Research Area B - Publications 2017
20-Dec-2017
Nature Communications, volume 8, Article number: 2213, doi:10.1038/s41467-017-02199-4
Nature Communications, online article
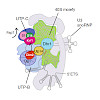
Ribosome biogenesis begins in the nucleolus with the formation of 90S pre-ribosomes, from which pre-40S and pre-60S particles arise that subsequently follow separate maturation pathways. Here, we show how structurally related assembly factors, the KH domain proteins Krr1 and Dim2, participate in ribosome assembly. Initially, Dim2 (Pno1) orchestrates an early step ...
16-Dec-2017
JMB, Volume 430, Issue 5, Pages 611-627, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2017.11.016
JMB, online article
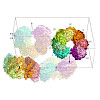
Ancestral β-subunit (Anbu) is homologous to HslV and 20S proteasomes. Based on its phylogenetic distribution and sequence clustering, Anbu has been proposed as the “ancestral” form of proteasomes. Here, we report biochemical data, small-angle X-ray scattering results, negative-stain electron microscopy micrographs and a crystal structure of the Anbu particle from ...
14-Dec-2017
BMC Biology 2017, 15:119, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-017-0468-1
BMC Biology, online article
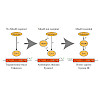
The disulfide relay system found in the intermembrane space (IMS) of mitochondria is an essential pathway for the import and oxidative folding of IMS proteins. Erv1, an essential member of this pathway, has been previously found to be ubiquitously present in mitochondria-containing eukaryotes. However, the other essential protein, Mia40, was found to be absent or ...
30-Nov-2017
ACS Chem. Biol.,13 (1), pp 161–170, DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.7b00792
ACS Chem. Biol.,online article
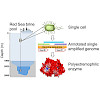
Because only 0.01% of prokaryotic genospecies can be cultured and in situ observations are often impracticable, culture-independent methods are required to understand microbial life and harness potential applications of microbes. Here, we report a methodology for the production of proteins with desired functions based on single amplified genomes (SAGs) from ...
02-Nov-2017
Molecular Cell, Volume 68, Issue 3, p515–527.e6, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.014
Molecular Cell, online article
Ribosomes synthesizing proteins containing consecutive proline residues become stalled and require rescue via the action of uniquely modified translation elongation factors, EF-P in bacteria, or archaeal/eukaryotic a/eIF5A. To date, no structures exist of EF-P or eIF5A in complex with translating ribosomes stalled at polyproline stretches, and thus structural ...
02-Oct-2017
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, volume 24, 954–964, doi:10.1038/nsmb.3476
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article

The 40S small ribosomal subunit is cotranscriptionally assembled in the nucleolus as part of a large chaperone complex called the 90S preribosome or small-subunit processome. Here, we present the 3.2-Å-resolution structure of the Chaetomium thermophilum 90S preribosome, which allowed us to build atomic structures for 34 assembly factors, including the Mpp10 ...
28-Sep-2017
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15737 –15741, https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201706927
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article

The characterization of low‐affinity protein complexes is challenging due to their dynamic nature. Here, we present a method to stabilize transient protein complexes in vivo by generating a covalent and conformationally flexible bridge between the interaction partners. A highly active pyrrolysyl tRNA synthetase mutant directs the incorporation of unnatural amino ...
27-Sep-2017
PNAS, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1701797114
PNAS, online article
Professional secretory cells can produce large amounts of high-quality complex molecules, including IgM antibodies. Owing to their multivalency, polymeric IgM antibodies provide an efficient first-line of defense against pathogens. To decipher the mechanisms of IgM assembly, we investigated its biosynthesis in living cells and faithfully reconstituted the ...
25-Sep-2017
Scientific Reports,volume 7, Article number: 12276, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-12519-9
Scientific Reports, online article

The antibody Fv module which binds antigen consists of the variable domains VL and VH. These exhibit a conserved ß-sheet structure and comprise highly variable loops (CDRs). Little is known about the contributions of the framework residues and CDRs to their association. We exchanged conserved interface residues as well as CDR loops and tested the effects on two ...
21-Sep-2017
Molecular Cell, Volume 67, Issue 6, p947–961.e5, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.08.004
Molecular Cell, online article
The Hsp90 system in the eukaryotic cytosol is characterized by a cohort of co-chaperones that bind to Hsp90 and affect its function. Although progress has been made regarding the underlying biochemical mechanisms, how co-chaperones influence Hsp90 client proteins in vivo has remained elusive. By investigating the effect of 12 Hsp90 co-chaperones on the activity ...
31-Aug-2017
Structure, Volume 25, Issue 10, p1473–1480.e3, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2017.07.013
Structure, online article
The heptameric proteasome activator (PA) 28αβ is known to modulate class I antigen processing by docking onto 20S proteasome core particles (CPs). The exact stoichiometry and arrangement of its α and β subunits, however, is still controversial. Here we analyzed murine PA28 complexes regarding structure and assembly. Strikingly, PA28α, PA28β, and PA28αβ ...
28-Aug-2017
J. Biol. Chem., (2017) 292(41), 17073–17083, DOI 10.1074/jbc.M117.797829
J. Biol. Chem., online article

The eukaryotic Hsp90 chaperone machinery comprises many co-chaperones and regulates the conformation of hundreds of cytosolic client proteins. Therefore, it is not surprising that the Hsp90 machinery has become an attractive therapeutic target for diseases such as cancer. The compounds used so far to target this machinery affect the entire Hsp90 system. However, ...
31-Jul-2017
Nature Communications, volume 8, Article number: 159, doi:10.1038/s41467-017-00188-1
Nature Communications, online article
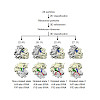
Translation arrest by polybasic sequences induces ribosome stalling, and the arrest product is degraded by the ribosome-mediated quality control (RQC) system. Here we report that ubiquitination of the 40S ribosomal protein uS10 by the E3 ubiquitin ligase Hel2 (or RQT1) is required for RQC. We identify a RQC-trigger (RQT) subcomplex composed of the RNA ...
26-Jul-2017
PLoS ONE, 12(7): e0181799, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181799
PLoS ONE, online article

Little structural information is available so far on amyloid fibrils consisting of immunoglobulin light chains. It is not understood which features of the primary sequence of the protein result in fibril formation. We report here MAS solid-state NMR studies to identify the structured core of κ-type variable domain light chain fibrils. The core contains residues ...
24-Jul-2017
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, volume 24, 752–757, doi:10.1038/nsmb.3439
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article
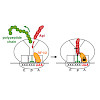
Many antibiotics stop bacterial growth by inhibiting different steps of protein synthesis. However, no specific inhibitors of translation termination are known. Proline-rich antimicrobial peptides, a component of the antibacterial defense system of multicellular organisms, interfere with bacterial growth by inhibiting translation. Here we show that Api137, a ...
07-Jul-2017
ACS Chem. Biol., 2017, 12 (8), pp 2132–2138, DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.7b00004
ACS Chem. Biol., online article

Enzymes of the nonmevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis are attractive targets for the development of herbicides and drugs against infectious diseases. While this pathway is essential for many pathogens and plants, mammals do not depend on it for the synthesis of isoprenoids. IspD, the third enzyme of the nonmevalonate pathway, is unique in that it has an ...
15-Jun-2017
Nature Communications, volume 8, Article number: 15804 (2017) doi:10.1038/ncomms15804
Nature Communications, online article
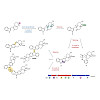
Terpenoid natural products comprise a wide range of molecular architectures that typically result from C–C bond formations catalysed by classical type I/II terpene cyclases. However, the molecular diversity of biologically active terpenoids is substantially increased by fully unrelated, non-canonical terpenoid cyclases. Their evolutionary origin has remained ...
30-May-2017
eLife 2017; 6:e25642, doi: 10.7554/eLife.25642
eLife, online article
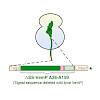
Interaction between the nascent polypeptide chain and the ribosomal exit tunnel can modulate the rate of translation and induce translational arrest to regulate expression of downstream genes. The ribosomal tunnel also provides a protected environment for initial protein folding events. Here, we present a 2.9 Å cryo-electron microscopy structure of a ribosome ...
23-May-2017
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Volume 56, Issue 26, Pages 7510-7514, https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201701761
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article
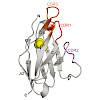
Systemic amyloidosis is caused by the misfolding of a circulating amyloid precursor protein and the deposition of amyloid fibrils in multiple organs. Chemical and biophysical analysis of amyloid fibrils from human AL and murine AA amyloidosis reveal the same fibril morphologies in different tissues or organs of one patient or diseased animal. The observed ...
19-May-2017
ACS Chem. Biol., 2017, 12 (7), pp 1874–1882, DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.6b00847
ACS Chem. Biol., online aticle
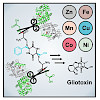
The formation of glutathione (GSH) conjugates, best known from the detoxification of xenobiotics, is a widespread strategy to incorporate sulfur into biomolecules. The biosynthesis of gliotoxin, a virulence factor of the human pathogenic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus, involves attachment of two GSH molecules and their sequential decomposition to yield two reactive ...
03-May-2017
The EMBO Journal, Vol 36, No 14, https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201696189
The EMBO Journal, online article

Under stress conditions, such as nutrient deprivation, bacteria enter into a hibernation stage, which is characterized by the appearance of 100S ribosomal particles. In Escherichia coli, dimerization of 70S ribosomes into 100S requires the action of the ribosome modulation factor (RMF) and the hibernation‐promoting factor (HPF). Most other bacteria lack RMF and ...
21-Apr-2017
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, volume 18, 345–360, doi:10.1038/nrm.2017.20
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, online article
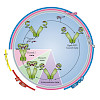
The heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) chaperone machinery is a key regulator of proteostasis under both physiological and stress conditions in eukaryotic cells. As HSP90 has several hundred protein substrates (or 'clients'), it is involved in many cellular processes beyond protein folding, which include DNA repair, development, the immune response and ...
10-Apr-2017
Amyloid, 24:1, 1-16, DOI:10.1080/13506129.2017.1304905
Amyloid, online article
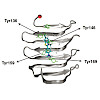
Thioflavin T (ThT) has been widely used to investigate amyloid formation since 1989. While concerns have recently been raised about its use as a probe specific for amyloid, ThT still continues to be a very valuable tool for studying kinetic aspects of fibrillation and associated inhibition mechanisms. This review aims to provide a conceptual instruction manual, ...
04-Apr-2017
Scientific Reports, volume 7, Article number: 613, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-00780-x
Scientific Reports, online article

Diphtheria toxin kills human cells because it delivers its enzyme domain DTA into their cytosol where it inhibits protein synthesis. After receptor-mediated uptake of the toxin, DTA translocates from acidic endosomes into the cytosol, which might be assisted by host cell factors. Here we investigated the role of Hsp90 and its co-chaperones during the uptake of ...
03-Apr-2017
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, volume 24, 453–460, doi:10.1038/nsmb.3396
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article
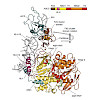
The essential ATP-binding cassette protein ABCE1 splits 80S ribosomes into 60S and 40S subunits after canonical termination or quality-control-based mRNA surveillance processes. However, the underlying splitting mechanism remains enigmatic. Here, we present a cryo-EM structure of the yeast 40S–ABCE1 post-splitting complex at 3.9-Å resolution. Compared to the ...
03-Apr-2017
Molecular Plant, Volume 10, Issue 4, p575–589, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2016.12.012
Molecular Plant, online article
The translocon on the outer membrane of mitochondria (TOM) facilitates the import of nuclear-encoded proteins. The principal machinery of mitochondrial protein transport seems conserved in eukaryotes; however, divergence in the composition and structure of TOM components has been observed between mammals, yeast, and plants. TOM9, the plant homolog of yeast Tom22, ...
30-Mar-2017
FEBS Letters, 591,1266–1277, https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12634
FEBS Letters, online article

Arabidopsis bZIP11 is a transcription factor that modulates amino acid metabolism under high‐sucrose conditions. Expression of bZIP11 is downregulated in a sucrose‐dependent manner during translation. Previous in vivo studies have identified the second upstream open reading frame (uORF2) as an essential regulatory element for the sucrose‐dependent translational ...
21-Mar-2017
JBC, doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.782284
JBC, online article
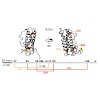
Members of the interleukin 12 (IL12) family perform essential functions in immunoregulation by connecting innate and adaptive immunity and are emerging therapeutic targets. They are unique among other interleukins in forming heterodimers that arise from extensive subunit sharing within the family, leading to the production of at least four functionally distinct ...
10-Mar-2017
Scientific Reports, 7, Article number: 44277, doi:10.1038/srep44277
Scientific Reports, online article
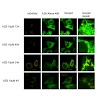
Cationic amphiphilic drugs (CADs) comprise a wide variety of different substance classes such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, and antiarrhythmics. It is well recognized that CADs accumulate in certain intracellular compartments leading to specific morphological changes of cells. So far, no adequate technique exists allowing for ultrastructural analysis of CAD ...
18-Feb-2017
Cell Stress and Chaperones, Volume 22, Issue 4, pp 541–552; DOI 10.1007/s12192-017-0772-2
Cell Stress and Chaperones, online aticle
In humans, ten genes encode small heat shock proteins with lens αA-crystallin and αB-crystallin representing two of the most prominent members. The canonical isoforms of αA-crystallin and αB-crystallin collaborate in the eye lens to prevent irreversible protein aggregation and preserve visual acuity. α-Crystallins form large polydisperse homo-oligomers and ...
08-Feb-2017
Front. Plant Sci., https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00168
Front. Plant Sci., online article
Chloroplasts originated from an endosymbiotic event in which a free-living cyanobacterium was engulfed by an ancestral eukaryotic host. During evolution the majority of the chloroplast genetic information was transferred to the host cell nucleus. As a consequence, proteins formerly encoded by the chloroplast genome are now translated in the cytosol and must be ...
27-Jan-2017
Scientific Reports, volume 7, Article number: 41515, doi:10.1038/srep41515
Scientific Reports, online article

Antibody light chain amyloidosis is a rare disease caused by fibril formation of secreted immunoglobulin light chains (LCs). The huge variety of antibody sequences puts a serious challenge to drug discovery. The green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) is known to interfere with fibril formation in general. Here we present solution- and solid-state ...
23-Jan-2017
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, volume 24, 221–225, doi:10.1038/nsmb.3355
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article

How do the key features of protein folding, elucidated from studies on native, isolated proteins, manifest in cotranslational folding on the ribosome? Using a well-characterized family of homologous α-helical proteins with a range of biophysical properties, we show that spectrin domains can fold vectorially on the ribosome and may do so via a pathway different ...










