delivery would benefit significantly from further improvements in targeting efficiency and endosomal release. We present a system based on colloidal mesoporous silica nanoparticles with targeting-ligands and a red-light photosensitizer. This nanoparticle system provides spatial and temporal control of the release of drugs into ...
11-May-2013
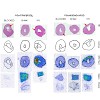
Expression of αvβ3 integrin is increased after myocardial infarction as part of the repair process. Increased expression of αvβ3 has been shown by molecular imaging with 18F-galacto-RGD in a rat model. The 68Ga-labelled RGD compounds 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD and 68Ga-TRAP(RGD)3 have high specificity and affinity, and may therefore serve as alternatives of 18F-galacto-RGD ...
10-May-2013
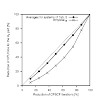
The calculation of molecular response properties in dynamic molecular systems is a major challenge that requires sampling over many steps of, e.g., Born–Oppenheimer molecular dynamics (BO-MD) simulations. We present an extrapolation scheme to accelerate such calculations for multiple steps within BO-MD trajectories or equivalently within other sampling methods of ...
08-May-2013

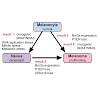
The tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) is a multifunctional cytokine playing a key role in tissue regeneration and remodeling. Dysregulation of TWEAK signaling is involved in various pathological processes like autoimmune diseases and cancer. The unique interaction with its cognate receptor Fn14 makes both ligand and receptor promising ...
08-May-2013
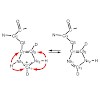
The amyloid β-peptide (Aβ) is the major structural component of amyloid fibrils in the plaques of brains of Alzheimer's disease patients. Numerous studies have addressed important aspects of secondary and tertiary structure of fibrils. In electron microscopic images, fibrils often bundle together. The mechanisms which drive the association of protofilaments into ...
01-May-2013

Most integral membrane proteins form dimeric or oligomeric complexes. Oligomerization is frequently supported by the non-covalent interaction of transmembrane helices. It is currently not clear how many high-affinity transmembrane domains (TMD) exist in a proteome and how specific their interactions are with respect to preferred contacting faces and their ...
01-May-2013
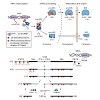
The production and processing of ribosomal RNA is a complex and well-coordinated nucleolar process for ribosome biogenesis. Progress in understanding nucleolar structure and function has lead to the unexpected discovery of the nucleolus as highly sensitive sensor of cellular stress and important regulator of the tumour suppressor p53. Inhibition of ribosomal RNA ...
01-May-2013
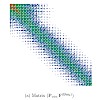
An atomic-orbital (AO) based formulation for calculating nuclear magnetic resonance chemical shieldings at the second-order Møller-Plesset perturbation theory level is introduced, which provides a basis for reducing the scaling of the computational effort with the molecular size from the fifth power to linear and for a specific nucleus to sublinear. The latter ...
01-May-2013

Protein synthesis in all cells is carried out by macromolecular machines called ribosomes. Although the structures of prokaryotic, yeast and protist ribosomes have been determined, the more complex molecular architecture of metazoan 80S ribosomes has so far remained elusive. Here we present structures of Drosophila melanogaster and Homo sapiens 80S ribosomes in ...
30-Apr-2013

Protein sequence databases are indispensable tools for life science research including mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomics. In current database construction processes, sequence similarity clustering is used to reduce redundancies in the source data. Albeit powerful, it ignores the peptide-centric nature of proteomic data and the fact that MS is able to ...
30-Apr-2013

Development, growth and adult survival are coordinated with available metabolic resources, ascertaining that the organism responds appropriately to environmental conditions. MicroRNAs are short (21–23 nt) regulatory RNAs that confer specificity on the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) to inhibit a given set of mRNA targets. We profiled changes in miRNA ...
30-Apr-2013
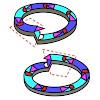
The 26S proteasome is a 2.5-MDa, ATP-dependent multisubunit proteolytic complex that processively destroys proteins carrying a degradation signal. The proteasomal ATPase heterohexamer is a key module of the 19S regulatory particle; it unfolds substrates and translocates them into the 20S core particle where degradation takes place. We used cryoelectron microscopy ...
28-Apr-2013
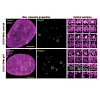
Cdc48 (also known as p97), a conserved chaperone-like ATPase, plays a strategic role in the ubiquitin system1, 2, 3. Empowered by ATP-driven conformational changes 4, Cdc48 acts as a segregase by dislodging ubiquitylated proteins from their environment1, 2, 5. Ufd1, a known co-factor of Cdc48, also binds SUMO (ref. 6), but whether SUMOylated proteins are subject ...
26-Apr-2013
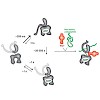
The numerous functions of the important class of molecular chaperones, heat shock proteins 70 (Hsp70), rely on cycles of intricate conformational changes driven by ATP-hydrolysis and regulated by cochaperones and substrates. Here, we used Förster resonance energy transfer to study the conformational dynamics of individual molecules of Ssc1, a mitochondrial Hsp70, ...
24-Apr-2013

Trifunctional biotin reagents incorporating cleavable linkers are evaluated for their usage in protein enrichment. A linker based on the Dde protecting group leads to efficient release of protein targets under mild conditions. It additionally contains a masked trypsin cleavage site, which eliminates the majority of the tag during tryptic digestion.
23-Apr-2013
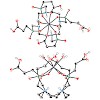
The cyclen-based tetraphosphinate chelator 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetrakis[methylene(2-carboxyethyl)phosphinic acid] (DOTPI) comprises four additional carboxylic acid moieties for bioconjugation. The thermodynamic stability constants (logKML) of metal complexes, as determined by potentiometry, were 23.11 for CuII, 20.0 for LuIII, 19.6 for YIII, ...
19-Apr-2013
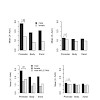
Conrad et al. (Reports, 10 August 2012, p. 742) reported that Drosophila dosage compensation might largely be due to increased recruitment of RNA polymerase II to promoters. A reassessment of the numerical operations revealed that the authors’ calculations are severely confounded by an inappropriate numerical procedure. A rectified analysis strongly suggests that ...
19-Apr-2013
In neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD) and prion diseases, deposits of aggregated disease-specific proteins are found. Oligomeric aggregates are presumed to be the key neurotoxic agent. Here we describe the novel oligomer modulator anle138b [3-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-5-(3-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrazole], an aggregation ...
19-Apr-2013

Extensive research on antiviral small molecules starting in the early 1970s has led to the identification of 10-carboxymethyl-9-acridanone (CMA) as a potent type I interferon (IFN) inducer. Up to date, the mode of action of this antiviral molecule has remained elusive. Here we demonstrate that CMA mediates a cell-intrinsic type I IFN response, depending on the ...
18-Apr-2013
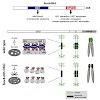
Cohesin plays an important role in chromatid cohesion and has additional functions in higher-order chromatin organization and in transcriptional regulation. The binding of cohesin to euchromatic regions is largely mediated by CTCF or the mediator complex. However, it is currently unknown how cohesin is recruited to pericentric heterochromatin in mammalian cells. ...
17-Apr-2013

Transcription steps are marked by different modifications of the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII). Phosphorylation of Ser5 and Ser7 by cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) as part of TFIIH marks initiation, whereas phosphorylation of Ser2 by CDK9 marks elongation. These processes are thought to take place in localized transcription foci in the nucleus, ...
15-Apr-2013
The last step in the biosynthetic pathway of the key strawberry flavor compound 4-hydroxy-2,5-dimethyl-3(2H)-furanone (HDMF) is catalyzed by Fragaria x ananassa enone oxidoreductase (FaEO), earlier putatively assigned as quinone oxidoreductase (FaQR). The ripening-induced enzyme catalyzes the reduction of the exocyclic double bond of the highly reactive precursor ...
15-Apr-2013

Archival formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded clinical samples represent a very diverse source of material for proteomic investigation of diseases, often with follow-up patient information. Here, we describe an analytical workflow for analysis of laser-capture microdissected formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded samples that allows studying proteomes to a depth of ...
15-Apr-2013
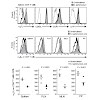
The trafficking of effector T cells is tightly regulated by the expression of site-specific sets of homing molecules. In contrast, naive T cells are generally assumed to express a uniform pattern of homing molecules and to follow a random distribution within the blood and secondary lymphoid organs. In this study, we demonstrate that systemic infection ...
04-Apr-2013
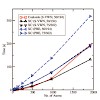
We present a simple but accurate preselection method based on Schwarz integral estimates to determine the significant elements of the exact exchange matrix before its evaluation, thus providing an asymptotical linear-scaling behavior for non-metallic systems. Our screening procedure proves to be highly suitable for exchange matrix calculations on massively ...
04-Apr-2013

Histone variants play important roles in eukaryotic genome organization, the control of gene expression, cell division and DNA repair. Unlike other organisms that employ several H2A variants for different functions, the parsimonious fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster gets along with just a single H2A variant, H2A.V. Remarkably, H2A.V unites within one molecule ...
02-Apr-2013
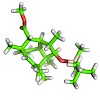
Pericyclic reaction cascades are unparalleled in their ability to quickly generate complex structures with excellent stereocontrol. Herein, the use of a biomimetic Stille/8π electrocyclization/Diels–Alder cascade to successfully assemble the core structure of (−)-PF-1018 is reported.
29-Mar-2013
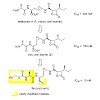
The natural product belactosin A (1) with a trans-cyclopropane structure is a useful prototype compound for developing potent proteasome (core particle, CP) inhibitors. To date, 1 and its analogues are the only CP ligands that bind to both the nonprimed S1 pocket as well as the primed substrate binding channel; however, these molecules harbor a high IC50 value of ...
29-Mar-2013
Noncovalent proteasome inhibitors introduce an alternative mechanism of inhibition to that of covalent inhibitors used in cancer therapy. Starting from a noncovalent linear mimic of TMC-95A, a series of dimerized inhibitors using polyaminohexanoic acid spacers has been designed and optimized to target simultaneously two of the six active sites of the eukaryotic ...
27-Mar-2013

DNA methyltransferase 1 (Dnmt1) reestablishes methylation of hemimethylated CpG sites generated during DNA replication in mammalian cells. Two subdomains, the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)-binding domain (PBD) and the targeting sequence (TS) domain, target Dnmt1 to the replication sites in S phase. We aimed to dissect the details of the cell ...
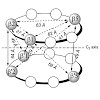
21-Mar-2013
A wide range of light-activated molecules (photoswitches and phototriggers) have been used to the study of computational properties of an isolated neuron by acting pre and postsynaptically. However, new tools are being pursued to elicit a presynaptic calcium influx that triggers the release of neurotransmitters, most of them based in calcium-permeable ...
21-Mar-2013

In vitro protein-folding studies using chemical denaturants such as urea are indispensible in elucidating the forces and mechanisms determining the stability, structure, and dynamics of water-soluble proteins. By contrast, α-helical membrane-associated proteins largely evade such approaches because they are resilient to extensive unfolding. We have used optical ...
20-Mar-2013

Corticothalamic slow oscillations of neuronal activity determine internal brain states. At least in the cortex, the electrical activity is associated with large neuronal Ca2+ transients. Here we implemented an optogenetic approach to explore causal features of the generation of slow oscillation-associated Ca2+ waves in the in vivo mouse brain. We demonstrate that ...
19-Mar-2013
Significant advances during the last decade in the field of small-molecule modulators of protein–protein interactions have raised general awareness of the fact that the modulation of protein–protein interactions has tremendous potential for both basic and applied science.[1] Some of the most advanced orthosteric inhibitors of protein–protein interactions[2–5] are ...
18-Mar-2013
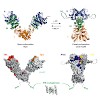
The heat shock protein (Hsp)90 chaperone machinery regulates the activity of hundreds of client proteins in the eukaryotic cytosol. It undergoes large conformational changes between states that are similar in energy. These transitions are rate-limiting for the ATPase cycle. It has become evident that several of the many Hsp90 co-chaperones affect the ...
15-Mar-2013

Kinases are involved in the regulation of many cellular processes and aberrant kinase signaling has been implicated in human disease. As a consequence, kinases are attractive drug targets. Assessing kinase function and drug selectivity in a more physiological context is challenging and often hampered by the generally low expression level of kinases and the ...
13-Mar-2013
The actin cytoskeleton is a central mediator of cellular morphogenesis, and rapid actin reorganization drives essential processes such as cell migration and cell division. Whereas several actin-binding proteins are known to be regulated by changes in intracellular pH, detailed information regarding the effect of pH on the actin dynamics itself is still lacking. ...
Deficiency of terminal ADP-ribose protein glycohydrolase TARG1/C6orf130 in neurodegenerative disease
12-Mar-2013
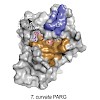
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-ribosylation is a post-translational protein modification implicated in the regulation of a range of cellular processes. A family of proteins that catalyse ADP-ribosylation reactions are the poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) polymerases (PARPs). PARPs covalently attach an ADP-ribose nucleotide to target proteins and some PARP family members can ...
10-Mar-2013
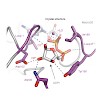
ADP-ribosylation is a reversible post-translational modification with wide-ranging biological functions in all kingdoms of life. A variety of enzymes use NAD+ to transfer either single or multiple ADP-ribose (ADPr) moieties onto distinct amino acid substrates, often in response to DNA damage or other stresses. Poly-ADPr-glycohydrolase readily reverses ...
05-Mar-2013
ADP-ribosyltransferases (ARTs) catalyze the transfer of ADP-ribose from NAD+ onto substrates. Some ARTs generate in an iterative process ADP-ribose polymers that serve as adaptors for distinct protein domains. Other ARTs, exemplified by ARTD10, function as mono-ADP-ribosyltransferases, but it has been unclear whether this modification occurs in cells and how it ...
05-Mar-2013

Although the ribosome is a very general catalyst, it cannot synthesize all protein sequences equally well. For example, ribosomes stall on the secretion monitor (SecM) leader peptide to regulate expression of a downstream gene. Using a genetic selection in Escherichia coli, we identified additional nascent peptide motifs that stall ribosomes. Kinetic studies show ...
04-Mar-2013

Maintaining homeostasis at the protein level is an important prerequisite for cellular viability for which prokaryotes exhibit several proteolytic machineries, including ClpXP. In 2008, we reported the first small-molecule inhibitor for the proteolytic subunit ClpP and demonstrated that the inhibition of the enzyme in living bacteria significantly attenuates ...
03-Mar-2013

Many processes in the regulation of gene expression and signaling involve the formation of protein complexes involving multi-domain proteins. Individual domains that mediate protein-protein and protein-nucleic acid interactions are typically connected by flexible linkers, which contribute to conformational dynamics and enable the formation of complexes with ...
03-Mar-2013
G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), the largest family of membrane signaling proteins, respond to neurotransmitters, hormones and small environmental molecules. The neuronal function of many GPCRs has been difficult to resolve because of an inability to gate them with subtype specificity, spatial precision, speed and reversibility. To address this, we developed ...
28-Feb-2013
The Grueneberg ganglion (GG) in the anterior nasal region of mice is considered as an olfactory compartment since its neurons were recently observed to be activated by chemical stimuli, in particular by the odorant 2,3-dimethylpyrazine (2,3-DMP). However, it is unclear whether the GG indeed serves an olfactory function since these findings are solely based on the ...
22-Feb-2013

In addition to its role in DNA-dependent transcription, RNA polymerase II (Pol II) possesses RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) activity (Lehmann et al, 2007). In a study published in this issue of The EMBO Journal, Wagner et al (2013) report the first native cellular function of the RdRP activity of Pol II. The authors find that a mammalian non-coding RNA ...
22-Feb-2013
Histone lysine (K) methylation has been shown to play a fundamental role in modulating chromatin architecture and regulation of gene expression. Here we report on the identification of histone H3K56, located at the pivotal, nucleosome DNA entry/exit point, as a novel methylation site that is evolutionary conserved. We identify trimethylation of H3K56 (H3K56me3) ...
22-Feb-2013
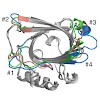
The oncofetal isoform of the extracellular matrix protein fibronectin (Fn), which carries the extra-domain B (ED-B) and is exclusively expressed in neovasculature, has gained interest for tumor diagnosis and therapy using engineered antibody fragments. We have employed the human lipocalin 2 (Lcn2) as a small and robust non-immunoglobulin scaffold to select ...
21-Feb-2013
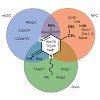
Tet proteins oxidize 5-methylcytosine (mC) to generate 5-hydroxymethyl (hmC), 5-formyl (fC), and 5-carboxylcytosine (caC). The exact function of these oxidative cytosine bases remains elusive. We applied quantitative mass-spectrometry-based proteomics to identify readers for mC and hmC in mouse embryonic stem cells (mESC), neuronal progenitor cells (NPC), and ...
19-Feb-2013
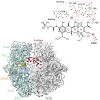
Here we present an X-ray crystallography structure of the clinically relevant tigecycline antibiotic bound to the 70S ribosome. Our structural and biochemical analysis indicate that the enhanced potency of tigecycline results from a stacking interaction with nucleobase C1054 within the decoding site of the ribosome. Single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy ...
18-Feb-2013
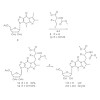
We report an efficient synthesis of the hypermodified natural tRNA modifications wybutosine (yW) and hydroxywybutosine (OHyW). We also describe the preparation of isotopically labeled analogues for precise quantification of yW and OHyW in different tissues including plant materials. The synthesis involved the formation of the unusual tricyclic ring structure of ...
18-Feb-2013
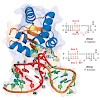
Both protonated and deuterated samples were employed in the study of the L7Ae box C/D RNA complex by 1H-detected solid-state NMR spectroscopy. This approach yielded high-resolution spectra and was used to determine the intermolecular interface and extract structural parameters with high accuracy.
18-Feb-2013
Resistance to drugs targeting human thymidylate synthase (TS) poses a major challenge in the field of anti-cancer therapeutics. Overexpression of the TS protein has been implicated as one of the factors leading to the development of resistance. Therefore, repressing translation by targeting the TS mRNA could help to overcome this problem. In this study, we report ...
15-Feb-2013
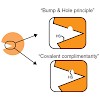
Covalent chemical probes enable investigation of a desired fraction of the proteome. It is possible to adjust the selectivity of these probes, so they either react with a certain amino acid in all proteins, a class of proteins or only a single protein species. A combination of specific reactive groups with additional recognition elements can fine tune probes to ...
15-Feb-2013
Antimicrobial peptides are important defense compounds of higher organisms that can be used as therapeutic agents against bacterial and/or viral infections. We designed several antimicrobial peptides containing hydrophobic and positively charged clusters that are active against plant and human pathogens. Especially peptide SP1-1 is highly active with a MIC value ...
11-Feb-2013

The iron–sulfur protein IspH catalyzes a key step in isoprenoid biosynthesis in bacteria and malaria parasites. Crystal structures of IspH complexed with three substrate analogues reveal their mode of binding and suggest new routes to inhibitor design.
10-Feb-2013
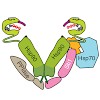
Heat-shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is an ATP-dependent molecular chaperone that associates dynamically with various co-chaperones during its chaperone cycle. Here we analyzed the role of the activating co-chaperone Aha1 in the progression of the yeast Hsp90 chaperone cycle and identified a critical ternary Hsp90 complex containing the co-chaperones Aha1 and Cpr6. Aha1 ...
08-Feb-2013

Hsp70s are molecular chaperones involved in the folding and assembly of proteins. They recognize hydrophobic amino acid stretches in their substrate binding groove. However, a detailed understanding of substrate specificity is still missing. Here, we use the endoplasmic reticulum-resident Hsp70 BiP to identify binding sites in a natural client protein. Two sites ...
07-Feb-2013
Here we provide a protocol for rapidly labeling different cell types, distinct subcellular compartments and key injury mediators in the spinal cord of living mice. This method is based on the application of synthetic vital dyes to the surgically exposed spinal cord. Suitable vital dyes applied in appropriate concentrations lead to reliable in vivo labeling, which ...
05-Feb-2013
This study examines the absolute quantification of particle uptake into cells. Methods: We developed a novel method to analyze stacks of confocal fluorescence images of single cells interacting with nano- and micro-particles. Particle_in_Cell-3D is a freely available ImageJ macro. During the image analysis routine, single cells are reconstructed in 3D and split ...
04-Feb-2013

Force spectroscopy has developed into an indispensable tool for studying folding and binding of proteins on a single molecule level in real time. Design of the pulling geometry allows tuning the reaction coordinate in a very precise manner. Many recent experiments have taken advantage of this possibility and have provided detailed insight the folding pathways on ...
04-Feb-2013
Eukaryotic cells critically depend on the correct regulation of intracellular vesicular trafficking to transport biological material. The Rab subfamily of small guanosine triphosphatases controls these processes by acting as a molecular on/off switch. To fulfill their function, active Rab proteins need to localize to intracellular membranes via ...
04-Feb-2013
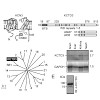
Most ion channels consist of the principal ion-permeating core subunit(s) and accessory proteins that are assembled with the channel core. The biological functions of the latter proteins are diverse and include the regulation of the biophysical properties of the ion channel, its connection to signaling pathways and the control of its cell surface expression. ...
03-Feb-2013
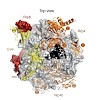
The exosome is the major 3′–5′ RNA-degradation complex in eukaryotes. The ubiquitous core of the yeast exosome (Exo-10) is formed by nine catalytically inert subunits (Exo-9) and a single active RNase, Rrp44. In the nucleus, the Exo-10 core recruits another nuclease, Rrp6. Here we crystallized an approximately 440-kilodalton complex of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ...
31-Jan-2013

Eukaryotic cells have a layer of heterochromatin at the nuclear periphery. To investigate mechanisms regulating chromatin distribution, we analyzed heterochromatin organization in different tissues and species, including mice with mutations in the lamin B receptor (Lbr) and lamin A (Lmna) genes that encode nuclear envelope (NE) proteins. We identified LBR- and ...
30-Jan-2013
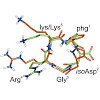
Integrins are the major class of cell adhesion proteins. Their interaction with different ligands of the extracellular matrix is diverse. To get more insight into these interactions, artificial ligands endowed with a well-defined activity/selectivity profile are necessary. Herein, we present a library of cyclic pentapeptides, based on our previously reported ...
28-Jan-2013
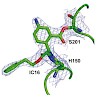
Rhomboid proteases are evolutionary conserved intramembrane serine proteases. Because of their emerging role in many important biological pathways, rhomboids are potential drug targets. Unfortunately, few chemical tools are available for their study. Here, we describe a mass spectrometry-based assay to measure rhomboid substrate cleavage and inhibition. We have ...
28-Jan-2013
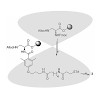
Stuck with the right choice: αvβ3- or α5β1-selective integrin ligands were functionalized for surface coating without losing activity and selectivity. The coating of nanostructured gold surfaces with these compounds stimulated subtype-selective cell adhesion of genetically modified αvβ3- or α5β1-expressing fibroblasts in vitro.
25-Jan-2013

DEAF-1 is an important transcriptional regulator that is required for embryonic development and is linked to clinical depression and suicidal behavior in humans. It comprises various structural domains, including a SAND domain that mediates DNA binding and a MYND domain, a cysteine-rich module organized in a Cys4-Cys2-His-Cys (C4-C2HC) tandem zinc binding motif. ...
24-Jan-2013
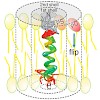
Lipid translocation from one lipid bilayer leaflet to the other, termed flip-flop, is required for the distribution of newly synthesized phospholipids during membrane biogenesis. However, a dedicated biogenic lipid flippase has not yet been identified. Here, we show that the efficiency by which model transmembrane peptides facilitate flip of reporter lipids with ...
23-Jan-2013
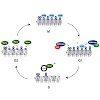
Maintenance of genomic integrity is essential to ensure normal organismal development and to prevent diseases such as cancer. Nuclear DNA is packaged into chromatin, and thus genome maintenance can be influenced by distinct chromatin environments. In particular, post-translational modifications of histones have emerged as key regulators of genomic integrity. ...
22-Jan-2013
The circadian clock is constituted by a complex molecular network that integrates a number of regulatory cues needed to maintain organismal homeostasis. To this effect, posttranslational modifications of clock proteins modulate circadian rhythms and are thought to convert physiological signals into changes in protein regulatory function. To explore reversible ...
21-Jan-2013
Deregulated TGF-β signaling in pancreatic cancer promotes tumor growth, invasion, metastasis, and a potent immunosuppressive network. A strategy for disrupting this tumor-promoting pathway is silencing TGF-β by siRNA. By introducing a triphosphate group at the 5′ end of siRNA (ppp-siRNA), gene silencing can be combined with immune activation via the cytosolic ...
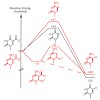
19-Jan-2013
The intramolecular and intermolecular vibrational energy flow in a polyproline peptide with a total number of nine amino acids in the solvent dimethyl sulfoxide is investigated using time-resolved infrared (IR) spectroscopy. Azobenzene covalently bound to a proline sequence containing nitrophenylalanine as a local sensor for vibrational excess energy serves as a ...
17-Jan-2013
The retinoic acid–inducible gene I (RIG-I)–like receptor (RLR) melanoma differentiation–associated protein 5 (MDA5) senses cytoplasmic viral RNA and activates antiviral innate immunity. To reveal how paramyxoviruses counteract this response, we determined the crystal structure of the MDA5 adenosine 5´-triphosphate (ATP)–hydrolysis domain in complex with the viral ...
15-Jan-2013
Sequential photo-bleaching provides a non-invasive way to label individual SCs at the NMJ. The NMJ is the largest synapse of the mammalian nervous system and has served as guiding model to study synaptic structure and function. In mouse NMJs motor axon terminals form pretzel-like contact sites with muscle fibers. The motor axon and its terminal are sheathed by ...
15-Jan-2013
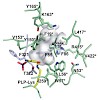
Apart from their crucial role in metabolism, pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (PLP)-dependent aminotransferases (ATs) constitute a class of enzymes with increasing application in industrial biotechnology. To provide better insight into the structure-function relationships of ATs with biotechnological potential we performed a fundamental bioinformatics analysis of 330 ...
15-Jan-2013
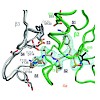
Proteasomes degrade the majority of proteins in mammalian cells by a concerted action of three distinct pairs of active sites. The chymotrypsin-like sites are targets of antimyeloma agents bortezomib and carfilzomib. Inhibitors of the trypsin-like site sensitize multiple myeloma cells to these agents. Here we describe systematic effort to develop inhibitors with ...
15-Jan-2013
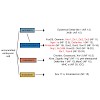
Post-translational modifications (PTMs) of histones exert fundamental roles in regulating gene expression. During development, groups of PTMs are constrained by unknown mechanisms into combinatorial patterns, which facilitate transitions from uncommitted embryonic cells into differentiated somatic cell lineages. Repressive histone modifications such as H3K9me3 or ...
14-Jan-2013

To form three-dimensional capillary tubes endothelial cells must establish contacts with the extracellular matrix that provides signals for their proliferation, migration, and differentiation. The transcription factor Fosl1 plays a key role in the vasculogenic and angiogenic processes, as Fosl1 knockout embryos die with vascular defects in extra-embryonic ...
09-Jan-2013
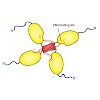
The tumor suppressor protein p53 is often referred to as the guardian of the genome. In the past, controversial findings have been presented for the role of the C-terminal regulatory domain (RD) of p53 as both a negative regulator and a positive regulator of p53 activity. However, the underlying mechanism remained enigmatic. To understand the function of the RD ...
09-Jan-2013

The post-translational modification of proteins with N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) is involved in the regulation of a wide variety of cellular processes and associated with a number of chronic diseases. Despite its emerging biological significance, the systematic identification of O-GlcNAc proteins is still challenging. In the present study, we demonstrate a ...
08-Jan-2013
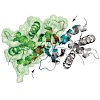
Gene silencing in budding yeast relies on the binding of the Silent Information Regulator (Sir) complex to chromatin, which is mediated by extensive interactions between the Sir proteins and nucleosomes. Sir3, a divergent member of the AAA+ ATPase-like family, contacts both the histone H4 tail and the nucleosome core. Here, we present the structure and function ...
04-Jan-2013
Legionella pneumophila is an intracellularly surviving pathogen that releases about 270 different proteins into the host cell during infection. A set of secreted proteins takes control of the vesicular trafficking regulator Rab1. Legionella LepB inactivates Rab1 by acting as a GTPase-activating protein (GAP). We present the crystal structure of the Rab1b:LepB ...
03-Jan-2013
The synthesis of the triphosphates of 5-hydroxymethyl-, 5-formyl-, and 5-carboxycytidine and the incorporation of these building blocks into long DNA fragments using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) are reported. In this way DNA fragments containing multiple hmC, fC, and caC nucleobases are readily accessible.
02-Jan-2013
Cytochrome c (cyt c) is one of the most widely studied biomolecules, but not much is known about this protein from nematodes. Recombinant expression of Caenorhabditis elegans CYC-2.1 and CYC-2.2 allowed for detailed characterization of their structural features, redox properties, stabilities, and interactions with cardiolipin (CL)-containing liposomes. Using a ...
01-Jan-2013
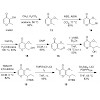
The total syntheses of the natural product 3-O-methylfunicone (1), a member of the funicone class of compounds, and its derivatives is reported. The key reactions in the construction of the biaryl ketone core are a regioselective TMPZnCl·LiCl halogenation and a carbonylative Stille cross-coupling reaction. In addition, the inhibitory activities of the funicones ...
01-Jan-2013

Recently new lysine modifications were detected in histones and other proteins. Using the pyrrolysine amber suppression system we genetically inserted three of the new amino acids ε-N-propionyl-, ε-N-butyryl-, and ε-N-crotonyl-lysine site specifically into histone H3. The lysine at position 9 (H3 K9), which is known to be highly modified in chromatin, was ...










