News 2017
17-Apr-2018
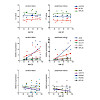
Reduced choroidal blood flow and tissue changes in the ageing human eye impair oxygen delivery to photoreceptors and the retinal pigment epithelium. As a consequence, mild but chronic hypoxia may develop and disturb cell metabolism, function and ultimately survival, potentially contributing to retinal pathologies such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD). ...
26-Dec-2017
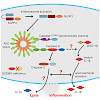
Inflammasomes activate the protease caspase-1, which cleaves interleukin-1β and interleukin-18 to generate the mature cytokines and controls their secretion and a form of inflammatory cell death called pyroptosis. By generating mice expressing enzymatically inactive caspase-1C284A, we provide genetic evidence that caspase-1 protease activity is required for ...
21-Dec-2017
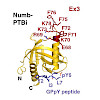
Numb functions as an oncosuppressor by inhibiting Notch signaling and stabilizing p53. This latter effect depends on the interaction of Numb with Mdm2, the E3 ligase that ubiquitinates p53 and commits it to degradation. In breast cancer (BC), loss of Numb results in a reduction of p53-mediated responses including sensitivity to genotoxic drugs and maintenance of ...
20-Dec-2017
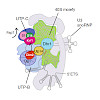
Ribosome biogenesis begins in the nucleolus with the formation of 90S pre-ribosomes, from which pre-40S and pre-60S particles arise that subsequently follow separate maturation pathways. Here, we show how structurally related assembly factors, the KH domain proteins Krr1 and Dim2, participate in ribosome assembly. Initially, Dim2 (Pno1) orchestrates an early step ...
19-Dec-2017
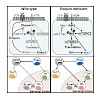
Roquin proteins preclude spontaneous T cell activation and aberrant differentiation of T follicular helper (Tfh) or T helper 17 (Th17) cells. Here we showed that deletion of Roquin-encoding alleles specifically in regulatory T (Treg) cells also caused the activation of conventional T cells. Roquin-deficient Treg cells downregulated CD25, acquired a follicular ...
19-Dec-2017
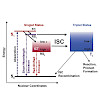
Background
Recently diphenyl-pyrazole (DPP) compounds and especially anle138b were found to reduce the aggregation of α-synuclein or Tau protein in vitro as well as in a mouse model of neurodegenerative diseases [1,2]. Direct interaction of the DPPs with the fibrillar structure was identified by fluorescence spectroscopy. Thereby a strong dependence of the ...
16-Dec-2017
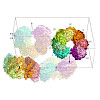
Ancestral β-subunit (Anbu) is homologous to HslV and 20S proteasomes. Based on its phylogenetic distribution and sequence clustering, Anbu has been proposed as the “ancestral” form of proteasomes. Here, we report biochemical data, small-angle X-ray scattering results, negative-stain electron microscopy micrographs and a crystal structure of the Anbu particle from ...
15-Dec-2017

A very short, high yielding, and convergent synthesis with broad substrate scope, enabling access to a very diverse range of hemithioindigos with 4-fold substituted double-bonds, is presented. With this method, carbon as well as nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur based substituents can easily be introduced, delivering a wide array of novel structural motifs. Irradiation ...
14-Dec-2017
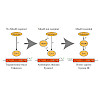
The disulfide relay system found in the intermembrane space (IMS) of mitochondria is an essential pathway for the import and oxidative folding of IMS proteins. Erv1, an essential member of this pathway, has been previously found to be ubiquitously present in mitochondria-containing eukaryotes. However, the other essential protein, Mia40, was found to be absent or ...
08-Dec-2017

Ubiquitination is a multifunctional posttranslational modification controlling the activity, subcellular localization and stability of proteins. The E3 ubiquitin ligase ubiquitin-like PHD and RING finger domain-containing protein 1 (UHRF1) is an essential epigenetic factor that recognizes repressive histone marks as well as hemi-methylated DNA and recruits DNA ...
07-Dec-2017
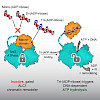
DNA damage triggers chromatin remodeling by mechanisms that are poorly understood. The oncogene and chromatin remodeler ALC1/CHD1L massively decompacts chromatin in vivo yet is inactive prior to DNA-damage-mediated PARP1 induction. We show that the interaction of the ALC1 macrodomain with the ATPase module mediates auto-inhibition. PARP1 activation suppresses ...
06-Dec-2017

DNA nanotechnology, in particular DNA origami, enables the bottom-up self-assembly of micrometre-scale, three-dimensional structures with nanometre-precise features. These structures are customizable in that they can be site-specifically functionalized or constructed to exhibit machine-like or logic-gating behavio. Their use has been limited to applications that ...
06-Dec-2017
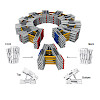
Natural biomolecular assemblies such as molecular motors, enzymes, viruses and subcellular structures often form by self-limiting hierarchical oligomerization of multiple subunits. Large structures can also assemble efficiently from a few components by combining hierarchical assembly and symmetry, a strategy exemplified by viral capsids. De novo protein design ...
04-Dec-2017

The Staphylococcus aureus ClpXP protease is an important regulator of cell homeostasis and virulence. We utilized a high‐throughput screen against the ClpXP complex and identified a specific inhibitor of the ClpX chaperone that disrupts its oligomeric state. Synthesis of 34 derivatives revealed that the molecular scaffold is restrictive for diversification, with ...
01-Dec-2017
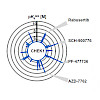
Kinase inhibitors are an important class of drugs that block certain enzymes involved in diseases such as cancer and inflammatory disorders. There are hundreds of kinases within the human body, so knowing the kinase “target” of each drug is essential for developing successful treatment strategies. Sometimes clinical trials can fail because drugs bind more than ...
30-Nov-2017
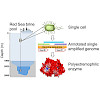
Because only 0.01% of prokaryotic genospecies can be cultured and in situ observations are often impracticable, culture-independent methods are required to understand microbial life and harness potential applications of microbes. Here, we report a methodology for the production of proteins with desired functions based on single amplified genomes (SAGs) from ...
29-Nov-2017

Direct random phase approximation (RPA) correlation energies have become increasingly popular as a post-Kohn-Sham correction, due to significant improvements over DFT calculations for properties such as long-range dispersion effects, which are problematic in conventional density functional theory. On the other hand, RPA still has various weaknesses, such as ...
27-Nov-2017
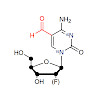
Tet enzymes oxidize 5-methyl-deoxycytidine (mdC) to 5-hydroxymethyl-dC (hmdC), 5-formyl-dC (fdC) and 5-carboxy-dC (cadC) in DNA. It was proposed that fdC and cadC deformylate and decarboxylate, respectively, to dC over the course of an active demethylation process. This would re-install canonical dC bases at previously methylated sites. However, whether such ...
27-Nov-2017
Engineering the interface between biomaterials and tissues is important to increase implant lifetime and avoid failures and revision surgeries. Permanent devices should enhance attachment and differentiation of stem cells, responsible for injured tissue repair, and simultaneously discourage bacterial colonization; this represents a major challenge. To take first ...
21-Nov-2017

HP1 is a structural component of heterochromatin. Mammalian HP1 isoforms HP1α, HP1β, and HP1γ play different roles in genome stability, but their precise role in heterochromatin structure is unclear. Analysis of Hp1α−/−, Hp1β−/−, and Hp1γ−/− MEFs show that HP1 proteins have both redundant and unique functions within pericentric heterochromatin (PCH) and also act ...
17-Nov-2017
IL-22 has been identified as a cancer-promoting cytokine that is secreted by infiltrating immune cells in several cancer models. We hypothesized that IL-22 regulation would occur at the interface between cancer cells and immune cells. Breast and lung cancer cells of murine and human origin induced IL-22 production from memory CD4+ T cells. In the present study, ...
17-Nov-2017
Conformational exchange in proteins is a major determinant in protein functionality. In particular, the μs–ms timescale is associated with enzymatic activity and interactions between biological molecules. We show here that a comprehensive data set of R1ρ relaxation dispersion profiles employing multiple effective fields and tilt angles can be easily obtained in ...
13-Nov-2017
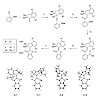
Hemithioindigo molecular motors undergo very fast unidirectional rotation upon irradiation with visible light, which has prevented a complete analysis of their working mechanism. In this work, we have considerably slowed down their motion by using a new synthesis for sterically hindered motor derivatives. This method allowed the first observation of all four ...
08-Nov-2017
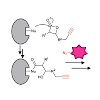
The spongiolactones are marine natural products with an unusual rearranged spongiane skeleton and a fused β-lactone ring. These compounds have potential anticancer properties but their mode of action has yet to be explored. Here we employ activity-based protein profiling to identify the targets of a more potent spongiolactone derivative in live cancer cells, and ...
03-Nov-2017

Most molecular cancer therapies act on protein targets but data on the proteome status of patients and cellular models for proteome‐guided pre‐clinical drug sensitivity studies are only beginning to emerge. Here, we profiled the proteomes of 65 colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines to a depth of > 10,000 proteins using mass spectrometry. Integration with proteomes ...
02-Nov-2017
Ribosomes synthesizing proteins containing consecutive proline residues become stalled and require rescue via the action of uniquely modified translation elongation factors, EF-P in bacteria, or archaeal/eukaryotic a/eIF5A. To date, no structures exist of EF-P or eIF5A in complex with translating ribosomes stalled at polyproline stretches, and thus structural ...
25-Oct-2017

An efficient scheme for the calculation of Born–Oppenheimer molecular dynamics (BOMD) simulations is introduced. It combines the corrected small basis set Hartree–Fock (HF-3c) method by Sure and Grimme [J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 43, 1672], extended Lagrangian BOMD (XL-BOMD) by Niklasson et al. [J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 130, 214109], and the calculation of the two ...
23-Oct-2017
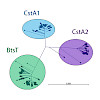
The peptide transporter carbon starvation (CstA) family (transporter classification [TC] 2.A.114) belongs to the second largest superfamily of secondary transporters, the amino acid/polyamine/organocation (APC) superfamily. No representative of the CstA family has previously been characterized either biochemically or structurally, but we have now identified the ...
16-Oct-2017

Fluctuating environments and individual physiological diversity force bacteria to constantly adapt and optimize the uptake of substrates. We focus here on two very similar two-component systems (TCSs) of Escherichia coli belonging to the LytS/LytTR family: BtsS/BtsR (formerly YehU/YehT) and YpdA/YpdB. Both TCSs respond to extracellular pyruvate, albeit with ...
16-Oct-2017
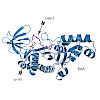
A method for identifying probe modification of proteins via tandem mass spectrometry was developed. Azide bearing molecules are immobilized on functionalised sepharose beads via copper catalysed Huisgen-type click chemistry and selectively released under acidic conditions by chemical cleavage of the triazene linkage. We applied this method to identify the ...
13-Oct-2017
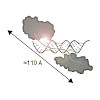
RNA interference defends against RNA viruses and retro-elements within an organism's genome. It is triggered by duplex siRNAs, of which one strand is selected to confer sequence-specificity to the RNA induced silencing complex (RISC). In Drosophila, Dicer-2 (Dcr-2) and the double-stranded RNA binding domain (dsRBD) protein R2D2 form the RISC loading complex (RLC) ...
12-Oct-2017
Detection of cytosolic DNA constitutes a central event in the context of numerous infectious and sterile inflammatory conditions. Recent studies have uncovered a bipartite mode of cytosolic DNA recognition, in which the cGAS-STING axis triggers antiviral immunity, whereas AIM2 triggers inflammasome activation. Here, we show that AIM2 is dispensable for ...
10-Oct-2017

Gene transcription can be activated by decreasing the duration of RNA polymerase II pausing in the promoter-proximal region, but how this is achieved remains unclear. Here we use a 'multi-omics' approach to demonstrate that the duration of polymerase pausing generally limits the productive frequency of transcription initiation in human cells ('pause-initiation ...
09-Oct-2017

Histone variants are structural components of eukaryotic chromatin that can replace replication-coupled histones in the nucleosome. The histone variant macroH2A1.1 contains a macrodomain capable of binding NAD+-derived metabolites. Here we report that macroH2A1.1 is rapidly induced during myogenic differentiation through a switch in alternative splicing, and that ...
09-Oct-2017
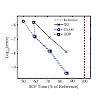
We introduce both rigorous and non-rigorous distance-dependent integral estimates for four-center two-electron integrals derived from a distance-including Schwarz-type inequality. The estimates are even easier to implement than our so far most efficient distance-dependent estimates [S. A. Maurer et al., J. Chem. Phys. 136, 144107 (2012)] and, in addition, do not ...
03-Oct-2017
Green fluorescent protein (GFP) variants are widely used as genetically encoded fluorescent fusion tags, and there is an increasing interest in engineering their structure to develop in vivo optical sensors, such as for optogenetics and force transduction. Ensemble experiments have shown that the fluorescence of GFP is quenched upon denaturation. Here we study ...
02-Oct-2017

The 40S small ribosomal subunit is cotranscriptionally assembled in the nucleolus as part of a large chaperone complex called the 90S preribosome or small-subunit processome. Here, we present the 3.2-Å-resolution structure of the Chaetomium thermophilum 90S preribosome, which allowed us to build atomic structures for 34 assembly factors, including the Mpp10 ...
28-Sep-2017

The characterization of low‐affinity protein complexes is challenging due to their dynamic nature. Here, we present a method to stabilize transient protein complexes in vivo by generating a covalent and conformationally flexible bridge between the interaction partners. A highly active pyrrolysyl tRNA synthetase mutant directs the incorporation of unnatural amino ...
27-Sep-2017
Professional secretory cells can produce large amounts of high-quality complex molecules, including IgM antibodies. Owing to their multivalency, polymeric IgM antibodies provide an efficient first-line of defense against pathogens. To decipher the mechanisms of IgM assembly, we investigated its biosynthesis in living cells and faithfully reconstituted the ...
26-Sep-2017

Glycosylation is a universal strategy to posttranslationally modify proteins. The recently discovered arginine rhamnosylation activates the polyproline-specific bacterial translation elongation factor EF-P. EF-P is rhamnosylated on arginine 32 by the glycosyltransferase EarP. However, the enzymatic mechanism remains elusive. In the present study, we solved the ...
26-Sep-2017
The N‐methylation of backbone amide bonds in peptide natural products was thought to be exclusive to non‐ribosomal peptides. A newly discovered methylation mechanism now brings this structural feature into the world of ribosomal peptides, thereby significantly expanding the structural diversity of ribosomally synthesized and post‐translationally modified peptides ...
25-Sep-2017

The antibody Fv module which binds antigen consists of the variable domains VL and VH. These exhibit a conserved ß-sheet structure and comprise highly variable loops (CDRs). Little is known about the contributions of the framework residues and CDRs to their association. We exchanged conserved interface residues as well as CDR loops and tested the effects on two ...
25-Sep-2017
Hemiindigo is a long known chromophore that absorbs in the blue part of the spectrum but has almost completely been ignored as potential photoswitch. Herein we show how the absorption of hemiindigo is shifted to the red part of the visible spectrum and how nearly perfect photoswitching can be achieved using blue or green and red light. Five derivatives were ...
22-Sep-2017

The molecular recognition of carbohydrates plays a fundamental role in many biological processes. However, the development of carbohydrate-binding reagents for biomedical research and use poses a challenge due to the generally poor affinity of proteins toward sugars in aqueous solution. Here, we describe the effective molecular recognition of pyranose ...
21-Sep-2017
The Hsp90 system in the eukaryotic cytosol is characterized by a cohort of co-chaperones that bind to Hsp90 and affect its function. Although progress has been made regarding the underlying biochemical mechanisms, how co-chaperones influence Hsp90 client proteins in vivo has remained elusive. By investigating the effect of 12 Hsp90 co-chaperones on the activity ...
18-Sep-2017
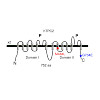
Two-pore channels (TPCs) are endolysosomal cation channels. Two members exist in humans, TPC1 and TPC2. Functional roles associated with the ubiquitously expressed TPCs include VEGF-induced neoangiogenesis, LDL-cholesterol trafficking and degradation, physical endurance under fasting conditions, autophagy regulation, the acrosome reaction in sperm, cancer cell ...
18-Sep-2017
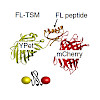
Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based tension sensor modules (TSMs) are available for investigating how distinct proteins bear mechanical forces in cells. Yet, forces in the single piconewton (pN) regime remain difficult to resolve, and tools for multiplexed tension sensing are lacking. Here, we report the generation and calibration of a genetically ...
18-Sep-2017

Successful pathogens use complex signaling mechanisms to monitor their environment and reprogram global gene expression during specific stages of infection. Group A Streptococcus (GAS) is a major human pathogen that causes significant disease burden worldwide. A secreted cysteine protease known as streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin B (SpeB) is a key virulence ...
18-Sep-2017
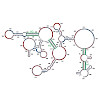
Segmented RNA viruses are ubiquitous pathogens, which include influenza viruses and rotaviruses. A major challenge in understanding their assembly is the combinatorial problem of a non-random selection of a full genomic set of distinct RNAs. This process involves complex RNA-RNA and protein-RNA interactions, which are often obscured by non-specific binding at ...
13-Sep-2017

Cytosolic DNA arising from intracellular pathogens triggers a powerful innate immune response. It is sensed by cyclic GMP–AMP synthase (cGAS), which elicits the production of type I interferons by generating the second messenger 2′3′-cyclic-GMP–AMP (cGAMP). Endogenous nuclear or mitochondrial DNA can also be sensed by cGAS under certain conditions, resulting in ...
12-Sep-2017
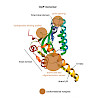
Maintaining the cellular protein homeostasis means managing life on the brink of death. This balance is largely based on precise fine-tuning of enzyme activities. For instance, the ClpP protease possesses several conformational switches which are fundamental to regulating its activity. Efforts have focused on revealing the structural basis of ClpP's ...
07-Sep-2017

The nuclear exosome and the associated RNA helicase Mtr4 participate in the processing of several ribonucleoprotein particles (RNP), including the maturation of the large ribosomal subunit (60S). S. cerevisiae Mtr4 interacts directly with Nop53, a ribosomal biogenesis factor present in late pre-60S particles containing precursors of the 5.8S rRNA. The Mtr4–Nop53 ...
05-Sep-2017
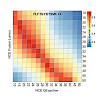
Beyond specific applications, such as the relative or absolute quantification of peptides in targeted proteomic experiments, synthetic spike‐in peptides are not yet systematically used as internal standards in bottom‐up proteomics. A number of retention time standards have been reported that enable chromatographic aligning of multiple LC–MS/MS experiments. ...
04-Sep-2017
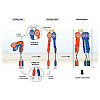
Integrins are key regulators of communication between cells and with their microenvironment. Eight members of the integrin superfamily recognize the tripeptide motif Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) within extracelluar matrix (ECM) proteins. These integrins constitute an important subfamily and play a major role in cancer progression and metastasis via their tumor biological ...
01-Sep-2017
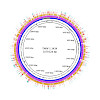
Lactic acid bacteria are broadly employed as starter cultures in the manufacture of foods. Upon technological preparation, they are confronted with drying stress that amalgamates numerous stress conditions resulting in losses of fitness and survival. To better understand and differentiate physiological stress responses, discover general and specific markers for ...
31-Aug-2017
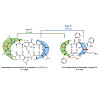
The renaissance of peptides in pharmaceutical industry results from their importance in many biological functions. However, low metabolic stability and the lack of oral availability of most peptides is a certain limitation. Whereas metabolic instability may be often overcome by development of small cyclic peptides containing d-amino acids, the very low oral ...
31-Aug-2017
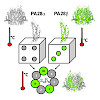
The heptameric proteasome activator (PA) 28αβ is known to modulate class I antigen processing by docking onto 20S proteasome core particles (CPs). The exact stoichiometry and arrangement of its α and β subunits, however, is still controversial. Here we analyzed murine PA28 complexes regarding structure and assembly. Strikingly, PA28α, PA28β, and PA28αβ ...
30-Aug-2017

Two-pore channels (TPCs) are localized in endo-lysosomal compartments and assumed to play an important role for vesicular fusion and endosomal trafficking. Recently, it has been shown that both TPC1 and 2 were required for host cell entry and pathogenicity of Ebola viruses. Here, we investigate the cellular function of TPC1 using protein toxins as model ...
30-Aug-2017
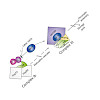
Newly synthesized histones H3 and H4 undergo a cascade of maturation steps to achieve proper folding and to establish post-translational modifications prior to chromatin deposition. Acetylation of H4 on lysines 5 and 12 by the HAT1 acetyltransferase is observed late in the histone maturation cascade. A key question is to understand how to establish and regulate ...
29-Aug-2017

The formation of new types of sensitive conductive surfaces for the detection and transduction of cell–extracellular matrix recognition events in a real time, label-free manner is of great interest in the field of biomedical research. To study molecularly defined cell functions, biologically inspired materials that mimic the nanoscale order of extracellular ...
29-Aug-2017
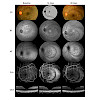
Ocular gene therapy has evolved rapidly into the clinical realm due to promising pre-clinical proof-of-concept studies, recognition of the high unmet medical need of blinding disorders, and the excellent safety profile of the most commonly used vector system, the adeno-associated virus (AAV). With several trials exposing subjects to AAV, investigators ...
28-Aug-2017

The eukaryotic Hsp90 chaperone machinery comprises many co-chaperones and regulates the conformation of hundreds of cytosolic client proteins. Therefore, it is not surprising that the Hsp90 machinery has become an attractive therapeutic target for diseases such as cancer. The compounds used so far to target this machinery affect the entire Hsp90 system. However, ...
21-Aug-2017
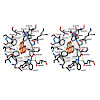
Benzo[a]pyrene, which is produced during the incomplete combustion of organic material, is an abundant noxious pollutant because of its carcinogenic metabolic degradation products. The high‐affinity (KD≈3 nm) monoclonal antibody 22F12 allows facile bioanalytical quantification of benzo[a]pyrene even in complex matrices. We report the functional and X‐ray ...
17-Aug-2017
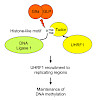
DNA methylation is an essential epigenetic mark in mammals that has to be re-established after each round of DNA replication. The protein UHRF1 is essential for this process; it has been proposed that the protein targets newly replicated DNA by cooperatively binding hemi-methylated DNA and H3K9me2/3, but this model leaves a number of questions unanswered. Here, ...
17-Aug-2017

The mitochondrial calcium uniporter complex is essential for calcium (Ca2+) uptake into mitochondria of all mammalian tissues, where it regulates bioenergetics, cell death, and Ca2+ signal transduction. Despite its involvement in several human diseases, we currently lack pharmacological agents for targeting uniporter activity. Here we introduce a high-throughput ...
16-Aug-2017
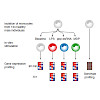
The immune system plays a major role in human health and disease, and understanding genetic causes of interindividual variability of immune responses is vital. Here, we isolate monocytes from 134 genotyped individuals, stimulate these cells with three defined microbe-associated molecular patterns (LPS, MDP, and 5′-ppp-dsRNA), and profile the transcriptomes at ...
12-Aug-2017

Telethonin anchors the N-terminal region of titin in the Z-disk of the sarcomere by binding to two immunoglobulin-like (Ig) domains (Z1 and Z2) of titin (Z1Z2). Thereby telethonin plays an important role in myofibril assembly and in muscle development and functional regulation. The expression and purification of recombinant telethonin is very challenging. In ...
10-Aug-2017
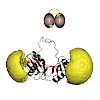
Fluorescence‐based techniques are widely used to study biomolecular conformations, intra‐ and intermolecular interactions, and conformational dynamics of macromolecules. Especially for fluorescence‐based single‐molecule experiments, the choice of the fluorophore and labeling position are highly important. In this work, we studied the biophysical and structural ...
10-Aug-2017

Bacterial histidine kinase/response regulator systems operate at the interface between environmental cues and physiological states. Escherichia coli contains two LytS/LytTR-type histidine kinase/response regulator systems, BtsS/BtsR (formerly YehU/YehT) and YpdA/YpdB, which have been identified as pyruvate-responsive two-component systems. Since they exhibit ...
09-Aug-2017
X chromosome dosage compensation in Drosophila requires chromosome‐wide coordination of gene activation. The male‐specific lethal dosage compensation complex (DCC) identifies and binds to X‐chromosomal high‐affinity sites (HAS) from which it boosts transcription. A sub‐class of HAS, PionX sites, represent first contacts on the X. Here, we explored the chromosomal ...
03-Aug-2017
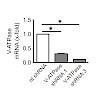
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) induces tumor-initiating cells (TIC), which account for tumor recurrence, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance. Strategies to interfere with EMT are rare but urgently needed to improve cancer therapy. By using the myxobacterial natural compound Archazolid A as a tool, we elucidate the V-ATPase, a multimeric proton pump ...
03-Aug-2017
Natural products are a virtually inexhaustible source of small molecules with spectacular molecular architectures and biomedical potential. Their structural complexity generates formidable challenges to total synthesis but often also precludes time‐ and resource‐efficient, stereoselective synthetic access. Biosynthetically, nature frequently uses dimerization and ...
01-Aug-2017
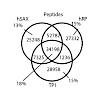
Offline two-dimensional chromatography is a common means to achieve deep proteome coverage. To reduce sample complexity and dynamic range and to utilize mass spectrometer (MS) time efficiently, high chromatographic resolution of and good orthogonality between the two dimensions are needed. Ion exchange and high pH reversed phase chromatography are often used for ...
01-Aug-2017

Snail-like transcription factors affect stem cell function through mechanisms that are incompletely understood. In the Caenorhabditis elegans neurosecretory motor neuron (NSM) neuroblast lineage, CES-1 Snail coordinates cell cycle progression and cell polarity to ensure the asymmetric division of the NSM neuroblast and the generation of two daughter cells of ...
31-Jul-2017
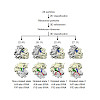
Translation arrest by polybasic sequences induces ribosome stalling, and the arrest product is degraded by the ribosome-mediated quality control (RQC) system. Here we report that ubiquitination of the 40S ribosomal protein uS10 by the E3 ubiquitin ligase Hel2 (or RQT1) is required for RQC. We identify a RQC-trigger (RQT) subcomplex composed of the RNA ...
31-Jul-2017
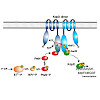
The two-component system KdpD/KdpE governs K+ homeostasis by controlling synthesis of the high affinity K+ transporter KdpFABC. When sensing low environmental K+ concentrations, the dimeric kinase KdpD autophosphorylates in trans and transfers the phosphoryl-group to the response regulator KdpE, which subsequently activates kdpFABC transcription. In Escherichia ...
26-Jul-2017

Little structural information is available so far on amyloid fibrils consisting of immunoglobulin light chains. It is not understood which features of the primary sequence of the protein result in fibril formation. We report here MAS solid-state NMR studies to identify the structured core of κ-type variable domain light chain fibrils. The core contains residues ...
24-Jul-2017
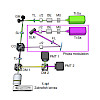
Optical imaging approaches have revolutionized our ability to monitor neural network dynamics, but by themselves are unable to link a neuron’s activity to its functional connectivity. We present a versatile genetic toolbox, termed ‘Optobow’, for all-optical discovery of excitatory connections in vivo. By combining the Gal4-UAS system with Cre/lox recombination, ...
24-Jul-2017
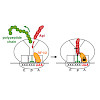
Many antibiotics stop bacterial growth by inhibiting different steps of protein synthesis. However, no specific inhibitors of translation termination are known. Proline-rich antimicrobial peptides, a component of the antibacterial defense system of multicellular organisms, interfere with bacterial growth by inhibiting translation. Here we show that Api137, a ...
24-Jul-2017
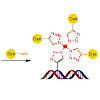
The in vivo incorporation of alkyne-modified bases into the genome of cells is today the basis for the efficient detection of cell proliferation. Cells are grown in the presence of ethinyl-dU (EdU), fixed and permeabilised. The incorporated alkynes are then efficiently detected by using azide-containing fluorophores and the CuI-catalysed alkyne–azide click ...
20-Jul-2017

According to proteomics analyses, more than 70 different ion channels and transporters are harbored in membranes of intracellular compartments such as endosomes and lysosomes. Malfunctioning of these channels has been implicated in human diseases such as lysosomal storage disorders, neurodegenerative diseases and metabolic pathologies, as well as in the ...
20-Jul-2017

To resolve the subcellular distribution of endolysosomal ion channels, we have established a novel experimental approach to selectively patch clamp Rab5 positive early endosomes (EE) versus Rab7/LAMP1-positive late endosomes/lysosomes (LE/LY). To functionally characterize ion channels in endolysosomal membranes with the patch-clamp technique, it is important to ...
17-Jul-2017
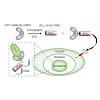
Functional antibody delivery in living cells would enable the labelling and manipulation of intracellular antigens, which constitutes a long-thought goal in cell biology and medicine. Here we present a modular strategy to create functional cell-permeable nanobodies capable of targeted labelling and manipulation of intracellular antigens in living cells. The ...
17-Jul-2017
Systematic N-methylated derivatives of the melanocortin receptor ligand, SHU9119, lead to multiple binding and functional selectivity toward melanocortin receptors. However, the relationship between N-methylation-induced conformational changes in the peptide backbone and side chains and melanocortin receptor selectivity is still unknown. We conducted ...
17-Jul-2017
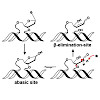
5-Formyl-dC (fdC) and 5-carboxy-dC (cadC) are newly discovered bases in the mammalian genome that are supposed to be substrates for base excision repair (BER) in the framework of active demethylation. The bases are recognized by the monofunctional thymine DNA glycosylase (Tdg), which cleaves the glycosidic bond of the bases to give potentially harmful abasic ...
14-Jul-2017

NMR spectroscopy is a powerful technique to study ribonucleic acids (RNAs) which are key players in a plethora of cellular processes. Although the NMR toolbox for structural studies of RNAs expanded during the last decades, they often remain challenging. Here, we show that solvent paramagnetic relaxation enhancements (sPRE) induced by the soluble, paramagnetic ...
10-Jul-2017

An efficient implementation of energy gradients and of hyperfine coupling constants in second-order Møller-Plesset perturbation theory (MP2) is presented based on our fully atomic orbital (AO)-based approach. For the latter, an unrestricted AO-based MP2 formulation is introduced. A reduction in the dependency of the computational efficiency on the size of the ...
07-Jul-2017

Enzymes of the nonmevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis are attractive targets for the development of herbicides and drugs against infectious diseases. While this pathway is essential for many pathogens and plants, mammals do not depend on it for the synthesis of isoprenoids. IspD, the third enzyme of the nonmevalonate pathway, is unique in that it has an ...
05-Jul-2017

Multi-domain proteins play critical roles in fine-tuning essential processes in cellular signaling and gene regulation. Typically, multiple globular domains that are connected by flexible linkers undergo dynamic rearrangements upon binding to protein, DNA or RNA ligands. RNA binding proteins (RBPs) represent an important class of multi-domain proteins, which ...
03-Jul-2017

Vector-borne trypanosomatid parasite infections in tropical and sub-tropical countries constitute a major threat to humans and livestock. Trypanosoma brucei parasites are transmitted by tsetse fly and lead to African sleeping sickness in humans and Nagana in cattle. In Latin American countries, Trypanosoma cruzi infections spread by triatomine kissing bugs lead ...
02-Jul-2017

Das Institut für chemische Epigenetik (ICEM) mit einer Nutzfläche von 3.430 m² und einer Fördersumme von 38,73 Millionen Euro hat eine Förderempfehlung von Seiten des Wissenschaftsrates erhalten.
Das ICEM basiert auf dem CIPSM und wird den Forschungsschwerpunkt der chemischen Epigenetik erforschen.
Der Forschungsbau wird auf dem HighTech Campus ...
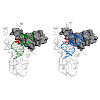
23-Jun-2017
Replacement of canonical histones with specialized histone variants promotes altering of chromatin structure and function. The essential histone variant H2A.Z affects various DNA-based processes via poorly understood mechanisms. Here, we determine the comprehensive interactome of H2A.Z and identify PWWP2A as a novel H2A.Z-nucleosome binder. PWWP2A is a ...
21-Jun-2017

We present a parallel integral algorithm for two-electron contributions occurring in Hartree–Fock and hybrid density functional theory that allows for a strong scaling parallelization on inhomogeneous compute clusters. With a particular focus on graphic processing units, we show that our approach allows an efficient use of CPUs and graphics processing units ...
21-Jun-2017

The receptor tyrosine kinase EPHA2 has gained attention as a therapeutic drug target for cancer and infectious diseases. However, EPHA2 research and EPHA2‐based therapies have been hampered by the lack of selective small‐molecule inhibitors. Herein we report the synthesis and evaluation of dedicated EPHA2 inhibitors based on the clinical BCR‐ABL/SRC inhibitor ...
19-Jun-2017

The pig is one of the earliest domesticated animals in the history of human civilization and represents one of the most important livestock animals. The recent sequencing of the Sus scrofa genome was a major step toward the comprehensive understanding of porcine biology, evolution, and its utility as a promising large animal model for biomedical and ...
19-Jun-2017

Caspases have apoptotic and non-apoptotic functions, both of which depend on their abilities to cleave proteins at specific sites. What distinguishes apoptotic from non-apoptotic substrates has so far been unclear. In this issue of Developmental Cell, Weaver et al. (2017) now provide an answer to this crucial question.
16-Jun-2017

The precise mechanisms through which insoluble, cell-adhesive ligands induce and regulate directional cell migration remain obscure. We recently demonstrated that elevated surface density of physically adsorbed plasma fibronectin (FN) promotes high directional persistence in fibroblast migration. While cell-FN association through integrins α5β1 and αvβ3 was ...
15-Jun-2017
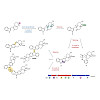
Terpenoid natural products comprise a wide range of molecular architectures that typically result from C–C bond formations catalysed by classical type I/II terpene cyclases. However, the molecular diversity of biologically active terpenoids is substantially increased by fully unrelated, non-canonical terpenoid cyclases. Their evolutionary origin has remained ...
12-Jun-2017

Histone H2AX phosphorylation is an early signalling event triggered by DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). To elucidate the elementary units of phospho-H2AX-labelled chromatin, we integrate super-resolution microscopy of phospho-H2AX during DNA repair in human cells with genome-wide sequencing analyses. Here we identify phospho-H2AX chromatin domains in the ...
07-Jun-2017

We present a method to improve upon the resolution-of-the-identity (RI) for correlation methods. While RI is known to allow for drastic speedups, it relies on a cancellation of errors. Our method eliminates the errors introduced by RI which are known to be problematic for absolute energies. In this way, independence of the error compensation assumption for ...
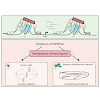
05-Jun-2017
Photopharmacological control of neuronal activity using synthetic photochromic ligands, or photoswitches, is a promising approach for restoring visual function in patients suffering from degenerative retinal diseases. Azobenzene photoswitches, such as AAQ and DENAQ, have been shown to restore the responses of retinal ganglion cells to light in mouse models of ...
02-Jun-2017

Parallel and antiparallel transmembrane helix–helix interactions support the folding and non-covalent assembly of many integral membrane proteins. While several genetic tools are currently in use to study parallel transmembrane helix–helix interactions, antiparallel associations have been difficult to determine. Here, we present a novel genetic approach, termed ...
31-May-2017

We present an extension of our graphics processing units (GPU)-accelerated quantum chemistry package to employ OpenCL compute kernels, which can be executed on a wide range of computing devices like CPUs, Intel Xeon Phi, and AMD GPUs. Here, we focus on the use of AMD GPUs and discuss differences as compared to CUDA-based calculations on NVIDIA GPUs. First ...
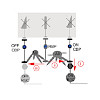
30-May-2017
Aromatic amines are strongly carcinogenic. They are activated in the liver to give reactive nitrenium ions that react with nucleobases within the DNA duplex. The reaction occurs predominantly at the C8 position of the dG base, thereby giving C8-acetyl-aryl- or C8-aryl-dG adducts in an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. Alternatively, reaction with the ...
30-May-2017
Interaction between the nascent polypeptide chain and the ribosomal exit tunnel can modulate the rate of translation and induce translational arrest to regulate expression of downstream genes. The ribosomal tunnel also provides a protected environment for initial protein folding events. Here, we present a 2.9 Å cryo-electron microscopy structure of a ribosome ...
24-May-2017
Mutations in the photoreceptor outer segment (OS) specific peripherin-2 lead to autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa (adRP). By contrast, mutations in the peripherin-2 homolog Rom-1 cause digenic RP in combination with certain heterozygous mutations in peripherin-2. The mechanisms underlying the differential role of peripherin-2 and Rom-1 in RP pathophysiology ...
24-May-2017
Achromatopsia type 2 (ACHM2) is a severe, inherited eye disease caused by mutations in the CNGA3 gene encoding the α subunit of the cone photoreceptor cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) channel. Patients suffer from strongly impaired daylight vision, photophobia, nystagmus, and lack of color discrimination. We have previously shown in the Cnga3 knockout (KO) mouse ...
23-May-2017
Systemic amyloidosis is caused by the misfolding of a circulating amyloid precursor protein and the deposition of amyloid fibrils in multiple organs. Chemical and biophysical analysis of amyloid fibrils from human AL and murine AA amyloidosis reveal the same fibril morphologies in different tissues or organs of one patient or diseased animal. The observed ...
23-May-2017
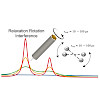
This paper deals with the theoretical foundation of proton magic angle spinning rotating-frame relaxation (R1ρ) and establishes the range of validity and accuracy of the presented approach to describe low-amplitude microsecond time scale motion in the solid state. Beside heteronuclear dipolar and chemical shift anisotropy interactions, a major source of ...
22-May-2017
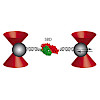
Owing to the cooperativity of protein structures, it is often almost impossible to identify independent subunits, flexible regions, or hinges simply by visual inspection of static snapshots. Here, we use single-molecule force experiments and simulations to apply tension across the substrate binding domain (SBD) of heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) to pinpoint ...
22-May-2017
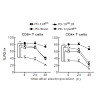
Inherent intermediate-to-low affinity T cell receptors (TCR) that develop during the natural course of immune responses may not allow sufficient activation for tumor elimination, making the majority of T cells suboptimal for adoptive T cell therapy (ATT). TCR affinity enhancement has been implemented to provide stronger T cell activity but carries the risk of ...
19-May-2017
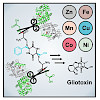
The formation of glutathione (GSH) conjugates, best known from the detoxification of xenobiotics, is a widespread strategy to incorporate sulfur into biomolecules. The biosynthesis of gliotoxin, a virulence factor of the human pathogenic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus, involves attachment of two GSH molecules and their sequential decomposition to yield two reactive ...
17-May-2017
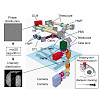
We introduce a flexible method for high-resolution interrogation of circuit function, which combines simultaneous 3D two-photon stimulation of multiple targeted neurons, volumetric functional imaging, and quantitative behavioral tracking. This integrated approach was applied to dissect how an ensemble of premotor neurons in the larval zebrafish brain drives a ...
16-May-2017
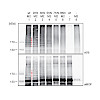
The nuclear acetyltransferase MOF (KAT8 in mammals) is a subunit of at least two multi-component complexes involved in transcription regulation. In the context of complexes of the ‘Non-Specific-Lethal’ (NSL) type it controls transcription initiation of many nuclear housekeeping genes and of mitochondrial genes. While this function is conserved in metazoans, MOF ...
11-May-2017
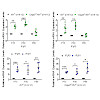
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and mislocalization of improperly folded proteins have been shown to contribute to photoreceptor death in models of inherited retinal degenerative diseases. In particular, mice with cone cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) channel deficiency, a model for achromatopsia, display both early-onset ER stress and opsin mistrafficking. By 2 ...
10-May-2017

The bromodomain protein Brd4 is an epigenetic reader and plays a critical role in the development and maintenance of leukemia. Brd4 binds to acetylated histone tails and activates transcription by recruiting the positive elongation factor P-TEFb. Small molecule inhibitor JQ1 competitively binds the bromodomains of Brd4 and displaces the protein from acetylated ...
04-May-2017
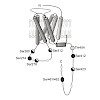
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) undergo phosphorylation at several intracellular residues by G protein-coupled receptor kinases. The resulting phosphorylation pattern triggers arrestin recruitment and receptor desensitization. The exact sites of phosphorylation and their function remained largely unknown for the human β1-adrenoceptor (ADRB1), a key GPCR in ...
03-May-2017
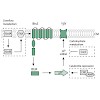
Two-component systems are crucial for signal perception and modulation of bacterial behavior. Nevertheless, to date, very few ligands have been identified that directly interact with histidine kinases. The histidine kinase/response regulator system YehU/YehT of Escherichia coli is part of a nutrient-sensing network. Here we demonstrate that this system senses the ...
03-May-2017

Under stress conditions, such as nutrient deprivation, bacteria enter into a hibernation stage, which is characterized by the appearance of 100S ribosomal particles. In Escherichia coli, dimerization of 70S ribosomes into 100S requires the action of the ribosome modulation factor (RMF) and the hibernation‐promoting factor (HPF). Most other bacteria lack RMF and ...
02-May-2017

The carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) orchestrates dynamic recruitment of specific cellular machines during different stages of transcription. Signature phosphorylation patterns of Y1S2P3T4S5P6S7 heptapeptide repeats of the CTD engage specific “readers.” Whereas phospho-Ser5 and phospho-Ser2 marks are ubiquitous, ...
01-May-2017

Genetic loss-of-function studies on development, cancer and somatic cell reprogramming have suggested that the group of macroH2A histone variants might function through stabilizing the differentiated state by a yet unknown mechanism. Here, we present results demonstrating that macroH2A variants have a major function in maintaining nuclear organization and ...
25-Apr-2017

The colonization of surfaces by bacterial biofilms constitutes a huge problem in healthcare and industry. When attempting biofilm inactivation or removal, it is crucial to sufficiently wet the biofilm surface with antibacterial agents; however, certain biofilms efficiently resist wetting, and the origin of this behavior remains to date unclear. Here, we ...
21-Apr-2017
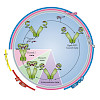
The heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) chaperone machinery is a key regulator of proteostasis under both physiological and stress conditions in eukaryotic cells. As HSP90 has several hundred protein substrates (or 'clients'), it is involved in many cellular processes beyond protein folding, which include DNA repair, development, the immune response and ...
21-Apr-2017
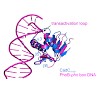
The transmembrane DNA-binding protein CadC of E. coli, a representative of the ToxR-like receptor family, combines input and effector domains for signal sensing and transcriptional activation, respectively, in a single protein, thus representing one of the simplest signalling systems. At acidic pH in a lysine-rich environment, CadC activates the transcription of ...
18-Apr-2017
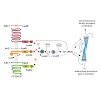
Quorum sensing (QS) is a process enabling a bacterial population to communicate via small molecules called autoinducers (AIs). This intercellular communication process allows single cells to synchronize their behavior within a population. The marine bacterium Vibrio harveyi ATCC BAA-1116 channels the information of three AI signals into one QS cascade. Three ...
18-Apr-2017
Vesicle transport is regulated at multiple levels including regulation by scaffolding proteins and the cytoskeleton. This tight regulation is essential since slowing or stoppage of transport can cause accumulation of obstacles and has been linked to diseases. Understanding the mechanisms by which transport is regulated as well as how motor proteins overcome ...
14-Apr-2017
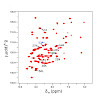
Solid-state NMR spectroscopy can provide site-resolved information about protein dynamics over many time scales. Here we combine protein deuteration, fast magic-angle spinning (~45–60 kHz) and proton detection to study dynamics of ubiquitin in microcrystals, and in particular a mutant in a region that undergoes microsecond motions in a β-turn region in the ...
14-Apr-2017

RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs) are cytosolic innate immune sensors that detect pathogenic RNA and induce a systemic antiviral response. During the last decade many studies focused on their molecular characterization and the identification of RNA agonists. Thereby it became more and more clear that RLR activation needs to be carefully regulated, since constitutive ...
13-Apr-2017

3D structured illumination microscopy (3D-SIM) is the super-resolution technique of choice for multicolor volumetric imaging. Here we provide a validated sample preparation protocol for labeling nuclei of cultured mammalian cells, image acquisition and registration practices, and downstream image analysis of nuclear structures and epigenetic marks. Using ...
12-Apr-2017
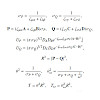
We present screening schemes that allow for efficient, linear-scaling short-range exchange calculations employing Gaussian basis sets for both CPU and GPU architectures. They are based on the LinK [C. Ochsenfeld et al., J. Chem. Phys. 109, 1663 (1998)] and PreLinK [J. Kussmann and C. Ochsenfeld, J. Chem. Phys. 138, 134114 (2013)] methods, but account for the ...
10-Apr-2017
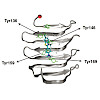
Thioflavin T (ThT) has been widely used to investigate amyloid formation since 1989. While concerns have recently been raised about its use as a probe specific for amyloid, ThT still continues to be a very valuable tool for studying kinetic aspects of fibrillation and associated inhibition mechanisms. This review aims to provide a conceptual instruction manual, ...
09-Apr-2017
We demonstrate measurement of non-equilibrium backbone amide hydrogen–deuterium exchange rates (HDX) for solid proteins. The target of this study are the slowly exchanging residues in solid samples, which are associated with stable secondary-structural elements of proteins. These hydrogen exchange processes escape methods measuring equilibrium exchange rates of ...
06-Apr-2017
Chromatin-remodeling enzymes perform the formidable task of reorganizing the structure of a stable macromolecular assembly, the nucleosome. Recently published work demonstrates that the SNF2H chromatin remodeler distorts the histone octamer structure upon binding to the nucleosome, then taps into this induced plasticity to productively achieve nucleosome sliding.
04-Apr-2017

Diphtheria toxin kills human cells because it delivers its enzyme domain DTA into their cytosol where it inhibits protein synthesis. After receptor-mediated uptake of the toxin, DTA translocates from acidic endosomes into the cytosol, which might be assisted by host cell factors. Here we investigated the role of Hsp90 and its co-chaperones during the uptake of ...
03-Apr-2017
The translocon on the outer membrane of mitochondria (TOM) facilitates the import of nuclear-encoded proteins. The principal machinery of mitochondrial protein transport seems conserved in eukaryotes; however, divergence in the composition and structure of TOM components has been observed between mammals, yeast, and plants. TOM9, the plant homolog of yeast Tom22, ...
03-Apr-2017
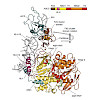
The essential ATP-binding cassette protein ABCE1 splits 80S ribosomes into 60S and 40S subunits after canonical termination or quality-control-based mRNA surveillance processes. However, the underlying splitting mechanism remains enigmatic. Here, we present a cryo-EM structure of the yeast 40S–ABCE1 post-splitting complex at 3.9-Å resolution. Compared to the ...
31-Mar-2017

The parasitic protists of the Trypanosoma genus infect humans and domestic mammals, causing severe mortality and huge economic losses. The most threatening trypanosomiasis is Chagas disease, affecting up to 12 million people in the Americas. We report a way to selectively kill Trypanosoma by blocking glycosomal/peroxisomal import that depends on the PEX14-PEX5 ...
30-Mar-2017
Until recently, it was believed that the genomes of higher organisms contain, in addition to the four canonical DNA bases, only 5-methyl-dC (m5dC) as a modified base to control epigenetic processes. In recent years, this view has changed dramatically with the discovery of 5-hydroxymethyl-dC (hmdC), 5-formyl-dC (fdC), and 5-carboxy-dC (cadC) in DNA from stem cells ...
30-Mar-2017

Arabidopsis bZIP11 is a transcription factor that modulates amino acid metabolism under high‐sucrose conditions. Expression of bZIP11 is downregulated in a sucrose‐dependent manner during translation. Previous in vivo studies have identified the second upstream open reading frame (uORF2) as an essential regulatory element for the sucrose‐dependent translational ...
30-Mar-2017

The present review summarizes the current status of achromatopsia (ACHM) gene therapy-related research activities and provides an outlook for their clinical application. ACHM is an inherited eye disease characterized by a congenital absence of cone photoreceptor function. As a consequence, ACHM is associated with strongly impaired daylight vision, photophobia, ...
29-Mar-2017
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), the main causative agent of tuberculosis (Tb), has a complex cell envelope which forms an efficient barrier to antibiotics, thus contributing to the challenges of anti-tuberculosis therapy. However, the unique Mtb cell wall can be considered an advantage and be utilized to selectively label Mtb bacteria. Here we introduce three ...
29-Mar-2017
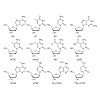
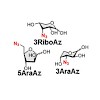
In chemical biology, azides are used to chemically manipulate target structures in a bioorthogonal manner for a plethora of applications ranging from target identification to the synthesis of homogeneously modified protein conjugates. While a variety of methods have been established to introduce the azido group into recombinant proteins, a method that directly ...
28-Mar-2017
Host–microbe communication via small molecule signals is important for both symbiotic and pathogenic relationships, but is often poorly understood at the molecular level. Under conditions of host stress, levels of the human opioid peptide dynorphin are elevated, triggering virulence in the opportunistic pathogenic bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa via an unknown ...
24-Mar-2017
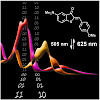
Photoswitches reacting to visible light instead of harmful UV irradiation are of very high interest due to the mild and broadly compatible conditions of their operation. Shifting the absorption into the red region of the electromagnetic spectrum usually comes at the cost of losing thermal stability of the metastable state—the switch switches off by itself. Only ...
24-Mar-2017
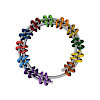
Controlling the spatial arrangement of functional components in biological systems on the scale of higher-order macromolecular assemblies is an important goal in synthetic biology. Achieving this goal could yield new research tools and pave the way for interesting applications in health and biotechnology. DNA origami enables constructing arbitrary shapes on the ...
21-Mar-2017
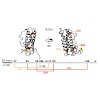
Members of the interleukin 12 (IL12) family perform essential functions in immunoregulation by connecting innate and adaptive immunity and are emerging therapeutic targets. They are unique among other interleukins in forming heterodimers that arise from extensive subunit sharing within the family, leading to the production of at least four functionally distinct ...
20-Mar-2017
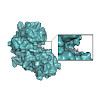
The broad substrate tolerance of tubulin tyrosine ligase is the basic rationale behind its wide applicability for chemoenzymatic protein functionalization. In this context, we report that the wild-type enzyme enables ligation of various unnatural amino acids that are substantially bigger than and structurally unrelated to the natural substrate, tyrosine, without ...
17-Mar-2017

Twisted intramolecular charge transfer (TICT) formation in hemithioindigo photoswitches has recently been reported and constitutes a second deexcitation pathway complementary to photoisomerization. Typically, this behavior is not found for this type of photoswitches, and it takes special geometric and electronic conditions to realize it. Here we present a ...
16-Mar-2017
Recent advances in RNA sequencing technologies have greatly expanded our knowledge of the RNA landscape in cells, often with spatiotemporal resolution. These techniques identified many new (often non-coding) RNA molecules. Large-scale studies have also discovered novel RNA binding proteins (RBPs), which exhibit single or multiple RNA binding domains (RBDs) for ...
13-Mar-2017
Rationale: The sympathetic nervous system is a major mediator of heart function. Intercalated discs composed of desmosomes, adherens junctions, and gap junctions provide the structural backbone for coordinated contraction of cardiac myocytes.
Objective: Gap junctions dynamically remodel to adapt to sympathetic signaling. However, it is unknown whether such rapid ...
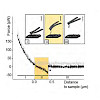
10-Mar-2017
Cationic amphiphilic drugs (CADs) comprise a wide variety of different substance classes such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, and antiarrhythmics. It is well recognized that CADs accumulate in certain intracellular compartments leading to specific morphological changes of cells. So far, no adequate technique exists allowing for ultrastructural analysis of CAD ...
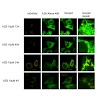
10-Mar-2017
The transport of peroxisomal membrane proteins (PMPs) requires the soluble PEX19 protein as chaperone and import receptor. Recognition of cargo PMPs by the C-terminal domain (CTD) of PEX19 is required for peroxisome biogenesis in vivo. Farnesylation at a C-terminal CaaX motif in PEX19 enhances the PMP interaction, but the underlying molecular mechanisms are ...
08-Mar-2017

Eukaryotic RNA polymerase II catalyzes the transcription of DNA into mRNA very efficiently and with an extremely low error rate with regard to matching base and sugar moiety. Despite its importance, little is known about how it discriminates against 2′-deoxy NTPs during the chemical reaction. To investigate the differences in the addition reactions of ATP and ...
07-Mar-2017
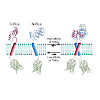
The assembly of integral membrane protein complexes is frequently supported by transmembrane domain (TMD) interactions. Here, we present the BLaTM assay that measures homotypic as well as heterotypic TMD-TMD interactions in a bacterial membrane. The system is based on complementation of β-lactamase fragments genetically fused to interacting TMDs, which confers ...
06-Mar-2017
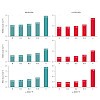
A reformulation of the random phase approximation within the resolution-of-the-identity (RI) scheme is presented, that is competitive to canonical molecular orbital RI-RPA already for small- to medium-sized molecules. For electronically sparse systems drastic speedups due to the reduced scaling behavior compared to the molecular orbital formulation are ...
03-Mar-2017

DNMT1 is recruited to substrate sites by PCNA and UHRF1 to maintain DNA methylation after replication. The cell cycle dependent recruitment of DNMT1 is mediated by the PCNA-binding domain (PBD) and the targeting sequence (TS) within the N-terminal regulatory domain. The TS domain was found to be mutated in patients suffering from hereditary sensory and autonomic ...
01-Mar-2017
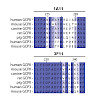
BACKGROUND
Prostate‐specific membrane antigen (PSMA) is a validated target for the imaging and therapy of prostate cancer. Here, we report the detailed characterization of four novel murine monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) recognizing human PSMA as well as PSMA orthologs from different species.
METHODS
Performance of purified mAbs was assayed using a comprehensive ...
27-Feb-2017
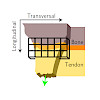
The exceptional mechanical properties of the load-bearing connection of tendon to bone rely on an intricate interplay of its biomolecular composition, microstructure and micromechanics. Here we identify that the Achilles tendon–bone insertion is characterized by an interface region of ∼500 μm with a distinct fibre organization and biomolecular composition. Within ...
23-Feb-2017
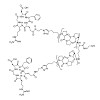
In this study we investigate the impact of ligand presentation by various molecular spacers on integrin-based focal adhesion formation. Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) arranged in hexagonal patterns were biofunctionalized with the same ligand head group, cyclic Arg-Gly-Asp [c(-RGDfX-)], but with different molecular spacers, each of which couples the head group to the ...
18-Feb-2017
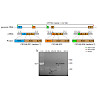
In humans, ten genes encode small heat shock proteins with lens αA-crystallin and αB-crystallin representing two of the most prominent members. The canonical isoforms of αA-crystallin and αB-crystallin collaborate in the eye lens to prevent irreversible protein aggregation and preserve visual acuity. α-Crystallins form large polydisperse homo-oligomers and ...
16-Feb-2017
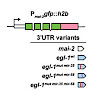
Programmed cell death occurs in a highly reproducible manner during Caenorhabditis elegans development. We demonstrate that, during embryogenesis, miR-35 and miR-58 bantam family microRNAs (miRNAs) cooperate to prevent the precocious death of mothers of cells programmed to die by repressing the gene egl-1, which encodes a proapoptotic BH3-only protein. In ...
16-Feb-2017

Hybrid incompatibility between Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans is caused by a lethal interaction of the proteins encoded by the Hmr and Lhr genes. In D. melanogaster the loss of HMR results in mitotic defects, an increase in transcription of transposable elements and a deregulation of heterochromatic genes. To better understand the molecular mechanisms ...
16-Feb-2017

HER2/ERBB2–overexpressing breast cancers targeted effectively by the small-molecule kinase inhibitor lapatinib frequently acquire resistance to this drug. In this study, we employed explorative mass spectrometry to profile proteome, kinome, and phosphoproteome changes in an established model of lapatinib resistance to systematically investigate initial inhibitor ...
14-Feb-2017

The influence of embedding and coupling schemes on the convergence of the QM size in the QM/MM approach is investigated for the transfer of a proton in a DNA base pair. We find that the embedding scheme (mechanical or electrostatic) has a much greater impact on the convergence behavior than the coupling scheme (additive QM/MM or subtractive ONIOM). To achieve ...
10-Feb-2017

Natural and synthetic scaffolds support enzyme organization in complexes, and they regulate their function and activity. Here we report that CipA and CipB, two small proteins that form protein crystalline inclusions (PCIs) in the cytoplasm of Photorhabdus luminescens, can be utilized as scaffolds to efficiently incorporate exogenous proteins into PCIs. We ...
10-Feb-2017

β-Lactones have recently been introduced as the first selective ClpP inhibitors that attenuate virulence of both sensitive Staphylococcus aureus and multiresistant strains (MRSA). Although previous knockout studies showed that ClpP is essential for S. aureus alpha-toxin production, a link between β-lactone inhibition and molecular virulence mechanisms has been ...
09-Feb-2017

Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) offers new possibilities to address biological and medical questions. However, systematic comparisons of the performance of diverse scRNA-seq protocols are lacking. We generated data from 583 mouse embryonic stem cells to evaluate six prominent scRNA-seq methods: CEL-seq2, Drop-seq, MARS-seq, SCRB-seq, Smart-seq, and ...
08-Feb-2017
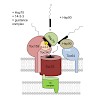
Chloroplasts originated from an endosymbiotic event in which a free-living cyanobacterium was engulfed by an ancestral eukaryotic host. During evolution the majority of the chloroplast genetic information was transferred to the host cell nucleus. As a consequence, proteins formerly encoded by the chloroplast genome are now translated in the cytosol and must be ...
05-Feb-2017
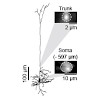
In vivo two-photon Ca2+ imaging has become an effective approach for the functional analysis of neuronal populations, individual neurons and subcellular neuronal compartments in the intact brain. When imaging individually labelled neurons, depth penetration can often reach up to 1 mm below the cortical surface. However, for densely labelled neuronal populations, ...
03-Feb-2017
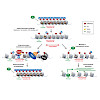
Endogenous retroviruses (ERV) are an abundant class of repetitive elements in mammalian genomes. To ensure genomic stability, ERVs are largely transcriptionally silent. However, these elements also feature physiological roles in distinct developmental contexts, under which silencing needs to be partially relieved. ERV silencing is mediated through a ...
31-Jan-2017
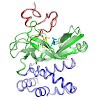
Protein lysine methyltransferases (PKMTs) regulate diverse physiological processes including transcription and the maintenance of genomic integrity. Genetic studies suggest that the PKMTs SUV420H1 and SUV420H2 facilitate proficient nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ)-directed DNA repair by catalyzing the di- and trimethylation (me2 and me3, respectively) of lysine ...
30-Jan-2017
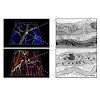
Advances in the engineering of nanoparticles (NPs), which represent particles of less than 100 nm in one external dimension, led to an increasing utilization of nanomaterials for biomedical purposes. A prerequisite for their use in diagnostic and therapeutic applications, however, is the targeted delivery to the site of injury. Interactions between blood-borne ...
30-Jan-2017
Glia play crucial roles in the development and homeostasis of the nervous system. While the GLIA in the Drosophila embryo have been well characterized, their study in the adult nervous system has been limited. Here, we present a detailed description of the glia in the adult nervous system, based on the analysis of some 500 glial drivers we identified within a ...
30-Jan-2017
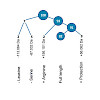
We describe ProteomeTools, a project building molecular and digital tools from the human proteome to facilitate biomedical research. Here we report the generation and multimodal liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry analysis of >330,000 synthetic tryptic peptides representing essentially all canonical human gene products, and we exemplify the utility of ...
27-Jan-2017

Antibody light chain amyloidosis is a rare disease caused by fibril formation of secreted immunoglobulin light chains (LCs). The huge variety of antibody sequences puts a serious challenge to drug discovery. The green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) is known to interfere with fibril formation in general. Here we present solution- and solid-state ...
27-Jan-2017
Nature provides an inexhaustible diversity of small organic molecules with beautiful molecular architectures that have strong and selective inhibitory activities. However, this tremendous biomedical potential often remains inaccessible, as the structural complexity of natural products can render their synthetic preparation extremely challenging. This problem is ...
27-Jan-2017

BceRS and PsdRS are paralogous two-component systems in Bacillus subtilis controlling the response to antimicrobial peptides. In the presence of extracellular bacitracin and nisin, respectively, the two response regulators (RRs) bind their target promoters, PbceA or PpsdA, resulting in a strong up-regulation of target gene expression and ultimately antibiotic ...
26-Jan-2017

Fibrillar aggregates of Aβ and Tau in the brain are the major hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease. Most Tau fibers have a twisted appearance but the twist can be variable and even absent. This ambiguity, which has also been associated with different phenotypes of tauopathies, has led to controversial assumptions about fibril constitution, and it is unclear to-date ...
24-Jan-2017
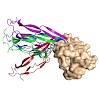
Protein-protein docking protocols aim to predict the structures of protein-protein complexes based on the structure of individual partners. Docking protocols usually include several steps of sampling, clustering, refinement and re-scoring. The scoring step is one of the bottlenecks in the performance of many state-of-the-art protocols. The performance of scoring ...
23-Jan-2017

How do the key features of protein folding, elucidated from studies on native, isolated proteins, manifest in cotranslational folding on the ribosome? Using a well-characterized family of homologous α-helical proteins with a range of biophysical properties, we show that spectrin domains can fold vectorially on the ribosome and may do so via a pathway different ...
21-Jan-2017
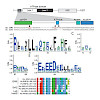
ISWI-family nucleosome remodeling enzymes need the histone H4 N-terminal tail to mobilize nucleosomes. Here we mapped the H4-tail binding pocket of ISWI. Surprisingly the binding site was adjacent to but not overlapping with the docking site of an auto-regulatory motif, AutoN, in the N-terminal region (NTR) of ISWI, indicating that AutoN does not act as a simple ...
20-Jan-2017

Metastatic invasion is the major cause of cancer-related deaths. In this study, we introduce two-pore channels (TPC), a recently described class of NAADP- and PI(3,5)P2–sensitive Ca2+-permeable cation channels in the endolysosomal system of cells, as candidate targets for the treatment of invasive cancers. Inhibition of the channel abrogated migration of ...
20-Jan-2017
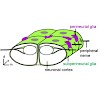
During development, many epithelia are formed by a mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET). Here, we examine the major stages and underlying mechanisms of MET during blood-brain barrier formation in Drosophila. We show that contact with the basal lamina is essential for the growth of the barrier-forming subperineurial glia (SPG). Septate junctions (SJs), which ...
17-Jan-2017

Stable anchoring of titin within the muscle Z-disk is essential for preserving muscle integrity during passive stretching. One of the main candidates for anchoring titin in the Z-disk is the actin cross-linker α-actinin. The calmodulin-like domain of α-actinin binds to the Z-repeats of titin. However, the mechanical and kinetic properties of this important ...
16-Jan-2017
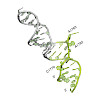
mRNA localization is an essential mechanism of gene regulation and is required for processes such as stem-cell division, embryogenesis and neuronal plasticity. It is not known which features in the cis-acting mRNA localization elements (LEs) are specifically recognized by motor-containing transport complexes. To the best of our knowledge, no high-resolution ...
11-Jan-2017

Integrins, a diverse class of heterodimeric cell surface receptors, are key regulators of cell structure and behaviour, affecting cell morphology, proliferation, survival and differentiation. Consequently, mutations in specific integrins, or their deregulated expression, are associated with a variety of diseases. In the last decades, many integrin-specific ...
17-Jan-0207
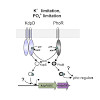
Two-component signal transduction constitutes the predominant strategy used by bacteria to adapt to fluctuating environments. The KdpD/KdpE system is one of the most widespread, and is crucial for K+ homeostasis. In Escherichia coli, the histidine kinase KdpD senses K+ availability, whereas the response regulator KdpE activates synthesis of the high-affinity K+ ...
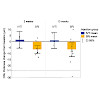
Purpose: Despite ever-growing adoption of subretinal (SRi) and intravitreal injections (IVTi) in ocular gene therapy trials, concerns regarding possible deleterious effects of the SRi on the outer retina are yet to be addressed. SRi offers several advantages over IVTi, such as a better photoreceptor transduction efficiency and a limited off-target exposure. We ...
NLRP3 is the most studied inflammasome sensor due to its crucial involvement in sterile and infection-triggered inflammation. Although its molecular mode of activation remains to be defined, it is well established that low intracellular potassium concentrations result in its activation. This functionality allows the classical NLRP3 pathway to serve as a highly ...










