Research Area E - Publications 2014
19-Dec-2014
ACS Synth. Biol., 3 (12), pp 990–994, DOI: 10.1021/sb5000302
Heterologous enzymes and binding proteins were secreted by the moss Physcomitrella patens or anchored extracellularly on its cell membrane in order to functionalize the apoplast as a biochemical reaction compartment. This modular membrane anchoring system utilizes the signal peptide and the transmembrane segment of the somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase ...
17-Dec-2014
Angewandte Chemie International Edition, online article
We report the development of dendritic siRNA nanostructures that are able to penetrate even difficult to transfect cells such as neurons with the help of a special receptor ligand. The nanoparticles elicit strong siRNA responses, despite the dendritic structure. An siRNA dendrimer directed against the crucial rabies virus (RABV) nucleoprotein (N protein) and ...
17-Dec-2014

CIPSM wishing you and your family a wonderful holiday season and a healthy & peaceful New Year 2015!
08-Dec-2014
ACS Chem. Biol., online article
Essential cell division protein FtsZ is considered an attractive target in the search for antibacterials with novel mechanisms of action to overcome the resistance problem. FtsZ undergoes GTP-dependent assembly at midcell to form the Z-ring, a dynamic structure that evolves until final constriction of the cell. Therefore, molecules able to inhibit its activity ...
04-Dec-2014
FEMS Microbiology Letters, online article

In Escherichia coli, detoxification of methylglyoxal (MG) requires glyoxalases I and II. Glyoxalase I (gloA/GlxI) isomerizes the hemithioacetal, formed spontaneously from MG and glutathione (GSH) to S-lactoylglutathione (SLG), which is hydrolyzed by glyoxalase II (gloB/GlxII) to lactate and GSH. YcbL from Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium is an unusual type ...
04-Dec-2014
Cell Death and Disease, 5, e1558; doi:10.1038/cddis.2014.512
Cell Death and Disease, online article
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) defines a group of inherited degenerative retinal diseases causing progressive loss of photoreceptors. To this day, RP is still untreatable and rational treatment development will require a thorough understanding of the underlying cell death mechanisms. Methylation of the DNA base cytosine by DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) is an ...
24-Nov-2014
Nature Medicine, 20, 1401–1409, doi:10.1038/nm.3740
Nature Medicine, online article

We searched for genetic alterations in human B cell lymphoma that affect the ubiquitin-proteasome system. This approach identified FBXO25 within a minimal common region of frequent deletion in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). FBXO25 encodes an orphan F-box protein that determines the substrate specificity of the SCF (SKP1–CUL1–F-box)FBXO25 ubiquitin ligase complex. An ...
21-Nov-2014
mAbs, Volume 7, Issue 1, pages 96-109, DOI:10.4161/19420862.2014.985522
Although antigen-binding fragments (Fabs) of antibodies constitute established tracers for in vivo radiodiagnostics, their functionality is hampered by a very short circulation half-life. PASylation, the genetic fusion with a long, conformationally disordered amino acid chain comprising Pro, Ala and Ser, provides a convenient way to expand protein size and, ...
17-Nov-2014
J. Nat. Prod., online article
Fluorine-containing natural products are extremely rare. The recent report on the isolation and biological activity of the bacterial secondary metabolite 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-fluorophenyl)propionic acid was thus highly remarkable. The compound contained the first aromatic fluorine substituent known to date in any natural product. The promise to discover an ...
13-Nov-2014
Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 14, 205-215, doi: 10.1074/mcp.M114.043109
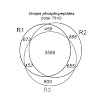
Advances in phosphopeptide enrichment methods enable the identification of thousands of phosphopeptides from complex samples. Current offline enrichment approaches using TiO2, Ti, and Fe immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography (IMAC) material in batch or microtip format are widely used, but they suffer from irreproducibility and compromised selectivity. To ...
28-Oct-2014

Die LMU vereinbart bislang umfangreichsten Lizenzvertrag im Bereich der Proteinforschung: BASF kauft aussichtsreiche Patente für innovative Entwicklungen in der Biomedizin. Die LMU hat mit dem Unternehmen BASF SE einen Lizenzvertrag im Bereich neuer chemischer Methoden zur Modifizierung von Biomolekülen geschlossen, die am Exzellenzcluster Center for integrated ...
20-Oct-2014
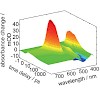
Hemithioindigo (HTI) photoswitches have a tremendous potential for biological and supramolecular applications due to their absorptions in the visible-light region in conjunction with ultrafast photoisomerization and high thermal bistability. Rational tailoring of the photophysical properties for a specific application is the key to exploit the full potential of ...
13-Oct-2014
Angewandte Chemie International Edition, online article
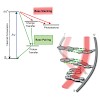
Excited-state dynamics are essential to understanding the formation of DNA lesions induced by UV light. By using femtosecond IR spectroscopy, it was possible to determine the lifetimes of the excited states of all four bases in the double-stranded environment of natural DNA. After UV excitation of the DNA duplex, we detected a concerted decay of base pairs ...
25-Sep-2014
Proteomics, online article

Mass spectrometers equipped with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI-MS) require frequent multipoint calibration to obtain good mass accuracy over a wide mass range and across large numbers of samples. In this study, we introduce a new synthetic peptide mass calibration standard termed PAS-cal tailored for MALDI-MS based bottom-up proteomics. This ...
22-Sep-2014
Angewandte Chemie International Edition, online article
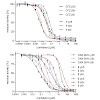
The concept of proteasome inhibition ranks among the latest achievements in the treatment of blood cancer and represents a promising strategy for modulating autoimmune diseases. In this study, we describe peptidic sulfonyl fluoride inhibitors that selectively block the catalytic β5 subunit of the immunoproteasome by inducing only marginal cytotoxic effects. ...
19-Sep-2014
Chemical Communications, online article
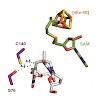
The radical SAM enzyme, spore photoproduct lyase, requires an H-atom transfer (HAT) pathway to catalyze DNA repair. By rational engineering, we demonstrate that it is possible to rewire its HAT pathway, a first step toward the development of novel catalysts based on the radical SAM enzyme scaffold.
16-Sep-2014
Chem. Sci., online article
Acivicin is a natural product with diverse biological activities. Several decades ago its clinical application in cancer treatment was explored but failed due to unacceptable toxicity. The causes behind the desired and undesired biological effects have never been elucidated and only limited information about acivicin-specific targets is available. In order to ...
05-Sep-2014
JBC, online article
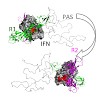
IFNβ is a common therapeutic option to treat multiple sclerosis (MS). It is unique amongst the family of type I IFNs in that it binds to the interferon receptors with high affinity, conferring exceptional biological properties. We have previously reported the generation of an interferon superagonist (dubbed YNSα8) that is built on the backbone of a low affinity ...
21-Aug-2014
Nature Communications, online article
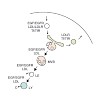
Endolysosomal organelles play a key role in trafficking, breakdown and receptor-mediated recycling of different macromolecules such as low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholesterol, epithelial growth factor (EGF) or transferrin. Here we examine the role of two-pore channel (TPC) 2, an endolysosomal cation channel, in these processes. Embryonic mouse fibroblasts ...
08-Aug-2014
Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 2014, doi: 10.1074/mcp.M114.041038, 13, 3709-3715, published on 08.08.2014
Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, online article
One of the limiting factors in determining the sensitivity of tandem mass spectrometry using hybrid quadrupole orthogonal acceleration time-of-flight instruments is the duty cycle of the orthogonal ion injection system. As a consequence, only a fraction of the generated fragment ion beam is collected by the time-of-flight analyzer. Here we describe a method ...
25-Jul-2014
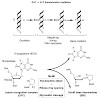
Living organisms protect the genome against external influences by recognizing and repairing damaged DNA. A common source of gene mutation is the oxidized guanine, which undergoes base excision repair through cleavage of the glycosidic bond between the ribose and the nucleobase of the lesion. We unravel the repair mechanism utilized by bacterial glycosylase, ...
14-Jul-2014

DNA structure functions as an overlapping code to the DNA sequence. Rapid progress in understanding the role of DNA structure in gene regulation, DNA damage recognition and genome stability has been made. The three dimensional structure of both proteins and DNA plays a crucial role for their specific interaction, and proteins can recognise the chemical signature ...
09-Jul-2014
Angewandte Chemie, online article

The catalytic and selective construction of carbon–carbon bonds for the generation of complex molecules is one of the most important tasks in organic chemistry. This was clearly highlighted by the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, which was awarded for the development of Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions. The underlying concept of cross-linking building blocks ...
09-Jul-2014

Das Exzellenzcluster „Center for Integrated Protein Science Munich (CIPSM)“ der LMU startet am 9. Juli gemeinsam mit dem Feodor-Lynen-Gymnasium in Planegg im Landkreis München ein Projekt in dem Forscher/innen Schülern/innen der Klassenstufe 8 wissenschaftliche Zusammenhänge anschaulich und spannend vermitteln um sie frühzeitig für die Natur und ihre ...
01-Jul-2014

Patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) frequently harbor mutations in genes involved in the DNA (hydroxy)methylation pathway (DNMT3A, TET2, IDH1 and IDH2). In this study, we measured 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) levels in 206 clinically and molecularly well-characterized younger adult AML patients (≤60 years) included in the EORTC/GIMEMA AML-12 06991 ...
19-Jun-2014
J. Proteome Res., 13 (8), pp 3628–3634, DOI: 10.1021/pr500163r
J. Proteome Res., online article

Many neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease, can be directly correlated with the deregulation in neuronal signaling. Hence, it is indispensable for therapy development to understand the participating signaling processes. Because the activity of the involved protein kinases is of major interest for the investigation of these signaling processes, ...
29-May-2014
BMC Bioinformatics, online article

To leverage the potential of multi-omics studies, exploratory data analysis methods that provide systematic integration and comparison of multiple layers of omics information are required. We describe multiple co-inertia analysis (MCIA), an exploratory data analysis method that identifies co-relationships between multiple high dimensional datasets. Based on a ...
29-May-2014
Biochem. J., online article
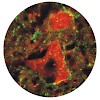
Lack of permissive mechanisms and abundance of inhibitory molecules in the lesioned central nervous system of adult mammals contribute to the failure of functional recovery, which leads to severe disabilities in motor functions or pain. Previous studies have indicated that the neural cell adhesion molecule L1 constitutes a viable target to promote regeneration. ...
28-May-2014
Journal of The American Society for Mass Spectrometry, online article

We describe the design, preparation, and mass-spectrometric characterization of a new recombinant peptide calibration standard with uniform biophysical and ionization characteristics for mass spectrometry. “PAS-cal” is an artificial polypeptide concatamer of peptide cassettes with varying lengths, each composed of the three small, chemically stable amino acids ...
28-May-2014

Proteomes are characterized by large protein-abundance differences, cell-type- and time-dependent expression patterns and post-translational modifications, all of which carry biological information that is not accessible by genomics or transcriptomics. Here we present a mass-spectrometry-based draft of the human proteome and a public, high-performance, in-memory ...
18-May-2014
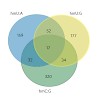
Ten eleven translocation (Tet) enzymes oxidize the epigenetically important DNA base 5-methylcytosine (mC) stepwise to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (hmC), 5-formylcytosine and 5-carboxycytosine. It is currently unknown whether Tet-induced oxidation is limited to cytosine-derived nucleobases or whether other nucleobases are oxidized as well. We synthesized isotopologs ...
29-Apr-2014
ChemBioChem, online article
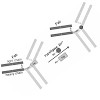
Bioconjugates, such as antibody–drug conjugates, have gained recent attention because of their increasing use in therapeutic and diagnostic applications. Commonly used conjugation reactions based upon chemoselective reagents exhibit a number of drawbacks: most of these reactions lack regio- and stereospecificity, thus resulting in loss of protein functionality ...
23-Apr-2014
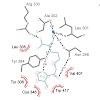
Posttranslational modifications (PTMs) of proteins determine their structure-function relationships, interaction partners, as well as their fate in the cell and are crucial for many cellular key processes. For instance chromatin structure and hence gene expression is epigenetically regulated by acetylation or methylation of lysine residues in histones, a ...
09-Apr-2014
Proteome Science, online article
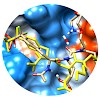
Many human diseases are correlated with the dysregulation of signal transduction processes. One of the most important protein interaction domains in the context of signal transduction is the Src homology 2 (SH2) domain that binds phosphotyrosine residues. Hence, appropriate methods for the investigation of SH2 proteins are indispensable in diagnostics and ...
09-Apr-2014
J. Proteome Res., online article
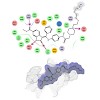
Solid tumors are dependent for growth on nutrients and the supply of oxygen, which they often acquire via neoangiogenesis. Vascular endothelial growth factors and the corresponding receptors (VEGFRs) play central roles in this process, and consequently, the blockade of this pathway is one therapeutic strategy for cancer treatment. A number of small molecules ...
01-Apr-2014
Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, Volume 14, Number 7, April 2014, pp. 840-854(15)
Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, online article

Regarding its many roles for lead optimization and drug development, fluorine will definitely continue to be of major importance in medicinal chemistry. With safe and selective fluorinating agents at hands, the use of fluorinated compounds has become routine in pharmaceutical and material sciences and many of the well-appreciated organofluorine inductive effects ...
10-Mar-2014

Base stacking in DNA is related to long-living excited states whose molecular nature is still under debate. To elucidate the molecular background we study well-defined oligonucleotides with natural bases, which allow selective UV excitation of one single base in the strand. IR probing in the picosecond regime enables us to dissect the contribution of different ...
06-Mar-2014
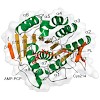
Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (PLP) is the active vitamer of vitamin B6 and acts as an essential cofactor in many aspects of amino acid and sugar metabolism. The virulence and survival of pathogenic bacteria such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis depend on PLP, and deficiencies in humans have also been associated with neurological disorders and inflammation. While PLP can ...
24-Feb-2014
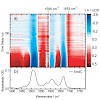
Methylated cytidine plays an important role as an epigenetic signal in gene regulation. Its oxidation products are assumed to be involved in active demethylation processes but also in damaging DNA. Here, we report the photochemical production of the 5-methyl-2′-deoxycytidine radical cation via a two-photon ionization process. The radical cation is detected by ...
20-Feb-2014
ChemMedChem, online article

Skin infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus are a major clinical concern, especially if they are caused by multi-resistant strains. In these cases, a spread into deeper soft tissues or the bloodstream results in life-threatening conditions that are difficult to treat by conventional antibiotics. Previous in vitro experiments with a small β-lactone-based ...
19-Feb-2014

We want to deeply thank you for all your great contributions at this years’ Wildbad Kreuth conference! We enjoyed each one of your lectures and posters. Because of the good overall standard presented by the members of the CIPSM Graduate Forum it was hard to come down to the laureates of our CIPSM AWARDS: The CIPSM AWARD for the best lecture goes to: Dr. Eva Huber ...
13-Feb-2014
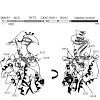
The N-terminal regulatory part of DNA methyltransferase 1 (Dnmt1) contains a replication foci targeting sequence (RFTS) domain, which is involved in the recruitment of Dnmt1 to replication forks. The RFTS domain has been observed in a crystal structure to bind to the catalytic domain of the enzyme and block its catalytic centre. Removal of the RFTS domain led to ...
07-Feb-2014
Applied and Environmental Microbiology, online article
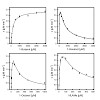
The noncanonical alcohol dehydrogenase AlkJ is encoded on the alkane-metabolizing alk operon of the mesophilic bacterium Pseudomonas putida GPo1. To gain insight into the enzymology of AlkJ, we have produced the recombinant protein in Escherichia coli and purified it to homogeneity using His6 tag affinity and size exclusion chromatography (SEC). Despite synthesis ...
05-Feb-2014
Journal of Structural Biology, online article
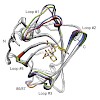
Modern strategies in radio-immuno therapy and in vivo imaging require robust, small, and specific ligand-binding proteins. In this context we have previously developed artificial lipocalins, so-called Anticalins, with high binding activity toward rare-earth metal–chelate complexes using combinatorial protein design. Here we describe further improvement of the ...
31-Jan-2014
Direct repair of UV-induced DNA lesions represents an elegant method for many organisms to deal with these highly mutagenic and cytotoxic compounds. Although the participating proteins are structurally well investigated, the exact repair mechanism of the photolyase enzymes remains a vivid subject of current research. In this review, we summarize and highlight the ...
23-Jan-2014

The synthesis of a variety of α-branched trifluoroethyl amines was achieved by reaction of N-aryl hemiaminal ethers with organomagnesium reagents.
21-Jan-2014
FEBSLetters, online article
Antibodies, which can recognize a plethora of possible antigens, have been considered as a paradigm of protein engineering performed by nature itself. Lipocalins constitute a distinct family of proteins with functions in ligand binding and transport that occur in many organisms, including man. Like antibodies, lipocalins exhibit a structurally conserved framework ...
16-Jan-2014
Journal of Proteomics, online article
Recent advances in mass spectrometry-based chemical proteomics allow unbiased analysis of drug-target interactions under close to physiological conditions. In this study, we designed and synthesized two small molecule probes targeting fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs) and applied them to evaluate the selectivity profiles of the FGFR inhibitors Dovitinib ...
07-Jan-2014
Despite their structural similarity, the natural products omuralide and vibralactone have different biological targets. While omuralide blocks the chymotryptic activity of the proteasome with an IC50 value of 47 nM, vibralactone does not have any effect at this protease up to a concentration of 1 mM. Activity-based protein profiling in HeLa cells revealed that ...
03-Jan-2014
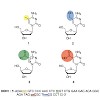
A 5-formyl-2’-deoxycytidine (fdC) phosphoramidite building block that enables the synthesis of fdC-containing DNA with excellent purity and yield has been developed. In combination with phosphoramidites for 5-methyl-dC, 5-hydroxymethyl-dC, and carboxy-dC, it was possible to prepare a segment of the OCT-4 promoter that contains all four epigenetic bases. Because ...