Research Area E - Publications 2009
01-Dec-2009
Folding and oligomerization of integral membrane proteins frequently depend on specific interactions of transmembrane helices. Interacting amino acids of helix-helix interfaces may form complex motifs and exert different types of molecular forces. Here, a set of strongly self-interacting transmembrane domains (TMDs), as isolated from a combinatorial library, was ...
23-Nov-2009
The Journal of Clinical Investigation, online article

Hypertension and its complications represent leading causes of morbidity and mortality. Although the cause of hypertension is unknown in most patients, genetic factors are recognized as contributing significantly to an individual’s lifetime risk of developing the condition. Here, we investigated the role of the G protein regulator phosducin (Pdc) in hypertension. ...
06-Nov-2009

Eukaryotic proteins and in particular cell-surface proteins are frequently glycosylated, which has fueled the interest of chemist to develop new methods for the synthesis of glycosylated proteins. Protein glycosylation is essential for the proper function of the respective proteins and in the case of glycosylated protein therapeutics, such as erythropoietin, the ...
04-Nov-2009
Online article
Chemical Biology: Photosensitive reaction opens or shuts potassium's flow. Drugs that are modulated by light may have a more controllable cousin on the horizon. Researchers led by Dirk Trauner, a chemist at the University of Munich, have figured out the mechanism by which molecules with the ability to block voltage-gated ion channels can be turned on and off ...
23-Oct-2009
Chem. Eur. J., online article

Solutions of butylzinc iodide in tetrahydrofuran, acetonitrile, and N,N-dimethylformamide were analyzed by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. In all cases, microsolvated butylzinc cations [ZnBu(solvent)n]+, n=1-3, were detected. The parallel observation of the butylzincate anion [ZnBuI2]- suggests that these ions result from disproportionation of neutral ...
22-Oct-2009
Journal of Proteom Research, 2009, 8, 12, 5674 - 78 published on 22.10.2009
Journal of Proteome Research, online article

Membrane proteomics is challenging because the desirable strong detergents are incompatible with downstream analysis. Recently, we demonstrated efficient removal of SDS by the filter aided sample preparation method (FASP). Here we combine FASP with our previously described small-scale membrane enrichment protocol. Analysis of a single mouse hippocampus enables ...
19-Oct-2009

Many biopharmaceuticals comprise small proteins that are quickly eliminated from the body. CIPSM PI and board member Arne Skerra and his new spin-off XL-protein GmbH combine such small proteins with a kind of molecular balloon that swells and thus prolongs the half-life of these proteins in the body. The CIPSM spin-off XL-protein GmbH has now started to further ...
16-Oct-2009
Proteins, online article
Molecular docking programs play an important role in drug development and many well-established methods exist. However, there are two situations for which the performance of most approaches is still not satisfactory, namely inclusion of receptor flexibility and docking of large, flexible ligands like peptides. In this publication a new approach is presented for ...
A Photolabile Linker for the Mild and Selective Cleavage of Enriched Biomolecules from Solid Support
12-Oct-2009
Selective release of enriched biomolecules from solid support is a desirable goal in proteomic and metabolomic studies. Here we demonstrate that photocleavage of a light-sensitive phenacyl ester bond is a suitable alternative cleavage strategy for the selective release of enriched biomolecules form avidin beads circumventing the disadvantages of conventional heat ...
01-Oct-2009
Acta Chrystallographica D, online article
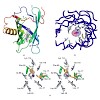
Tear lipocalin (TLC) with the bound artificial ligand 1,4-butanediol has been crystallized in space group P21 with four protein molecules in the asymmetric unit and its X-ray structure has been solved at 2.6 Å resolution. TLC is a member of the lipocalin family that binds ligands with diverse chemical structures, such as fatty acids, phospholipids and ...
11-Sep-2009
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2009, 48, 1–4, DOI:10.1002/anie.200902740 published on 11.09.2009
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article
Modifications make a difference: An isotope-based mass spectrometry method allows the facile and quantitative analysis of modified tRNA nucleosides in various types of cells. This method could be capable of distinguishing between individual cell lines as well as between healthy tissue and cancer cells.
11-Sep-2009

The natural product syringolin A (SylA) is a potent proteasome inhibitor with promising anticancer activities. To further investigate its potential as a lead structure, selectivity profiling with cell lysates was performed. At therapeutic concentrations, a rhodamine-tagged SylA derivative selectively bound to the 20 S proteasome active sites without detectable ...
08-Sep-2009
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article
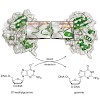
The DNA of a cell is continuously exposed to numerous endogenous and exogenous factors. The resulting DNA damage can lead to mutations or cell death. Some of the major DNA lesions are generated by the reaction of alkylating reagents with DNAbases. The alkylated reaction products can arise endogenously from cellular alkylating reagents as Sadenosylmethionine or ...
31-Aug-2009
Chem. Eur. J., online article
UV-light irradiation induces the formation of highly mutagenic lesions in DNA, such as cis-syn cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPD photoproducts), pyrimidine(6-4)pyrimidone photoproducts ((6-4) photoproducts) and their Dewar valence isomers ((Dew) photoproducts). Here we describe the synthesis of defined DNA strands containing these lesions by direct irradiation. ...
13-Aug-2009
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, online article
Many marketed drugs contain fluorine, reflecting its ability to modulate a variety of biological responses. The unique 20S proteasome inhibition profile of fluorosalinosporamide compared to chlorinated anticancer agent salinosporamide A (NPI-0052) is exemplary and relates to each halogen’s leaving group potential. Crystal structures of fluoro-, hydroxy-, and ...
04-Aug-2009

The increasing emergence of multiresistant bacterial pathogens represents a dramatic global health problem. One major reason for this dilemma is the high selective pressure that is exerted on bacteria by classical antibiotic therapies, leading to a steady increase in the number of strains resistant to the majority of all currently available antibiotic drugs. In ...
01-Aug-2009
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, online article
Cyclization of recently reported linear phosphino dipeptide isostere inhibitors of BACE1 via side chain olefin metathesis yielded macrocyclic BACE1 inhibitors. The most potent compound II-P1 (IC50 of 47 nM) and the corresponding linear analog I were tested for serum stability. The approach led to three times prolonged half life serum stability of 44 min for the ...
28-Jul-2009
A new photoinducible single electron donor has been developed, which, when linked to thymidine, is shown to be an efficient ground state reducing agent in DNA; the donor can be activated at wavelengths where standard DNA does not absorb.
30-Jun-2009
Angewandte Chemie, online article

Eukaryotes and most prokaryotes require isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) as biosynthetic precursors of terpenes. Whereas animals generate these essential metabolites via the mevalonate pathway,[1] many human pathogens including Plasmodium falciparum and Mycobacterium tuberculosis are known to use the more recently identified ...
29-Jun-2009
Biochem., 2009, 48 (31), 7411–7419, doi:10.1021/bi900535j published on 29.06.2009
Biochemistry, online article

The NMR structure of the 21 kDa lipocalin FluA, which was previously obtained by combinatorial design, elucidates a reshaped binding site specific for the dye fluorescein resulting from 21 side chain replacements with respect to the parental lipocalin, the naturally occurring bilin-binding protein (BBP). As expected, FluA exhibits the lipocalin fold of BBP, ...
19-Jun-2009
CIPSM Events

CIPSM sponsors the "Alpenforum 2009" which will rock Oberammergau from 26.-28. of June 2009! The event is dedicated to straighten contacts between young chemists and companies. Be there or be square!
30-May-2009
Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., online article

Photolyases repair cytotoxic and mutagenic UV-induced photolesions in DNA by using an amazing light-dependent repair mechanism. It involves light absorption, electron transfer from an excited reduced and deprotonated FADH− to the flipped-out photolesion, followed by the fragmentation of the photolesions. Cryptochromes are highly related proteins that no longer ...
29-May-2009
CIPSM Events

The LMU-Harvard Young Scientists’ Forum (YSF) seeks to unite Ph.D. students and postdoctoral fellows from the Harvard University and the Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität (LMU) with core faculty from the two universities to create a framework for an interdisciplinary exchange of ideas. This year’s conference entiteled "From Molecules to Organisms" will be held at ...
19-May-2009
Chemical Communcations, online article
Michael acceptor based natural product derived probes are selective and sensitive chemical tools for the identification and characterization of pathologically relevant enzymes in MRSA.
13-May-2009
Protein Science, online article

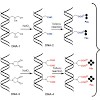
Within 1 or 2 decades, the reputation of membrane-spanning -helices has changed dramatically. Once mostly regarded as dull membrane anchors, transmembrane domains are now recognized as major instigators of protein-protein interaction. These interactions may be of exquisite specificity in mediating assembly of stable membrane protein complexes from cognate ...
13-May-2009
Protein Science, online article
Acylation of proteins is known to mediate membrane attachment and to influence subcellular sorting. Here, we report that acylation can stabilize secondary structure. Circular dichroism spectroscopy showed that N-terminal attachment of acyl chains decreases the ability of an intrinsically flexible hydrophobic model peptide to refold from an -helical state to ...
07-May-2009
CIPSM Events

Click here and keep on scrolling if you care for pictures form the event "CIPSM - Ausgewählter Ort im Land der Ideen 2009" which was held on the 4th of May 2009 in the Deutsche Museum. Click here for all pictures
05-May-2009
Biomolecular reagents that enable the specific molecular recognition of proteins play a crucial role in basic research as well as medicine. Up to now, antibodies (immunoglobulins) have been widely used for this purpose. Their predominant feature is the vast repertoire of antigen-binding sites that arise from a set of 6 hypervariable loops. However, antibodies ...
04-May-2009
CIPSM Events

CIPSM ist „Ausgewählter Ort im Land der Ideen“. Damit ist CIPSM Teil der Veranstaltungsreihe „365 Orte im Land der Ideen“, die gemeinsam von der Standortinitiative „Deutschland – Land der Ideen“ und der Deutschen Bank durchgeführt wird. Als „Ausgewählter Ort“ wird CIPSM unter der Schirmherrschaft von Bundespräsident Horst Köhler im Jahr 2009 Deutschland als das ...
01-May-2009
PNAS, 2009, 106, 11504-11545 published on 01.05.2009
PNAS, online article
Archae possess unique biochemical systems quite distinct from the pathways present in eukaryotes and eubacteria. 7,8-Dimethyl-8-hydroxy-5deazaflavin (F0) and F420 are unique deazaflavin-containing coenzyme and methanogenic signature molecules, essential for a variety of biochemical transformations associated with methane biosynthesis and light-dependent DNA ...
28-Apr-2009

Prion disease is characterized by the α→β structural conversion of the cellular prion protein (PrPC) into the misfolded and aggregated “scrapie” (PrPSc) isoform. It has been speculated that methionine (Met) oxidation in PrPC may have a special role in this process, but has not been detailed and assigned individually to the 9 Met residues of full-length, ...
23-Apr-2009
Bioorganic & Medical Chemistry Letters, online article
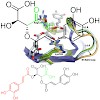
In this Letter, we report the natural products salvianolic acid A, salvianolic acid B, and caftaric acid as inhibitors of the protein–protein interactions mediated by the SH2 domains of the Src-family kinases Src and Lck, two established disease targets. Moreover, we propose a binding mode for the inhibitors based on molecular modeling, which will facilitate ...
21-Apr-2009
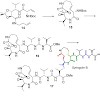
Syrbactins, a family of natural products belonging either to the syringolin or glidobactin class, are highly potent proteasome inhibitors. Although sharing similar structural features, they differ in their macrocyclic lactam core structure and exocyclic side chain. These structural variations critically influence inhibitory potency and proteasome subsite ...
19-Apr-2009

We describe a method, filter-aided sample preparation (FASP), which combines the advantages of in-gel and in-solution digestion for mass spectrometry–based proteomics. We completely solubilized the proteome in sodium dodecyl sulfate, which we then exchanged by urea on a standard filtration device. Peptides eluted after digestion on the filter were pure, allowing ...
14-Apr-2009
Journal of Molecular Biology, online article

The transmembrane domains of fusion proteins are known to be functionally important and display an overabundance of helix-destabilizing Ile and Val residues. In an effort to systematically study the relationship of fusogenicity and helix stability, we had previously designed LV-peptides, a low-complexity model system whose hydrophobic core consists of Leu and Val ...
08-Apr-2009
JACS, online article
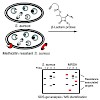
With the development of antibiotic resistant bacterial strains, infectious diseases have become again a life threatening problem. One of the reasons for this dilemma is the limited number and breadth of current therapeutic targets for which several resistance strategies have evolved over time. To identify resistance associated targets and to understand their ...
01-Apr-2009
Org. Lett., 2009, 11, 2405-2408 published on 01.04.2009
Org. Lett., online article
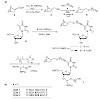
Nitrile oxides react smoothly and rapidly with norbornene-modified DNA in a copper-free click reaction. The reaction allows high density functionalization of oligodeoxyribonucleotides (ODNs) with a large variety of molecules directly on solid supports and even in synthesizers without the need for an additional catalyst.
31-Mar-2009
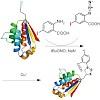
Upon development of radioimmunoassay techniques,[1] radioiodination of peptides and proteins has gradually become an indispensable tool for controlling and monitoring protein and peptide functions in vivo and in vitro, and for studying ligand–receptor interactions, ligand uptake and clearance. In addition, protein iodination has developed into a useful technique ...
23-Mar-2009
DFG comment box
2009 is great! If you have time, take 5 minutes to watch CIPSM on silverscreen. english german
11-Mar-2009
Angewandte Chemie, online article

Chemical biology has multiple aims,[1] one of which is the identification of small-molecule modulators for individual functions of as many human proteins as possible. Various approaches towards this goal have been developed, which converge to create a toolbox of small molecules for chemical biologists.[2–4] This endeavor constitutes a long and winding road, ...
02-Mar-2009
ChemBioChem, online article

Saghatelian and colleagues recently introduced a global metabolite-profiling approach that allows protein-metabolite interactions (PMI) to be identified. This approach represents an excellent strategy and valuable tool for unraveling the many secrets of the metabolome. The key features of the methodology will be summarized here.
01-Mar-2009
Neuro-Oncology, 2009, 11(6), 861-870, doi:10.1215/15228517-2009-024 published on 01.03.2009
Neuro-Oncology, online article

Inhibitors targeting the integrin {alpha}vβ3 are promising new agents currently tested in clinical trials for supplemental therapy of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). The aim of our study was to evaluate 18F-labeled glycosylated Arg-Gly-Asp peptide ([18F]Galacto-RGD) PET for noninvasive imaging of {alpha}vβ3 expression in patients with GBM, suggesting eligibility ...
19-Feb-2009
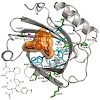
Human lipocalin 2 (Lcn2), also known as neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), which naturally scavenges bacterial ferric siderophores, has been engineered to specifically bind rare-earth and related metal ions as chelate complexes with [(R)-2-amino-3-(4-aminophenyl)propyl]-trans-(S,S)-cyclohexane-1,2-diaminepentaacetic acid (p-NH(2)-Bn-CHX-A''-DTPA). ...
16-Feb-2009
ChemBioChem, 2009, 10, 728-734 published on 16.02.2009
ChemBioChem, online article
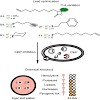
The cytidine analogue 5-fluoro-2-deoxycytidine (dCF) is a mechanism-based inhibitor of DNA methyltransferases. We report the synthesis of short 18-mer dsDNA oligomers containing a triple-hemimethylated CpG motive as a recognition sequence for the human methyltransferase Dnmt1. The DNA strands carry within these CpG islands dCF building blocks that function as ...
10-Feb-2009
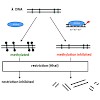
With decreasing efficiency of antibiotic therapies against hospital- and community-acquired bacterial pathogens, the treatment of infectious diseases again represents a tremendous challenge for medicinal research. This challenge seems to be particularly difficult if one considers the sophisticated resistance strategies, which are effective against almost all ...
04-Feb-2009
Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., online article
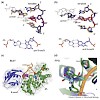
Selective base pairing of the four canonical nucleobases is fundamental for the integrity of the genetic system. Information loss associated with DNA damage is a constant challenge and in response, organisms have evolved specialized defence systems consisting of DNA repair and lesion tolerance. DNA repair requires the action of different lesion recognition ...
04-Feb-2009
Polo-like kinases (Plks) are a conserved family of serine/threonine kinases.[1, 2] The family member Plk1 is a key regulator of mitosis[1, 2] and has been identified as a negative prognostic marker for tumor patients.[3, 4] The widespread recognition of Plk1 as a therapeutic target for the treatment of human tumors has triggered numerous drug discovery ...
22-Jan-2009
Cell, 2009, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.12.023, published on 22.01.2009
Cell, online article
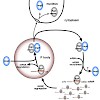
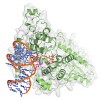
Small regulatory RNAs including small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs) guide Argonaute (Ago) proteins to specific target RNAs leading tomRNA destabilization or translational repression. Here, we report the identification of Importin 8 (Imp8) as a component of miRNA-guided regulatory pathways. We show that Imp8 interacts with Ago proteins and ...
15-Jan-2009
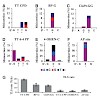
DNA replication across blocking lesions occurs by translesion DNA synthesis (TLS), involving a multitude of mutagenic DNA polymerases that operate to protect the mammalian genome. Using a quantitative TLS assay, we identified three main classes of TLS in human cells: two rapid and error-free, and the third slow and error-prone. A single gene, REV3L, encoding the ...
06-Jan-2009
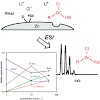
Tetrahydrofuran solutions of the products formed in LiCl-mediated zinc insertion reactions into various organic halides RHal were analyzed by anion-mode electrospray ionization (ESI) mass spectrometry. In all cases, organozincate anions were observed. The reactions with RHal, Hal ) Br and I, yielded predominantly mononuclear complexes, such as ZnRHal2 - and ...
28-Nov-2008
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article
Silver-plated DNA: The deposit of a thin metal layer on biomolecules, such as DNA, requires the formation of small, magic-sized metal nuclei. Through the careful design of a reducing chemical functionality in the form of a dialdehyde, the nucleation process and thus the metallization step can be controlled.



 niewski, Alexandre Zougman, Nagarjuna Nagaraj,
niewski, Alexandre Zougman, Nagarjuna Nagaraj, 






