News 2010
11-Jan-2011
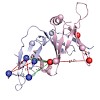
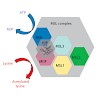
Higher-order multi-protein complexes such as RNA polymerase II (Pol II) complexes with transcription initiation factors are often not amenable to X-ray structure determination. Here, we show that protein cross-linking coupled to mass spectrometry (MS) has now sufficiently advanced as a tool to extend the Pol II structure to a 15-subunit, 670 kDa complex of Pol II ...
29-Dec-2010
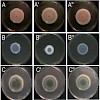
The mannosyltransferase Och1 is the key enzyme for synthesis of elaborated protein N-glycans in yeast. In filamentous fungi genes implicated in outer chain formation are present, but their function is unclear. In this study we have analyzed the Och1 protein of Aspergillus fumigatus. We provide first evidence that poly-mannosylated N-glycans exist in A. fumigatus ...
28-Dec-2010
The discovery of novel and unique target−drug pairs for the treatment of human diseases such as cancer and bacterial infections is an urgent goal of chemical and pharmaceutical sciences. Natural products represent an inspiring source of compounds for designing chemical biology methods with applications in target identification and characterization. Inspired by ...
25-Dec-2010
Posttranslational histone modifications play an important role in modulating gene expression and chro- matin structure. Here we report the identification of histone H3K79 dimethylation in the simple eukary- ote Dictyostelium discoideum. We have deleted the D. discoideum Dot1/KMT4 homologue and demonstrate that it is the sole enzyme responsible for histone ...
23-Dec-2010
5–Hydroxymethylcytosine (hmC) was recently detected as the sixth base in mammalian tissue at so far controversial levels. The function of the modified base is currently unknown, but it is certain that the base is generated from 5-methylcytosine (mC). This fuels the hypothesis that it represents an intermediate of an active demethylation process, which could ...
19-Dec-2010
The chaperone cycle of heat shock protein-90 (Hsp90) involves progression through defined complexes with different cochaperones. It is still enigmatic how the exchange of cochaperones is regulated. The first cochaperone entering the cycle is the Hsp90 ATPase inhibitor Sti1 (Hop in human), which later is replaced by a prolyl isomerase (PPIase) and p23. We found, ...
13-Dec-2010
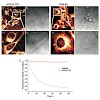
Three new photostable rylene dyes for applications in single molecule studies and membrane labelling have been synthesized and their photophysical properties were characterized. These dyes differ in the number of polyethylene glycol (PEG) chains attached to the core structure which is either a perylene derivate or a terrylene derivate. One perylene and one ...
10-Dec-2010
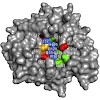
IspG protein serves as the penultimate enzyme of the recently discovered non-mevalonate pathway for the biosynthesis of the universal isoprenoid precursors, isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl diphosphate. The enzyme catalyzes the reductive ring opening of 2C-methyl-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate, which affords 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl ...
09-Dec-2010
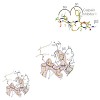
The proteasome's participation in essential biological processes such as stress response, cell proliferation, apoptosis, and antigen presentation has been well established.[1] It is, therefore, not surprising that academia and the pharmaceutical industry have made efforts to develop a range of small synthetic inhibitors against this proteolytic molecular machine ...
07-Dec-2010
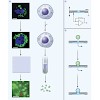
Since its launch in the early 1980s, the patch clamp method has been extensively used to study ion channels in the plasma membrane, but its application to the study of intracellular ion channels has been limited. Unlike the plasma membrane, intracellular membranes are usually not stable enough to withstand mechanical manipulation by glass electrodes during seal ...
05-Dec-2010
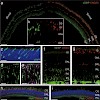
Congenital absence of cone photoreceptor function is associated with strongly impaired daylight vision and loss of color discrimination in human achromatopsia. Here, we introduce viral gene replacement therapy as a potential treatment for this disease in the CNGA3(-/-) mouse model. We show that such therapy can restore cone-specific visual processing in the ...
03-Dec-2010

The filter-aided sample preparation (FASP) method allows gel-free processing of biological samples sol- ubilized with detergents for proteomic analysis by mass spectrometry. In FASP detergents are removed by ultrafiltration, and after protein digestion peptides are separated from undigested material. Here we compare the effectiveness of different filtration ...
02-Dec-2010
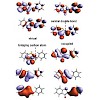
A combined experimental and theoretical investigation of photoinduced Z/E isomerizations is presented. Unsubstituted Hemithioindigo is selected as a representative minimal model to unravel the reaction mechanis in the presence of heteroatoms on an atomic level. Time-resolved spectroscopy reveals multiexponential reaction dynamics on the few picoseconds time ...
01-Dec-2010
The elongation cycle of protein synthesis involves the delivery of aminoacyl-transfer RNAs to the aminoacyl-tRNA-binding site (A site) of the ribosome, followed by peptide-bond formation and translocation of the tRNAs through the ribosome to reopen the A site1, 2. The translocation reaction is catalysed by elongation factor G (EF-G) in a GTP-dependent manner3. ...
01-Dec-2010
RNA oligonucleotides have emerged as a new class of biologicals that can silence gene expression but also stimulate immune responses through specific pattern-recognition receptors. The development of effective delivery systems remains a major challenge for the therapeutic application of the RNA oligonucleotides. In this study, we have established a novel ...
29-Nov-2010
Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes (SMC) proteins are essential for a wide range of processes including chromosome structure and dynamics, gene regulation, and DNA repair. While bacteria and archaea have one SMC protein that forms a homodimer, eukaryotes possess three distinct SMC complexes, consisting of heterodimeric pairs of six different SMC proteins. SMC ...
23-Nov-2010
Histone modifications play an important role in the formation of an epigenetic memory system that maintains cellular identity. Their complex patterns have been suggested to constitute a histone code, which encodes for specific forms of chromatin. According to the histone code hypothesis these specific patterns are passed on from one cell generation to the next. ...
23-Nov-2010

Today, the European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO) announced the selection of 21 of Europeʼs most talented young researchers as 2010 beneficiaries of the EMBO Young Investigator Programme. We congratulate CIPSM's Daniel Wilson to be one of them. Daniel received the EMBO Young Investigators Award for his development and research of new antiobiotics that ...
19-Nov-2010

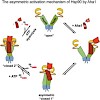
To initiate gene transcription, RNA polymerase II (Pol II) requires the transcription factor IIB (B). Here we present the crystal structure of the complete Pol II–B complex at 4.3 Å resolution, and complementary functional data. The results indicate the mechanism of transcription initiation, including the transition to RNA elongation. Promoter DNA is positioned ...
18-Nov-2010
A synthetic strategy toward maoecrystal V has been identified. It has been shaped by the necessity to maneuver in sterically hindered molecular environments.
17-Nov-2010

Molecular motors have inspired many avenues of research for nanotechnology but most molecular motors studied so far allow only unidirectional movement. The archaeal RNA-exosome is a reversible motor that can either polymerize or degrade an RNA strand, depending on the chemical environments. We developed a single molecule fluorescence assay to analyze the real ...
16-Nov-2010

Protein biosynthesis, the translation of the genetic code into polypeptides, occurs on ribonucleoprotein particles called ribosomes. Although X-ray structures of bacterial ribosomes are available, high-resolution structures of eukaryotic 80S ribosomes are lacking. Using cryoelectron microscopy and single-particle reconstruction, we have determined the structure ...
16-Nov-2010
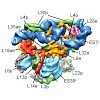
Protein synthesis in all living organisms occurs on ribonucleoprotein particles, called ribosomes. Despite the universality of this process, eukaryotic ribosomes are significantly larger in size than their bacterial counterparts due in part to the presence of 80 r proteins rather than 54 in bacteria. Using cryoelectron microscopy reconstructions of a translating ...
16-Nov-2010

With the help of single molecule force spectroscopy and molecular dynamics simulations, we determine the surface-induced structure of a single engineered spider silk protein. An amyloid like structure is induced in the vicinity of a surface with high surface energy and can be prohibited in the presence of a hydrophobic surface. The derived molecular energy ...
16-Nov-2010

Mesoporous materials have a high potential for a number of different applications in Materials Science such as in molecular sieving, as masks for the formation of nanometre-sized metallic wires, as novel drug-delivery systems or as advanced host systems for catalysis. For many of these applications a thorough understanding of the interaction of guest molecules ...
12-Nov-2010
Multiple DNA associated processes such as DNA repair, replication and recombination are crucial for the maintenance of genome integrity. Here, we show a novel interaction between the transcription elongation factor Bur1-Bur2 and replication protein A (RPA), the eukaryotic single-stranded DNA binding protein with functions in DNA repair, recombination, and ...
12-Nov-2010
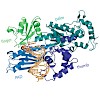
Heterocyclic aromatic amines produce bulky C8 guanine lesions in vivo, which interfere and disrupt DNA and RNA synthesis. These lesions are consequently strong replication blocks. In addition bulky adducts give rise to point and frameshift mutations. The translesion synthesis (TLS) DNA polymerase Eta is able to bypass slowly C8 bulky adduct lesions such as the ...
10-Nov-2010

We have previously reported that star shaped poly(ethylene oxide-stat-propylene oxide) macromers with 80% EO content and isocyanate functional groups at the distal ends [NCO-sP(EO-stat-PO)] can be used to generate coatings that are non-adhesive but easily functionalized for specific cell adhesion. In the present study, we investigated whether the ...
09-Nov-2010

Ferredoxin:NADPH oxidoreductase (FNR) is a key enzyme of photosynthetic electron transport required for generation of reduction equivalents. Recently, two proteins were found to be involved in membrane-anchoring of FNR by specific interaction via a conserved Ser/Pro-rich motif: Tic62 and Trol. Our crystallographic study reveals that the FNR-binding motif, which ...
06-Nov-2010
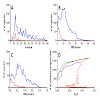
Large scale phosphorylation analysis is more and more getting into focus of proteomic research. While it is now possible to identify thousands of phosphorylated peptides in a biological system, confident site localization remains challenging. Here we validate the Mascot Delta Score (MD score) as a simple method that achieves similar sensitivity and specificity ...
05-Nov-2010
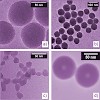
The increasing exposure of humans to nanoscaled particles requires well-defined systems that enable the investigation of the toxicity of nanoparticles on the cellular level. To facilitate this, surface-labeled silica nanoparticles, nanoparticles with a labeled core and a silica shell, and a labeled nanoparticle network—all designed for live-cell imaging—are ...
01-Nov-2010
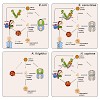
Most multi-cellular organisms adopt a specific gene expression pattern during cellular differentiation. Once established, this pattern is frequently maintained over several cell divisions despite the fact that the initiating signal is no longer present. Differential packaging into chromatin is one such mechanism that allows fixation of transcriptional activity. ...
24-Oct-2010

Classic nuclear export signals (NESs) confer CRM1-dependent nuclear export. Here we present crystal structures of the RanGTP−CRM1 complex alone and bound to the prototypic PKI or HIV-1 Rev NESs. These NESs differ markedly in the spacing of their key hydrophobic (Φ) residues, yet CRM1 recognizes them with the same rigid set of five Φ pockets. The different Φ ...
22-Oct-2010
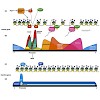
Organisms must survive a variety of stressful conditions, including sudden temperature increases that damage important cellular structures and interfere with essential functions. In response to heat stress, cells activate an ancient signaling pathway leading to the transient expression of heat shock or heat stress proteins (Hsps). Hsps exhibit sophisticated ...
20-Oct-2010

Ph1500 is a homohexameric, two-domain protein of unknown function from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii. The C-terminal hexamerization domain (Ph1500C) is of particular interest, as it lacks sequence homology to proteins of known structure. However, it resisted crystallization for X-ray analysis, and proteins of this size (49 kDa) present a ...
20-Oct-2010

The transmembrane domains (TMDs) of membrane-fusogenic proteins contain an overabundance of b-branched residues. In a previous effort to systematically study the relation among valine content, fusogenicity, and helix dynamics, we developed model TMDs that we termed LV-peptides. The content and position of valine in LV-peptides determine their fusogenicity and ...
20-Oct-2010
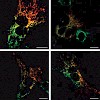
Aggregation of alpha-synuclein (alphaS) is involved in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease (PD) and a variety of related neurodegenerative disorders. The physiological function of alphaS is largely unknown. We demonstrate with in vitro vesicle fusion experiments that alphaS has an inhibitory function on membrane fusion. Upon increased expression in cultured ...
15-Oct-2010

We thank the CIPSM iGEM team members and Kirsten Jung and wish them good luck at this years competition! The International Genetically Engineered Machine competition (iGEM) is the premiere undergraduate Synthetic Biology competition. The iGEM team LMU-Munich works on the project: "Production of azobenzene derivates in Escherichia coli and selection of successful ...
08-Oct-2010
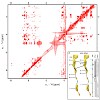
Specific regulatory nascent chains establish direct interactions with the ribosomal tunnel, leading to translational stalling. Despite a wealth of biochemical data, structural insight into the mechanism of translational stalling in eukaryotes is still lacking. Here we use cryo-electron microscopy to visualize eukaryotic ribosomes stalled during the translation of ...
08-Oct-2010

Target analysis of acivicin derived 3-halodihydroisoxazoles scaffolds in living non-pathogenic and pathogenic bacteria.
06-Oct-2010

Spt6 is an essential transcription elongation factor and histone chaperone that binds the C-terminal repeat domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase (Pol) II. We show here that Spt6 contains a tandem SH2 domain with a novel structure and CTD-binding mode. The tandem SH2 domain binds to a serine 2-phosphorylated CTD peptide in vitro, whereas its N-terminal SH2 subdomain, ...
04-Oct-2010
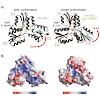
The biosynthesis of natural products is a treasure trove of unusual reaction mechanisms. This Minireview summarizes recent work on the structure and mechanism of IspH protein, which catalyzes the reductive dehydroxylation of an allyl alcohol in a biosynthetic pathway leading to isoprenoid precursors.
02-Oct-2010
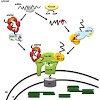
Chloroplasts originated from an endosymbiotic event, in which an ancestral photosynthetic cyanobacterium was engulfed by a mitochondriate eukaryotic host cell. During evolution, the endosymbiont lost its autonomy by means of a massive transfer of genetic information from the prokaryotic genome to the host nucleus. Consequently, the development of protein import ...
01-Oct-2010
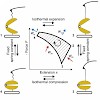
Since we have learned that biological organisms like ourselves are driven by tiny biological molecular motors we try to design and produce artificial molecular motors. However, despite the huge efforts since decades, man-made artificial molecular motors are still far from biological molecular motors or macroscopic motors with regard to performance, especially ...
01-Oct-2010
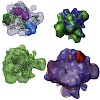
RNA polymerase III (Pol III) transcribes short RNAs required for cell growth. Under stress conditions, the conserved protein Maf1 rapidly represses Pol III transcription. We report the crystal structure of Maf1 and cryo-electron microscopic structures of Pol III, an active Pol III-DNA-RNA complex, and a repressive Pol III-Maf1 complex. Binding of DNA and RNA ...
20-Sep-2010

Nucleosome remodelling is an essential principle to assure that the packaging of eukaryotic genomes in chromatin remains flexible and adaptable to regulatory needs. Nucleosome remodelling enzymes spend the energy of ATP to alter histone–DNA interactions, to catalyse nucleosome displacement and reassembly, on histone exchange and on the relocation of histone ...
19-Sep-2010
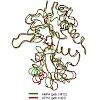
The impact of structural biology on the design of ligands (agonists, antagonists and modulators) for ionotropic glutamate receptors is reviewed.
15-Sep-2010
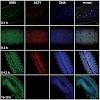
The nucleosome remodelling complexes CHRAC and ACF of Drosophila are thought to play global roles in chromatin assembly and nucleosome dynamics. Disruption of the gene encoding the common ACF1 subunit compromises fly viability. Survivors show defects in chromatin assembly and chromatin-mediated gene repression at all developmental stages. We now show that ACF1 ...
13-Sep-2010
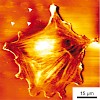
Despite tremendous progress in recent years, nanopatterning of hydrated polymeric systems such as hydrogels still represents a major challenge. Here, we employ block copolymer nanolithography to arrange gold nanoparticles on a solid template, followed by the transfer of the pattern to a polymeric hydrogel. In the next step, these nanoparticles serve as specific ...
08-Sep-2010

CIPSM spin-off AVIRU stands for anti virulence and is a biotechnology start-up that is currently funded as an EXIST transfer of technology project by the German Federal Ministry of Economics and Technology in compliance with a resolution of the German Parliament. AVIRU aims to develop the proof-of-concept for an innovative anti-infective drug for the treatment of ...
Identification and characterization of two novel primate-specific histone H3 variants, H3.X and H3.Y
06-Sep-2010
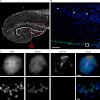
Nucleosomal incorporation of specialized histone variants is an important mechanism to generate different functional chromatin states. Here, we describe the identification and characterization of two novel primate-specific histone H3 variants, H3.X and H3.Y. Their messenger RNAs are found in certain human cell lines, in addition to several normal and malignant ...
05-Sep-2010

We present genome-wide occupancy profiles for RNA polymerase (Pol) II, its phosphorylated forms and transcription factors in proliferating yeast. Pol II exchanges initiation factors for elongation factors during a 5′ transition that is completed 150 nucleotides downstream of the transcription start site (TSS). The resulting elongation complex is composed of all ...
29-Aug-2010

Sequential modifications of the RNA polymerase II (Pol II) C-terminal domain (CTD) coordinate the stage-specific association and release of cellular machines during transcription. Here we examine the genome-wide distributions of the 'early' (phospho-Ser5 (Ser5-P)), 'mid' (Ser7-P) and 'late' (Ser2-P) CTD marks. We identify gene class–specific patterns and find ...
27-Aug-2010
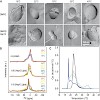
Hsp12 of S. cerevisiae is upregulated several 100-fold in response to stress. Our phenotypic analysis showed that this protein is important for survival of a variety of stress conditions, including high temperature. In the absence of Hsp12, we observed changes in cell morphology under stress conditions. Surprisingly, in the cell, Hsp12 exists both as a soluble ...
27-Aug-2010
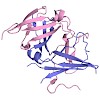
The eukaryotic RNA polymerases Pol I, II, and III use different promoters to transcribe different classes of genes. Promoter usage relies on initiation factors, including TFIIF and TFIIE, in the case of Pol II. Here, we show that the Pol I-specific subunits A49 and A34.5 form a subcomplex that binds DNA and is related to TFIIF and TFIIE. The N-terminal regions of ...
26-Aug-2010
Diploid genomes are exquisitely balanced systems of gene expression. The dosage-compensation systems that evolved along with monosomic sex chromosomes exemplify the intricacies of compensating for differences in gene copy number by transcriptional regulation.
24-Aug-2010

The molecular chaperone heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is an important and abundant protein in eukaryotic cells, essential for the activation of a large set of signal transduction and regulatory proteins. During the functional cycle, the Hsp90 dimer performs large conformational rearrangements. The transient N-terminal dimerization of Hsp90 has been extensively ...
24-Aug-2010
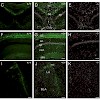
The role of the cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) channel CNGA3 is well established in cone photoreceptors and guanylyl cyclase-D-expressing olfactory neurons. To assess a potential function of CNGA3 in the mouse amygdala and hippocampus, we examined synaptic plasticity and performed a comparative analysis of spatial learning, fear conditioning and step-down ...
23-Aug-2010

Ribosomes arranged in pairs (100S) have been related with nutritional stress response and are believed to represent a “hibernation state.” Several proteins have been identified that are associated with 100S ribosomes but their spatial organization has hitherto not been characterized. We have used cryoelectron tomography to reveal the three-dimensional ...
20-Aug-2010
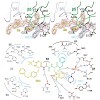
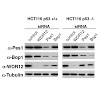
Nicastrin and its relative Nicalin (Nicastrin-like protein) are both members of larger protein complexes, namely gamma-secretase and the Nicalin-NOMO (Nodal modulator) complex. The gamma- secretase complex, which contains Presenilin, APH-1 and PEN-2 in addition to Nicastrin, catalyzes the proteolytic cleavage of the transmembrane domain of various proteins ...
18-Aug-2010

Although there are potent antimalarial drugs available, the spread of drug resistance has led to an increase in morbidity and mortality rates in malaria-endemic regions. To overcome these problems, new antimalarial drugs with novel modes of action have to be developed. The recently discovered nonmevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis (MEP pathway) is an ...
18-Aug-2010

During the evolution of photosynthesis, regulatory circuits were established that allow the precise coupling of light-driven electron transfer chains with downstream processes such as carbon fixation. The ferredoxin (Fd):ferredoxin–NADP+ oxidoreductase (FNR) couple is an important mediator for these processes because it provides the transition from exclusively ...
16-Aug-2010
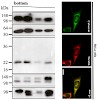
The ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) is responsible for the controlled degradation of proteins in eukaryotic cells through conjugation of ubiquitin molecules and subsequent cleavage by a multimeric protein complex known as the 26S proteasome. Proteolysis occurs within the 20S proteasome core particle (CP), a large barrel-shaped protein complex composed of four ...
15-Aug-2010
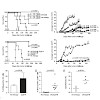
In stomach cancer, there is a need for new therapeutic strategies, in particular for the treatment of unresectable tumors and micrometastases. We investigated the efficacy of immunotherapy in an autochthonous model of gastric cancer, the CEA424-SV40 T Ag (TAg) transgenic mice. Treatment efficacy against both the autochthonous tumors and s.c. tumors induced by the ...
14-Aug-2010
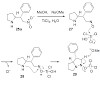
The first total synthesis of newbouldine has been achieved employing a new, reductive N - N bond forming reaction. The asymmetric synthesis confirms that the natural product is a racemate.
13-Aug-2010
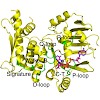
ATP-binding cassette (ABC) enzymes are involved in diverse biological processes ranging from transmembrane transport to chromosome cohesion and DNA repair. They typically use ATP hydrolysis to conduct energy-dependent biological reactions. However, the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator and the DNA repair protein Rad50 can also catalyze the ...
03-Aug-2010
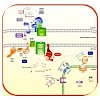
The import of chloroplast proteins synthesized in the cytosol of a plant cell is mediated by two multiprotein complexes or translocons located at the outer and inner membranes of the chloroplast envelope, respectively, TOC and TIC. These complexes integrate different signals to assure the timely transport of proteins into the chloroplast in accordance with the ...
02-Aug-2010
Redox-driven intracellular disulfide-cleavage is a promising strategy to achieve stimuli-responsive and controlled drug release. We synthesized colloidal mesoporous silica (CMS) nanoparticles with ATTO633-labeled cysteine linked to the inner particle core via disulfide-bridges and characterized their cysteine release behavior after internalization into HuH7 cells ...
30-Jul-2010

In biological systems, proteins rarely act as isolated monomers. Association to dimers or higher oligomers is a commonly observed phenomenon. As an example, small heat shock proteins form spherical homo-oligomers of mostly 24 subunits, with the dimeric αlpha-crystallin domain as the basic structural unit. The structural hierarchy of this complex is key to its ...
28-Jul-2010
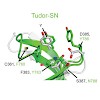
Post-translational modifications of histone tails are among the most prominent epigenetic marks and play a critical role in transcriptional control at the level of chromatin. The Polycomblike (Pcl) protein is part of a histone methyltransferase complex (Pcl-PRC2) responsible for high levels of histone H3 K27 trimethylation. Studies in Drosophila larvae suggest ...
21-Jul-2010
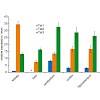
The recent discovery of genomic 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (hmC) and mutations affecting the respective Tet hydroxylases in leukemia raises fundamental questions about this epigenetic modification. We present a sensitive method for fast quantification of genomic hmC based on specific transfer of radiolabeled glucose to hmC by a purified glucosyltransferase. We ...
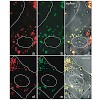
20-Jul-2010
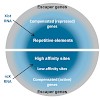
Does the three-dimensional (3D) conformation of interphase chromosomes merely reflect their function or does it actively contribute to gene regulation? The analysis of sex chromosomes that are subject to chromosome-wide dosage compensation processes promises new insight into this question. Chromosome conformations ar dynamic and largely determined by association ...
19-Jul-2010

Diels–Alder reactions of vinyl quinones may provide a rapid entry to highly functionalized bi- and polycyclic ring systems. They involve the inverse-electron-demand cycloaddition of a suitable dienophile to a vinyl quinone, which presumably generates an “isoquinone methide” (Scheme 1). This reactive intermediate could then tautomerize in several ways to yield ...
19-Jul-2010
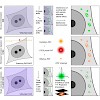
For centuries, cell biology has been based on light microscopy and at the same time been limited by its optical resolution. However, several new technologies have been developed recently that bypass this limit. These new super-resolution technologies are either based on tailored illumination, nonlinear fluorophore responses, or the precise localization of single ...
19-Jul-2010
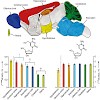
LC-MS has allowed the amount of the post-replicatively formed DNA base 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (see picture; left) to be quantified in brain tissue. The nucleoside is most abundant in areas that are associated with higher cognitive functions, and its content in mouse hippocampi seems to increase with age. The new method enables hydroxymethylcytosine to be ...
17-Jul-2010
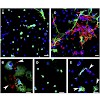
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) represent a distinct mechanism to control and eliminate microbial infections. Our results show that conidia and germ tubes of the human pathogenic mold Aspergillus fumigatus are able to trigger the formation of NETs. Viable fungal cells are not essentially required for this hostepathogen interaction. Neutrophils engulf ...
15-Jul-2010

Olfactory signals influence social interactions in a variety of species. In mammals, pheromones and other social cues can promote mating or aggression behaviors; can communicate information about social hierarchies, genetic identity and health status; and can contribute to associative learning [1,2,3,4,5]. However, the molecular, cellular, and neural mechanisms ...
15-Jul-2010

Importance of the field: Peptides are promising candidates as therapeutic agents due to their wide involvement in physiological processes. However, their often non-selective activity and their poor drug-like properties, mainly their inherent low stability to enzymatic degradation and poor oral bioavailability, limit their clinical potential. Somatostatin is a ...
12-Jul-2010
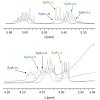
A convergent synthesis of SylA was developed and consists of the synthesis of a fully functionalized macrocycle, which is subsequently coupled with a urea moiety. For cyclization, ring-closing metathesis of a conformationally preorganized precursor was employed. The established synthetic route was then applied to the synthesis of SylA derivatives by using various ...
09-Jul-2010
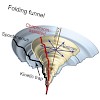
GroEL and GroES form a chaperonin nano-cage for single protein molecules to fold in isolation. The folding properties that render a protein chaperonin dependent are not yet understood. Here, we address this question using a double mutant of the maltosebinding protein DM-MBP as a substrate. Upon spontaneous refolding, DM-MBP populates a kinetically trapped ...
09-Jul-2010
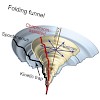
GroEL and GroES form a chaperonin nano-cage for single protein molecules to fold in isolation. The folding properties that render a protein chaperonin dependent are not yet understood. Here, we address this question using a double mutant of the maltosebinding protein DM-MBP as a substrate. Upon spontaneous refolding, DM-MBP populates a kinetically trapped ...
09-Jul-2010

The evolution of mass spectrometry–based proteomic technologies has advanced our understanding of the complex and dynamic nature of proteomes while concurrently revealing that no ‘one-size-fits-all’ proteomic strategy can be used to address all biological questions. Whereas some techniques, such as those for analyzing protein complexes, have matured and are ...
07-Jul-2010

CIPSM spin-off XL-protein with its revolutionary PASylation technology has been awarded the Science4Life Venture Cup 2010 for its excellent business concept for the development of novel biologics with prolonged action. XL-biologics, a spin-off of XL-protein, will focus on the development of superior biopharmaceuticals with extended plasma half-life utilising the ...
06-Jul-2010
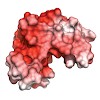
Sam68 (Src-associated during mitosis, 68 kDa) is a prototypical member of the STAR (signal transducer and activator of RNA) family of RNA-binding proteins. STAR proteins bind mRNA targets and modulate cellular processes such as cell cycle regulation and tissue development in response to extracellular signals. Sam68 has been shown to modulate alternative splicing ...
06-Jul-2010
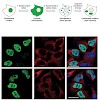
Mutations in fused in sarcoma (FUS) are a cause of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (fALS). Patients carrying point mutations in the C-terminus of FUS show neuronal cytoplasmic FUS-positive inclusions, whereas in healthy controls, FUS is predominantly nuclear. Cytoplasmic FUS inclusions have also been identified in a subset of frontotemporal lobar ...
06-Jul-2010

The large-conductance voltage- and calcium-activated potassium (BK) channels are ubiquitously expressed in the brain and play an important role in the regulation of neuronal excitation. Previous work has shown that the total deletion of these channels causes an impaired motor behavior, consistent with a cerebellar dysfunction. Cellular analyses showed that a ...
02-Jul-2010
The cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer (CPD) formed between two adjacent thymine bases is the most abundant DNA photolesion induced by UV radiation. The quantum yield of this reaction is on the order of ~1% in DNA. This small quantum yield hampers the study of damage formation in naturally occurring DNA. Investigations with increased accuracy become possible for a ...
01-Jul-2010

Nucleosome remodelling factors are regulators of DNA accessibility in chromatin and lubricators of all major functions of eukaryotic genomes. Their action is transient and reversible, yet can be decisive for irreversible cell-fate decisions during development. In addition to the well-known local actions of nucleosome remodelling factors during transcription ...
01-Jul-2010
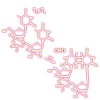
The synthesis, structural characterization and biological activity of eight ortho-quinone(N-aryl)-oximine rhenium(i) complexes are described. The reaction of the halogenido complexes (CO)5ReX (X=Cl (4), Br (5)) with 2-nitroso-N-arylanilines {(C6H3ClNO)NH(C6H4R)} (R = p-Cl, p-Me, o-Cl, H) (3a–d) in tetrahydrofurane (THF) yields the complexes ...
30-Jun-2010
The two proteases beta-secretase and gamma-secretase generate the amyloid beta peptide and are drug targets for Alzheimer’s disease. Here we tested the possibility of targeting the cellular environment of beta-secretase cleavage instead of the beta-secretase enzyme itself. beta-Secretase has an acidic pH optimum and cleaves the amyloid precursor protein in the ...
28-Jun-2010

Cosolutes, such as ions, ligands, or small biomolecules, can cause a protein to fold into its biologically functional native form, to associate, to adhere or desorb from an interface, or even change its mechanical properties.[1–5] At the same time, the interaction of cosolutes with macromolecules, such as proteins, lipids and DNA, are themselves modified by ...
25-Jun-2010
The translational apparatus of the bacterial cell remains one of the principal targets of antibiotics for the clinical treatment of infection worldwide. Since the introduction of specific translation inhibitors into clinical practice in the late 1940s, intense efforts have been made to understand their precise mechanisms of action. Such research has often ...
25-Jun-2010
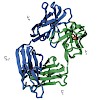
Intact antibodies and antigen binding fragments (Fab) have been previously shown to form an alternatively folded state (AFS) at low pH. This state consists primarily of secondary structure interactions, with reduced tertiary structure content. The AFS can be distinguished from the molten globule state by the formation of nonnative structure and, in particular, ...
25-Jun-2010
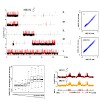
The H4K16 acetyltransferase MOF plays a crucial role in dosage compensation in Drosophila but has additional, global functions. We compared the molecular context and effect of MOF in male and female flies, combining chromosome-wide mapping and transcriptome studies with analyses of defined reporter loci in transgenic flies. MOF distributes dynamically between two ...
24-Jun-2010
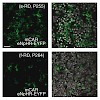
Retinitis pigmentosa refers to a diverse group of hereditary diseases that lead to incurable blindness, affecting two million people worldwide. As a common pathology, rod photoreceptors die early, whereas light-insensitive, morphologically altered cone photoreceptors persist longer. It is unknown if these cones are accessible for therapeutic intervention. Here, ...
21-Jun-2010
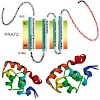
The membrane proteins of the plant preprotein and amino acid transporter (PRAT) superfamily all share common structural elements, such as four membrane-spanning α-helices. Interestingly they display diverse localisation to outer and inner membranes of chloroplasts and mitochondria. Furthermore, they fulfil different functions in preprotein translocation as well ...
15-Jun-2010
Rhomboids are a family of intramembrane serine proteases that are conserved in bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. They are required for numerous fundamental cellular functions such as quorum sensing, cell signaling, and mitochondrial dynamics. Mitochondrial rhomboids form an evolutionarily distinct class of rhomboids. It is largely unclear how their activity is ...
15-Jun-2010
Glycoside hydrolases represent a large class of enzymes that cleave carbohydrate motifs. Since some enzymes play crucial roles in bacterial resistance pathways, we here introduce the synthesis and application of small sugar-based probes to study the function of the glycoside hydrolase NagZ.
10-Jun-2010
The heart of the ubiquitin-mediated degradation pathway, the 26S proteasome, endoproteolytically cleaves most intracellular proteins, thereby maintaining biological homeostasis and regulating many crucial processes in the cell. This hydrolyzing machine comprises more than 30 different subunits, which perform different functions including the recognition, ...
10-Jun-2010
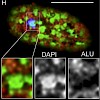
Extensive changes of higher order chromatin arrangements can be observed during prometaphase, terminal cell differentiation and cellular senescence. Experimental systems where major reorganization of nuclear architecture can be induced under defined conditions, may help to better understand the functional implications of such changes. Here, we report on profound ...
09-Jun-2010

Presenilin (PS1 or PS2) is the catalytic component of the gamma-secretase complex, which mediates the final proteolytic processing step leading to the Alzheimer's disease (AD)-characterizing amyloid β-peptide. PS is cleaved during complex assembly into its characteristic N- and C-terminal fragments. Both fragments are integral components of physiologically active ...
02-Jun-2010

The Grueneberg ganglion is a newly appreciated nasal subsystem with neural connections to the olfactory forebrain, but its functional role has not been well defined. Here, we assess whether Grueneberg ganglion neurons (GGNs) function as thermosensors. By investigating the effect of acute temperature changes on the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration of genetically ...
01-Jun-2010
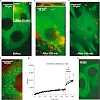
We report on a one-step assembly route where supported lipid bilayers (SLB) are deposited on functionalized colloidal mesoporous silica (CMS) nanoparticles, resulting in a core−shell hybrid system (SLB@CMS). The supported membrane acts as an intact barrier against the escape of encapsulated dye molecules. These stable SLB@CMS particles loaded with the anticancer ...
28-May-2010
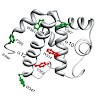
The plasmid pRN1 encodes for a multifunctional replication protein with primase, DNA polymerase and helicase activity. The minimal region required for primase activity encompasses amino-acid residues 40–370. While the N-terminal part of that minimal region (residues 47–247) folds into the prim/pol domain and bears the active site, the structure and function of ...
27-May-2010
Accumulating evidence suggests that, during translation, nascent chains can form specific interactions with ribosomal exit tunnel to regulate translation and promote initial folding events. The clinically important macrolide antibiotics bind within the exit tunnel and inhibit translation by preventing progression of the nascent chain and inducing peptidyl-tRNA ...
25-May-2010

Small heat shock proteins (sHsps) are molecular chaperones involved in maintaining protein homeostasis; they have also been implicated in protein folding diseases and in cancer. In this protein family, a conserved core domain, the so-called alpha-crystallin or Hsp20 domain, is flanked by highly variable, nonconserved sequences that are essential for chaperone ...
21-May-2010
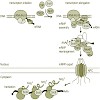
Diverse steps in gene expression are tightly coupled. Curiously, the La-motif-containing protein Sro9 has been shown to play a role in transcription and translation. Here, we show that Sro9 interacts with nuclear and cytoplasmic protein complexes involved in gene expression. In addition, Sro9 shuttles between nucleus and cytoplasm and is exported from the nucleus ...
19-May-2010

In order to amaze our next generations for science and chemistry in particular, CIPSM hosted a two day event at an elementary school with lots of do-it-yourself experiments for the school kids. On the first day (11th of May) Oliver Baron gave an experimentary lecture with lots of explosions and "magical" reactions at the Department of Chemistry of the LMU for ...
19-May-2010

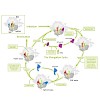
Ten years after the determination of the RNA polymerase II structure, the basic mechanism of mRNA synthesis during gene transcription is known. In the future, the initiation and regulation of transcription must be studied with a combination of structural biology, biochemistry, functional genomics, and computational methods. In this article, the efforts of our ...
19-May-2010

CIPSM researcher Jens Michaelis was awarded with the 2010 Nernst-Haber-Bodenstein Prize. The German Bunsen Society for Physical Chemistry awards the Nernst-Haber-Bodenstein Prize in remembrance of Max Bodenstein, Fritz Haber and Walter Nernst. Congratualtions Jens!
17-May-2010

Speedy couriers in the cell. Every single one of our cells contains so-called motor proteins that transport important substances from one location to another. However, very little is known about how exactly these transport processes occur. Biophysicists at CIPSM have now succeeded in explaining fundamental functions of a particularly interesting motor protein. ...
16-May-2010
Tissue samples in biobanks are typically formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE), in which form they are preserved for decades. It has only recently been shown that proteins in FFPE tissues can be identified by mass spectrometry-based proteomics but analysis of post-translational modifications is thought to be difficult or impossible. The filter aided sample ...
14-May-2010
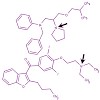
Multiple N-methylation is a novel technology to improve bioavailability of peptides and increase receptor subtype selectivity. This technique has been applied here to the superpotent but nonselective cyclic peptide MT-II. A library of all possible 31 backbone N-methylated derivatives has been synthesized and tested for binding and activation at melanocortin ...
14-May-2010
Cone dystrophies are genetic diseases characterized by loss of cone photoreceptor function and severe impairment of daylight vision. Loss of function is accompanied by a progressive degeneration of cones limiting potential therapeutic interventions. In this study we combined microarray-based gene-expression analysis with electroretinography and ...
13-May-2010

A huge variety of proteins are able to form fibrillar structures, especially at high protein concentrations. Hence, it is surprising that spider silk proteins can be stored in a soluble form at high concentrations and transformed into extremely stable fibres on demand. Silk proteins are reminiscent of amphiphilic block copolymers containing stretches of ...
12-May-2010

The measurement of 13C directed-detected paramagnetic relaxation enhancements (PREs) on spin-labeled proteins combines the efficacy of PREs for the detection of long-range distance information with the favorable sensitivity and resolution of 13C direct-detected experiments. The 13C PREs provide long-range distance restraints to map binding interfaces in proteins ...
12-May-2010

CIPSM hosts a two day event at an elementary school with lots of do-it-yourself experiments for the school kids. On the first day (11th of May) Oliver Baron gives a experimentary lecture at the Department of Chemistry of the LMU for around 300 kids focusing on water and matter in general. The following day the kids can experiment themselves and get a first ...
11-May-2010
Farnesol is known for inducing apoptosis in some fungi and mammalian cells. To evaluate its potential role as an antifungal agent, we studied its impact on the human pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. We found that growth of A. fumigatus wild type is inhib- ited, but two cell wall mutants, Dmnt1 and DglfA, are much more susceptible to farnesol. This susceptibil- ity ...
07-May-2010
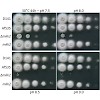
The cell wall integrity (CWI) pathway, best characterized in S. cerevisiae, is strikingly conserved in Aspergillus species. We analyzed the importance of AfMkk2, a CWI signaling kinase, for virulence and antifungal therapy in the human pathogen A. fumigatus. A mutant lacking AfMkk2 is less adherent to glass and plastic surfaces and shows increased sensitivity to ...
05-May-2010
Epigenetic mechanisms contribute to the establishment and maintenance of cell-type-specific gene expression patterns. In this review, we focus on the functions of histone lysine methylation in the context of epigenetic gene regulation during developmental transitions. Over the past few years, analysis of histone lysine methylation in active and repressive nuclear ...
04-May-2010

CIPSM speaker Thomas Carell was honored today by the Bavarian Prime Minister Horst Seehofer with the Cross of Merit on ribbon of the Federal Republic of Germany.
03-May-2010

We thank Kirsten Jung for heading the CIPSM Excursion to Bayer Schering Pharma as part of our graduate education series! We heard it was a great time and will enlightingly continue with a follow up excursion.
03-May-2010

CIPSM's Christian Haass received an honorary doctorate from the University of Zurich for his contributions to the characterisation of the intramembrane proteolysis and its importance in neurodegeneration. Congratulation Christian, well done!
01-May-2010
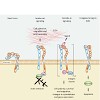
Cilengitide, a cyclic RGD pentapeptide, is currently in clinical phase III for treatment of glioblastomas and in phase II for several other tumors. This drug is the first anti-angiogenic small molecule targeting the integrins alphavbeta3, alphavbeta5 and alpha5beta1. It was developed by us in the early 90s by a novel procedure, the spatial screening. This ...
01-May-2010

A novel detection scheme for pump–repump–probe spectroscopy is presented, where the use of modulation and referencing allows to record the efficiency of a photochemical reaction as a function of the pump–repump delay in a single measurement. This new technique is applied to investigate the ringopening reaction of an indolylfulgide after pre-excitation. Here the ...
01-May-2010
Since its first description more than 30 years ago p53 has become a paradigm for a protein with versatile functions. P53 sensitizes a large variety of genetic alterations and has been entitled the guardian of the genome. Stabilization of p53 upon DNA damage is accompanied by a complex pattern of modifications, which ascertain the cellular response either in the ...
30-Apr-2010
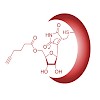
Showdomycin is a potent nucleoside antibiotic that displays a high structural similarity to uridine and pseudouridine. No detailed target analysis of this very unusual electrophilic natural product has been carried out so far. To unravel its biological function, we synthesized a showdomycin probe that can be appended with a fluorophor or a biotin marker via click ...
29-Apr-2010

Small nuclear and small nucleolar RNAs (snRNAs and snoRNAs) are critical components of snRNPs and snoRNPs and play an essential role in the maturation of, respectively, mRNAs and rRNAs within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Complex and specific pathways exist for the assembly of snRNPs and snoRNPs, involving, for instance, nucleocytoplasmic transport of snRNAs ...
29-Apr-2010
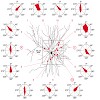
In sensory cortex regions, neurons are tuned to specific stimulus features. For example, in the visual cortex, many neurons fire predominantly in response to moving objects of a preferred orientation. However, the characteristics of the synaptic input that cortical neurons receive to generate their output firing pattern remain unclear. Here we report a novel ...
26-Apr-2010

Taking advantage of the recently developed Filter Assisted Sample Preparation (FASP) method for sample preparation, we performed an in-depth analysis of phosphorylation sites in mouse brain. To maximize the number of detected phosphorylation sites, we fractionated proteins by size exclusion chromatography (SEC) or separated tryptic peptides on an anion exchanger ...
20-Apr-2010
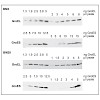
Evolution depends on the acquisition of genomic mutations that increase cellular fitness. Here, we evolved Escherichia coli MG1655 cells to grow at extreme temperatures. We obtained a maximum growth temperature of 48.5°C, which was not further increased upon continuous cultivation at this temperature for over 600 generations. Despite a permanently induced heat ...
14-Apr-2010

RNA exosomes are large multisubunit assemblies involved in controlled RNA processing. The archaeal exosome possesses a heterohexameric processing chamber with three RNase-PH-like active sites, capped by Rrp4- or Csl4-type subunits containing RNA-binding domains. RNA degradation by RNA exosomes has not been studied in a quantitative manner because of the complex ...
14-Apr-2010
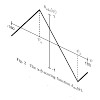
We study a monocyclic peptide called cAPB, whose conformations are light switchable due to the covalent integration of an azobenzene dye. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations using the CHARMM22 force field and its CMAP extension serve us to sample the two distinct conformational ensembles of cAPB, which belong to the cis and trans isomers of the dye, at room ...
09-Apr-2010
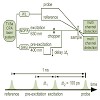
For three indolylfulgides the quantum efficiency of the ring-opening reaction upon pre-excitation is investigated in a multipulse experiment. The quantum efficiency grows by factor of up to 3.4, when the pre-excitation pulse immediately precedes the excitation process. The change in quantum efficiency after pre-excitation is discussed as a function of reaction ...
09-Apr-2010
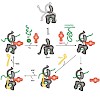
Heat shock proteins 70 (Hsp70) represent a ubiquitous and conserved family of molecular chaperones involved in a plethora of cellular processes. The dynamics of their ATP hydrolysis-driven and cochaperone- regulated conformational cycle are poorly understood. We used fluorescence spectroscopy to analyze, in real time and at single-molecule resolution, the effects ...
08-Apr-2010
Methylene blue is an FDA approved compound with a variety of pharmacologic activities. It inhibits aggregation of several amyloidogenic proteins known to be deposited in neurodegenerative diseases. Recently, it has been proposed that methylene blue shows significant beneficial effects in a phase 2 clinical trial by slowing cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease ...
08-Apr-2010
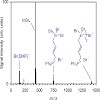
Solutions of allyl indium reagents formed in the reactions of indium with allyl bromide and allyl iodide, respectively, in N,N-dimethylformamide, tetrahydrofuran, and water were analyzed by a combination of electrospray-ionization mass spectrometry, temperature-dependent 1H NMR spectroscopy, and electrical conductivity measurements. Additional mass spectrometric ...
07-Apr-2010
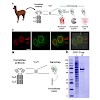
The understanding of cellular processes and their pathophysiological alterations requires comprehensive data on the abundance, distribution, modification, and interaction of all cellular components. On the one hand, artificially introduced fluorescent fusion proteins provide information about their distribution and dynamics in living cells but not about ...
06-Apr-2010
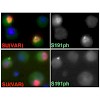
The histone methyltransferase SU(VAR)3–9 plays an important role in the formation of heterochromatin within the eukaryotic nucleus. Several studies have shown that the formation of condensed chromatin is highly regulated during development, suggesting that SU(VAR)3–9’s activity is regulated as well. However, no mechanism by which this may be achieved has been ...
01-Apr-2010
Heterochromatin is a repressive chromatin state which is characterized by densely packed DNA and low transcriptional activity. Heterochromatin-induced gene silencing is important for mediating developmental transitions, and in addition, it has more global functions in ensuring chromosome segregation and genomic integrity. Here we discuss how altered ...
31-Mar-2010
Local energetic effects of amino acid replacements are often considered to have only a moderate influence on the backbone conformation of proteins or peptides. As these effects are difficult to determine experimentally, no comparison has yet been performed. However, knowledge of the influence of side chain mutations is essential in protein homology modeling and ...
29-Mar-2010
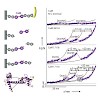
In recent years, single-molecule force spectroscopy has provided a wealth of insights into protein folding and unfolding.1–7 Using mechanical force as a denaturant offers distinct advantages over thermal or chemical denaturation, such as the possibility to locally probe the folding free-energy landscape8 or to actively steer the unfolding pathway of proteins.9 ...
26-Mar-2010

Proteolytic processing of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) by α-secretase prevents formation of the amyloid β-peptide (Aβ), which is the main constituent of amyloid plaques in brains of Alzheimer′s disease (AD) patients. α-Secretase activity is decreased in AD and overexpression of the α-secretase ADAM10 (a disintegrin and metalloprotease) in an AD animal ...
26-Mar-2010
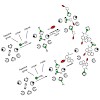
Pathogenic generation of the 42 amino acid variant of the amyloid beta-peptide (Abeta42) by beta- and gamma-secretase cleavage of the beta-amyloid precursor protein (APP) is believed to be causative for Alzheimer 's disease (AD). Lowering of Abeta42 production by gamma-secretase modulators (GSMs) is a hopeful approach towards AD treatment. The mechanism of GSM ...
23-Mar-2010

The primary structure of a 13.6 kDa single heavy chain camelid antibody (VHH) was determined by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight/time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF/TOF) top-down sequence analysis. The majority of the sequence was obtained by mass spectrometric de novo sequencing, with the N-terminal 14 amino acid residues being determined using ...
23-Mar-2010
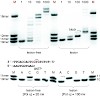
Flipped out: The cisplatin-(1,3-GTG) adduct, a strongly cytotoxic DNA lesion generated by the action of cisplatin therapeutics, is partially bypassed by Y-family DNA polymerase . Crystal structure data on this DNA-protein complex explain the partial-bypass process. The central dT unit of the lesion is turned out and blocks the movement of the enzyme along the DNA ...
23-Mar-2010
Activity-based protein profiling (ABPP) has matured into a standard method for the fast, sensitive, and selective identification of enzyme activity and inhibitors in proteomes. By using natural product based probes, the targets of many uncharacterized molecules can be easily identified in complex proteomes, and their exact function and mechanism of action ...
14-Mar-2010
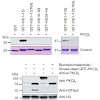
Demethylation at distinct lysine residues in histone H3 by lysinespecific demethylase 1 (LSD1) causes either gene repression or activation1,2. As a component of co-repressor complexes, LSD1 contributes to target gene repression by removing mono- and dimethyl marks from lysine 4 of histone H3 (H3K4)1,3. In contrast, during androgen receptor (AR)-activated gene ...
12-Mar-2010
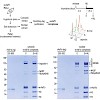
To restore chromatin on new DNA during replication, recycling of histones evicted ahead of the fork is combined with new histone deposition. The Asf1 histone chaperone, which buffers excess histones under stress, is a key player in this process. Yet how histones handled by human Asf1 are modified remains unclear. Here we identify marks on histones H3-H4 bound to ...
02-Mar-2010
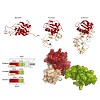
Spt5 is the only known RNA polymerase-associated factor that is conserved in all three domains of life. We have solved the structure of the Methanococcus jannaschii Spt4/5 complex by X-ray crystallography, and characterized its function and interaction with the archaeal RNAP in a wholly recombinant in vitro transcription system. Archaeal Spt4 and Spt5 form a ...
01-Mar-2010
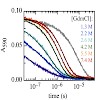
A reversible structural unlocking reaction, in which the close-packed van der Waals interactions break cooperatively, has been found for the villin headpiece subdomain (HP35) using triplet-triplet-energy transfer to monitor conformational fluctuations from equilibrium. Unlocking is associated with an unfavorable enthalpy change (ΔH0 = 35 ± 4 kJ/mol) which is ...
18-Feb-2010

Our ageing society is confronted with a dramatic increase in patients suffering from tauopathies such as Alzheimer’s disease, frontotemporal dementia and others. Typical neuropathological lesions including tangles composed of hyperphosphorylated tau protein as well as severe neuronal cell death characterize these disorders. No mechanism-based cures are available ...
18-Feb-2010
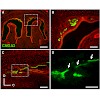
Localized to the vestibule of the nasal cavity, neurons of the Grueneberg ganglion (GG) respond to cool ambient temperatures. The molecular mechanisms underlying this thermal response are still elusive. Recently, it has been suggested that cool temperatures may activate a cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) pathway in the GG, which would be reminiscent of ...
18-Feb-2010
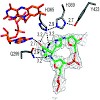
Repair of the Dewar valence isomers by (6-4) photolyases proceeds via an enzyme catalyzed ring-opening reaction of the Dewar lesion to the (6-4) photoproduct.
18-Feb-2010
Small metal clusters fill the gap between the atomic scale and the metallic state with its distinctive bulk phenomena.[1] Besides being of high fundamental interest, this intermediate character of metal clusters also gives rise to unique and potentially useful electronic, magnetic, and optical properties.[ 2] To bring these properties to real-world applications, ...
18-Feb-2010

Small heat shock proteins (sHsps) are a ubiquitous family of molecular chaperones. They form homo-oligomers, composed of mostly 24 subunits. The immunoglobulin-like α-crystallin domain, which is flanked by N- and C-terminal extensions, is the most conserved element in sHsps. It is assumed to be the dimeric building block from which the sHsp oligomers are ...
17-Feb-2010
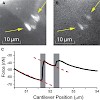
Spatial patterning of biochemical cues on the micro- and nanometer scale controls numerous cellular processes such as spreading, adhesion, migration, and proliferation. Using force microscopy we show that the lateral spacing of individual integrin receptor-ligand bonds determines the strength of cell adhesion. For spacings R90 nm, focal contact formation was ...
16-Feb-2010
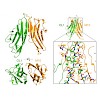
In the sarcomeric M-band, the giant ruler proteins titin and obscurin, its small homologue obscurin-like-1 (obsl1), and the myosin cross-linking protein myomesin form a ternary complex that is crucial for the function of the M-band as a mechanical link. Mutations in the last titin immunoglobulin (Ig) domain M10, which interacts with the N-terminal Ig-domains of ...
16-Feb-2010

Drugs for cancer therapy belong to different categories of chemical substances. The cellular targets for the therapeutic efficacy are often not unambiguously identified. Here, we describe the process of ribosome biogenesis as a target of a large variety of chemotherapeutic drugs. We determined the inhibitory concentration of 36 chemotherapeutic drugs for ...
Rapid time course of action potentials in spines and remote dendrites of mouse visual cortex neurons
15-Feb-2010
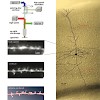
Axonally initiated action potentials back-propagate into spiny dendrites of central mammalian neurons and thereby regulate plasticity at excitatory synapses on individual spines as well as linear and supralinear integration of synaptic inputs along dendritic branches. Thus, the electrical behavior of individual dendritic spines and terminal dendritic branches is ...
12-Feb-2010
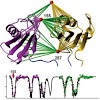
The chaperone Hsp90 is an ATP-dependent, dimeric molecular machine regulated by several cochaperones, including inhibitors and the unique ATPase activator Aha1. Here, we analyzed the mechanism of the Aha1-mediated acceleration of Hsp90 ATPase activity and identified the interaction surfaces of both proteins using multidimensional NMR techniques. For maximum ...
10-Feb-2010
Puzzle-Arbeit: Eine effiziente, allgemein anwendbare Methode zur Bestimmung der Struktur von Proteinkomplexen und Mehrdomänenproteinen in Lösung mithilfe der NMR-Spektroskopie wird vorgestellt. Ausgehend von den bekannten hochaufgelösten Strukturen einzelner Domänen oder Untereinheiten wird die Domänenanordnung des Gesamtsystems aus NMR-Daten abgeleitet, die auch ...
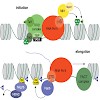
α-Helical nascent polypeptide chains visualized within distinct regions of the ribosomal exit tunnel
07-Feb-2010

As translation proceeds, the nascent polypeptide chain passes through a tunnel in the large ribosomal subunit. Although this ribosomal exit tunnel was once thought only to be a passive conduit for the growing nascent chain, accumulating evidence suggests that it may in fact play a more active role in regulating translation and initial protein folding events. Here ...
05-Feb-2010
Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes (SMC) proteins are vital for a wide range of processes including chromosome structure and dynamics, gene regulation and DNA repair. Eukaryotes have three SMC complexes, consisting of heterodimeric pairs of six different SMC proteins along with several specific regulatory subunits. In addition to their other functions, all ...
02-Feb-2010
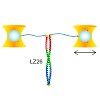
Kinetic bulk and single molecule folding experiments characterize barrier properties but the shape of folding landscapes between barrier top and native state is difficult to access. Here, we directly extract the full free energy landscape of a single molecule of the GCN4 leucine zipper using dual beam optical tweezers. To this end, we use deconvolution force ...
Redox-regulation of protein import into chloroplasts and mitochondria: Similarities and differences.
01-Feb-2010
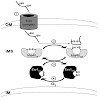
Redox signals play important roles in many developmental and metabolic processes, in particular in chloroplasts and mitochondria. Furthermore, redox reactions are crucial for protein folding via the formation of inter- or intramolecular disulfide bridges. Recently, redox signals were described to be additionally involved in regulation of protein import: in ...
31-Jan-2010
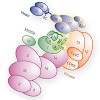
Mediator is the central coactivor complex required for regulated transcription by RNA polymerase (Pol) II. Mediator consists of 25 subunits arranged in the head, middle, tail and kinase modules. Structural and functional studies of Mediator are limited by the availability of protocols for the prep- aration of recombinant modules. Here, we describe protocols for ...
29-Jan-2010
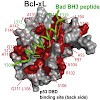
p53 can induce apoptosis through mitochondrial membrane permeabilization by interaction of its DNA binding region with the anti-apoptotic proteins BclxL and Bcl2. However, little is known about the action of p53 at the mitochondria in molecular detail. By using NMR spectroscopy and fluorescence polarization we characterized the binding of wildtype and mutant p53 ...
29-Jan-2010
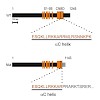
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a severe hereditary eye disorder characterized by progressive degeneration of photoreceptors and subsequent loss of vision. Two of the RP associated mutations were found in the CNGB1 gene that encodes the B subunit of the rod cyclic nucleotide-gated channel (CNGB1a). One of them (c.3444+1G>A) is located at the donor site of exon 32 ...
28-Jan-2010
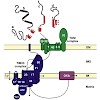
The TIM23 complex in the inner membrane of mitochondria mediates import of essentially all matrix proteins and a large number of inner membrane proteins. Here we present an overview on the latest insights into the structure and function of this remarkable molecular machine.
25-Jan-2010
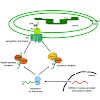
Chloroplasts originated from an endosymbiotic event, in which an ancestral photosynthetic cyanobacterium was engulfed by a mitochondriate eukaryotic host cell. During evolution, the endosymbiont lost its autonomy by means of a massive transfer of genetic information from the prokaryotic genome to the host nucleus. Consequently, the development of protein import ...
20-Jan-2010

In the course of infection, the detection of pathogen-associated molecular patterns by specialized pattern recognition receptors in the host leads to activation of the innate immune system. Whereas the subsequent induction of adaptive immune responses in secondary lymphoid organs is well described, little is known about the effects of pathogen-associated ...
20-Jan-2010
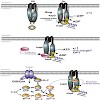
The KdpD/KdpE two-component system of Escherichia coli activates the expression of the kdpFABC operon encoding the high-affinity K+ uptake system KdpFABC in response to K+ limitation or salt stress. Earlier, it was proposed that the histidine kinase KdpD is a turgor sensor; recent studies suggest that KdpD integrates three chemical stimuli from the cytoplasm. ...
19-Jan-2010
Isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) represent the two central intermediates in the biosynthesis of isoprenoids. The recently discovered deoxyxylulose 5-phosphate pathway generates a mixture of IPP and DMAPP in its final step by reductive dehydroxylation of 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-butenyl 4-diphosphate. This conversion is catalyzed by ...
19-Jan-2010
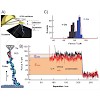
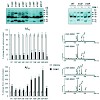
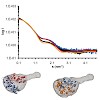
Single-molecule force spectroscopy experiments demonstrate that hydrogenation and oxidation of polycrystalline diamond effectively control molecular adhesion (see figure). Aging changes these properties and originates from the rapid formation of a thin and resistant contamination layer, as well as degradation of the artificial surface termination on longer time ...
15-Jan-2010
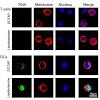
The role of immune suppression by regulatory T (Treg) cells in the maintenance of immune homeostasis is well established. However, little is known about how Treg cell function is inhibited on viral infection to allow the development of a protective immune response. As viral RNA is a crucial mediator for activation of antiviral immunity, we examined the effects of ...
14-Jan-2010
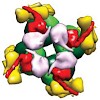
Form I Rubisco (ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase), a complex of eight large (RbcL) and eight small (RbcS) subunits, catalyses the fixation of atmospheric CO2 in photosynthesis. The limited catalytic efficiency of Rubisco has sparked extensive efforts to re-engineer the enzyme with the goal of enhancing agricultural productivity. To facilitate such ...
13-Jan-2010
Protein function such as catalytic activity or molecular recognition is tightly coupled to the conformation and dynamics. Since protein conformations may be controlled by forces, diverse active and passive mechanisms have evolved that allow biological systems to respond to mechanical signals. However, forces act in a predetermined direction on these biomolecules ...
12-Jan-2010
Dictyostelium discoideum Coronin7 (DdCRN7) together with human Coronin7 (CRN7) and Pod-1 of Drosophila melanogaster and Caenorhabditis elegans belong to the coronin family of WD repeat domain containing proteins. Coronin7 proteins are characterized by two WD repeat domains that presumably fold into two beta-propeller structures. DdCRN7 shares highest homology ...
12-Jan-2010
Dosage compensation in Drosophila melanogaster involves the selective targeting of the male X chromosome by the dosage compensation complex (DCC) and the coordinate, 2-fold activation of most genes. The principles that allow the DCC to distinguish the X chromosome from the autosomes are not understood. Targeting presumably involves DNA sequence elements whose ...
07-Jan-2010

The p53 tumor suppressor pathway is activated by defective ribosome synthesis. Ribosomal proteins are released from the nucleolus and block Hdm2 that targets p53 for degradation. However, it remained elusive how abrogation of individual rRNA processing pathways contributes to p53 stabilization. Here we show that selective inhibition of 18S rRNA processing ...
05-Jan-2010
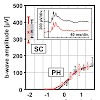
Purpose. To identify individual cone photoreceptors in a transgenic mouse line in vivo based on selective expression of green fluorescent protein (GFP) using cSLO (confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy) and to use this approach to monitor cone cell fate in mouse models of retinal degeneration. Methods. Transgenic mice expressing GFP under the control of a ...
01-Jan-2010
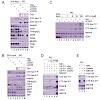
The largest subunit of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) C-terminal heptarepeat domain (CTD) is subject to phosphorylation during initiation and elongation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Here we study the molecular mechanisms leading to phosphorylation of Ser-7 in the human enzyme. Ser-7 becomes phosphorylated before initiation of transcription at promoter ...
01-Jan-2010
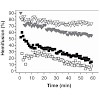
The transmembrane domains of fusion proteins areknownto beimportant for their fusogenic activity. Inaneffort to systematically investigate the structure/function relationships of transmembrane domains we had previously designed LV-peptides that mimic natural fusion proteinTMDsin their ability to drive fusion after incorporation into liposomalmembranes. ...
11-Dec-2009
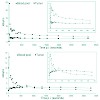
Inhibitors targeting the integrin avb3 are promising new agents currently tested in clinical trials for supplemental therapy of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). The aim of our study was to evaluate 18F-labeled glycosylated Arg-Gly-Asp peptide ([18F]Galacto-RGD) PET for noninvasive imaging of avb3 expression in patients with GBM, suggesting eligibility for this kind ...
13-Jul-2009
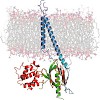
The formation of multicellular organisms requires concerted action by cells, which alter their adhesive and migratory behaviors. Cell adhesion and migration are tightly regulated by intra- and extracellular signals, which are conveyed through the cellular membrane by specialized receptors known as integrins. Integrins are the starting point of a variety of ...
12-May-2009
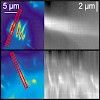
Focal adhesions are the anchoring points of cells to surfaces and are responsible for a large number of surface sensing processes. Nanopatterning studies have shown physiological changes in fibroblasts as a result of decreasing density of external binding ligands. The most striking of these changes is a decreased ability to form mature focal adhesions when ...
01-Mar-2009
Transport of essentially all matrix and a number of inner membrane proteins is governed, entirely or in part, by N-terminal presequences and requires a coordinated action of the translocases of outer and inner mitochondrial membranes (TOM and TIM23 complexes). Here, we have analyzed Tim50, a subunit of the TIM23 complex that is implicated in transfer of ...










