Research Area A - Publications 2011
15-Jul-2012
Supramolecular Structure and Function 10 online article

Twenty years ago, fluorescence measurements at low concentrations were difficult due to the weak fluorescence signal and intrinsic fluctuations of the sample. With the development of FCS and its implementation on a confocal microscope, it is possible to use the inherent fluctuations to gain information over the concentration, molecular brightness, microscopic ...
26-Dec-2011
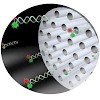
The diffusion dynamics of terrylene diimide (TDI) dye molecules and dye-labeled double-strand DNA were studied in micrometer long silica filaments containing collinear, oriented mesopores using single molecule fluorescence microscopy. TDI was used as a stable and hydrophobic probe molecule for single molecule structural analysis. We used template-free mesoporous ...
10-Dec-2011
Nucl. Acids Res., online article

DNA nanotechnology enables the programmed synthesis of intricate nanometer-scale structures for diverse applications in materials and biological science. Precise control over the 3D solution shape and mechanical flexibility of target designs is important to achieve desired functionality. Because experimental validation of designed nanostructures is time-consuming ...
05-Dec-2011
PNAS, online article
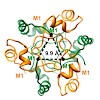
The molecular chaperone αB-crystallin, the major player in maintaining the transparency of the eye lens, prevents stress-damaged and aging lens proteins from aggregation. In nonlenticular cells, it is involved in various neurological diseases, diabetes, and cancer. Given its structural plasticity and dynamics, structure analysis of αB-crystallin presented ...
15-Nov-2011
Mol. Biol. Cell, online article
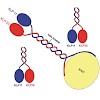
The heterotrimeric structure of kinesin-2 makes it a unique member of the kinesin superfamily; however, molecular details of the oligomer formation are largely unknown. Here we demonstrate that heterodimerization of the two distinct motor domains KLP11 and KLP20 of Caenorhabditis elegans kinesin-2 requires a dimerization seed of merely two heptads at the C ...
28-Oct-2011
Science, online article

Direct observation of the detailed conformational fluctuations of a single protein molecule en route to its folded state has so far been realized only in silico. We have used single-molecule force spectroscopy to study the folding transitions of single calmodulin molecules. High-resolution optical tweezers assays in combination with hidden Markov analysis reveal ...
24-Oct-2011
Advanced Functional Materials, online article
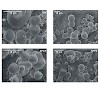
Oligonucleotides used in gene therapy and silencing are fragile compounds that degrade easily in biological environments. Porous biocompatible carrier particles may provide a useful strategy to deliver these therapeutics to their target sites. Development of appropriate delivery vehicles, however, requires a better understanding of the oligonucleotide-host ...
30-Sep-2011
Nanoscale, online article
Single particle tracking (SPT) in biological systems is a quickly growing field. Many new technologies are being developed providing new tracking capabilities, which also lead to higher demands and expectations for SPT. Following a single biomolecule as it performs its function provides quantitative mechanistic information that cannot be obtained in classical ...
08-Aug-2011
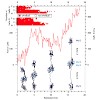
The highly oriented filamentous protein network of muscle constantly experiences significant mechanical load during muscle operation. The dimeric protein myomesin has been identified as an important M-band component supporting the mechanical integrity of the entire sarcomere. Recent structural studies have revealed a long αlpha-helical linker between the ...
06-Aug-2011
Journal of Controlled Release, online article
AlphavBeta3 and AlphavBeta5 integrins are attractive target structures for cancer therapy as they are upregulated in tumor 27 and tumor associated host cells and play a pivotal role for tumor growth and metastasis. Gene vectors such as 28 polyplex micelles consisting of thiolated PEG-block-poly(lysine) copolymers complexed with plasmid DNA 29 can be targeted to ...
22-Jul-2011
Molecular Cell, online article
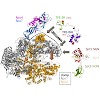
TFIIE and the archaeal homolog TFE enhance DNA strand separation of eukaryotic RNAPII and the archaeal RNAP during transcription initiation by an unknown mechanism. We have developed a fluorescently labeled recombinant M. jannaschii RNAP system to probe the archaeal transcription initiation complex, consisting of promoter DNA, TBP, TFB, TFE, and RNAP. We have ...
09-Jun-2011
ChemPhysChem, online article
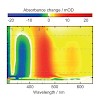
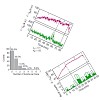
The photophysics of 1-methyl-2(1H)-pyrimidinone (1MP) dissolved in water is investigated by steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence, UV/Vis absorption, and IR spectroscopy. In the experiments, excitation light is tuned to the lowest-energy absorption band of 1MP peaking at 302 nm. At room temperature (291 K) its fluorescence lifetime amounts to 450 ps. With ...
07-Jun-2011
Molecular Therapy, online article
Highly sensitive fluorescence microscopy techniques allow single nanoparticles to be tracked during their uptake into living cells with high temporal and spatial resolution. From analysis of the trajectories, random motion can be discriminated from active transport and the average transport velocity and/or diffusion coefficient determined. Such an analysis ...
21-Mar-2011
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., online article
Mesoporous silica nanomaterials are a novel class of materials that offer a highly complex porous network with nanometre-sized channels into which a wide amount of differently sized guests can be incorporated. This makes them an ideal host for various applications for example in catalysis, chromatography and nanomedicine. For these applications, analyzing the ...
18-Mar-2011
Molecular Cell, online article
The metabolic processes of a cell comprise a network of interrelated molecular pathways. Control and regulation of these pathways under variable environmental conditions is vital and takes place at the transcriptional, translational, and posttranslational level. The eukaryotic molecular chaperone and heat-shock protein Hsp90, which is involved in the specific ...
16-Mar-2011
J. Phys. Chem. B, online article
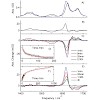
6,7-Dimethyl-8-ribityllumazine serves as fluorophore in lumazine proteins (LumP) of luminescent bacteria. The molecule exhibits several characteristic vibrational absorption bands between 1300 and 1750 cm-1 in its electronic ground state. The IR-absorption pattern of the singlet excited ππ* state was monitored via ultrafast infrared spectroscopy after ...
10-Mar-2011
Nature Cell Biology, online article
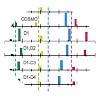
HIV (human immunode_ciency virus) diverts the cellular ESCRT (endosomal sorting complex required for transport) machinery to promote virion release from infected cells. The ESCRT consists of four heteromeric complexes (ESCRT-0 to ESCRT-III), which mediate different membrane abscission processes, most importantly formation of intralumenal vesicles at ...
03-Mar-2011
J. Phys. Chem. A, online article
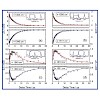
Femtosecond IR-pump-IR-probe experiments with independently tunable pulses are used to monitor the ultrafast response of selected IR absorption bands to vibrational excitation of other modes of Fmoc-nitrophenylalanine. The absorptions of both NO2-bands change rapidly within <2 ps upon excitation of other vibrational modes. The results point to considerable ...
25-Feb-2011
Nature Methods, online article

Molecular self-assembly with scaffolded DNA origami enables building custom-shaped nanometer-scale objects with molecular weights in the megadalton regime. Here we provide a practical guide for design and assembly of scaffolded DNA origami objects. We also introduce a computational tool for predicting the structure of DNA origami objects and provide information ...
25-Feb-2011
ChemPhysChem, online article
Self-assembly and aggregation of proteins or peptides into amyloid fibrils have attracted wide attention due to their high relevance for a variety of amyloid-related diseases.[1–3] Furthermore, amyloids show interesting material properties which make them ideal candidates for the production of nanostructures and molecular nanobiomaterials, where building blocks ...
09-Jan-2011
Nature Nanotechnology, online article

Self-assembled mesoporous structures with well-ordered nano- scale channels could be used in applications such as molecular separation, nano-optics, molecular electronics, nanomedicine and catalysis1–7. However, the domain sizes that can be created in such systems are limited by our lack of a detailed understanding of the relevant growth processes8–12. Here we ...
09-Jan-2011
Nature Strucrural & Molecular Biology, online article
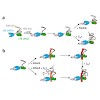
The endoplasmic reticulum is the site of folding, assembly and quality control for proteins of the secretory pathway. The ATP-regulated Hsp70 chaperone BiP (heavy chain–binding protein), together with cochaperones, has important roles in all of these processes. The functional cycle of Hsp70s is determined by conformational transitions that are required for ...
03-Jan-2011
J. Phys. Chem. B, online article
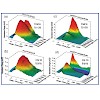
Ultrafast spectroscopy in the visible and midinfrared is used to study the reaction dynamics of two lighttriggered model peptides containing an azobenzene derivative as a switching element. One model peptide, the AzoTrp- Zip2, forms a beta-hairpin structure in the cis form of the chromophore. This peptide is compared to the core structure consisting of the ...










