Research Area D - Publications 2008
12-Dec-2008
PLOS Genetics, 2008, doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000302, published on 12.12.2008
PLOS genetics, online article
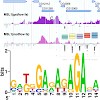
Dosage compensation in male Drosophila relies on the X chromosome–specific recruitment of a chromatin-modifying machinery, the dosage compensation complex (DCC). The principles that assure selective targeting of the DCC are unknown. According to a prevalent model, X chromosome targeting is initiated by recruitment of the DCC core components, MSL1 and MSL2, to a ...
11-Dec-2008
Journal of Molecular Biology , online article
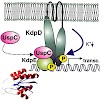
The sensor kinase KdpD and the response regulator KdpE control induction of the kdpFABC operon encoding the high-affinity K+-transport system KdpFABC in response to K+ limitation or salt stress. Under K+ limiting conditions the Kdp system restores the intracellular K+ concentration, while in response to salt stress K+ is accumulated far above the normal content. ...
01-Dec-2008
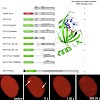
The multifunctional nuclear protein positive cofactor 4 (PC4) is involved in various cellular processes including transcription, replication, and chromatin organization. Recently, PC4 has been identifi ed as a suppressor of oxidative mutagenesis in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae . To investigate a potential role of PC4 in mammalian DNA repair, we ...
02-Nov-2008
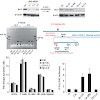
Genetic and epigenetic plasticity allows tumors to evade single-targeted treatments. Here we direct Bcl2-specific short interfering RNA (siRNA) with 5¢-triphosphate ends (3p-siRNA) against melanoma. Recognition of 5¢-triphosphate by the cytosolic antiviral helicase retinoic acid–induced protein I (Rig-I, encoded by Ddx58) activated innate immune cells such as ...
25-Oct-2008
Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2008, 10.1007/s00262-008-0606-2, published on 25.10.2008
Cancer Immunol Immunother, online article
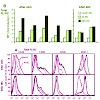
Dendritic cell (DC) vaccines have emerged as a promising strategy to induce antitumoral cytotoxic T cells for the immunotherapy of cancer. The maturation state of DC is of critical importance for the success of vaccination, but the most effective mode of maturation is still a matter of debate. Whereas immature DC carry the risk of inducing tolerance, extensive ...
24-Oct-2008
PNAS, 2008, DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0810692105, published on 24.10.2008
www.pnas.org, online article
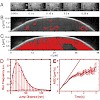
Messenger ribonucleoprotein particles (mRNPs) move randomly within nucleoplasm before they exit from the nucleus. To further understand mRNP trafficking, we have studied the intranuclear movement of a specific mRNP, the BR2 mRNP, in salivary gland cells in Chironomus tentans. Their polytene nuclei harbor giant chromosomes separated by vast regions of nucleoplasm, ...
20-Oct-2008

The identification of interaction partners in protein complexes is a major goal in cell biology. Here we present a reliable affi nity purifi cation strategy to identify specifi c interactors that combines quantitative SILAC-based mass spectrometry with characterization of common contaminants binding to affi nity matrices (bead proteomes). This strategy can be ...
17-Oct-2008
Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology, online article
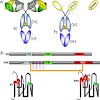
It is well established that all camelids have unique antibodies circulating in their blood. Unlike antibodies fromother species, these special antibodies are devoid of light chains and are composed of a heavy-chainhomodimer. These so-called heavy-chain antibodies (HCAbs) are expressed after a V–D–J rearrangement and require dedicated constant g-genes. An immune ...
05-Sep-2008
Molecular Cell, 2008, 31, 762-72 published on 05.09.2008
Molecular Cell, online article

RNA interference is a powerful way to study gene function and is frequently combined with microarray analysis. Here we introduce a similar technology at the protein level by simultaneously applying Stable Isotope Labeling by Amino acids in Cell culture (SILAC) and RNA interference (RNAi) to Drosophila SL2 cells. After knockdown of ISWI, an ATP-hydrolyzing motor ...
22-Aug-2008
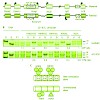
Imprinted genes are important in development and their allelic expression is mediated by imprinting control regions (ICRs). On their DNA-methylated allele, ICRs are marked by trimethylation at H3 Lys 9 (H3K9me3) and H4 Lys 20 (H4K20me3), similar to pericentric heterochromatin. Here, we investigate which histone methyltransferases control this methylation of ...
30-Jul-2008
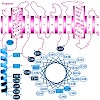
Selected residues of transmembrane domain (TM) IX were previously shown to play key roles in ligand binding and transport in members of the Na+/solute symporter family. Using the Na+/proline transporter PutP as a model, a complete Cys scanning mutagenesis of TM IX (positions 324 to 351) was performed here to further investigate the functional significance of the ...
12-Jul-2008
Molecular & Cellular Proteomics , online article
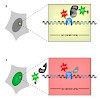
Genetic high-throughput screens have yielded large sets of potential protein-protein interactions now to be verified and further investigated. Here we present a simple assay to directly visualize protein-protein interactions in single living cells. Using a modified lac repressor system, we tethered a fluorescent bait at a chromosomal lac operator array and ...
01-Jul-2008
www.landesbioscience.com, online article

The precise coordination of the different steps of DNA replication is critical for the maintenance of genome stability. We have probed the mechanisms coupling various components of the replication machinery and their response to polymerase stalling by inhibition of the DNA polymerases in living mammalian cells with aphidicolin. We observed little change in the ...
21-Jun-2008
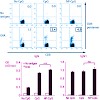
Viral nucleic acids are recognized by specific pattern-recognition receptors of the Toll-like and RIG-I-like receptor families. Synthetic DNA and RNA oligonucleotides can activate the immune system through these receptors and potentiate Ab and CD8 cytotoxic responses to Ags. Systemic application of immunostimulatory oligonucleotides however also results in a ...
20-Jun-2008
EMBO reports, online article
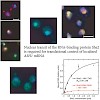
Cytoplasmic localization and localized translation of messenger RNAs contribute to asymmetrical protein distribution. Recognition of localized mRNAs by RNA-binding proteins can occur in the cytoplasm or, alternatively, co- or post-transcriptionally in the nucleus. In budding yeast, mRNAs destined for localization are bound by the She2 protein before their nuclear ...
06-Jun-2008
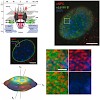
Fluorescence light microscopy allows multicolor visualization of cellular components with high specificity, but its utility has until recently been constrained by the intrinsic limit of spatial resolution. We applied three-dimensional structured illumination microscopy (3D-SIM) to circumvent this limit and to study the mammalian nucleus. By simultaneously imaging ...
30-May-2008
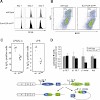
H4K20 methylation is a broad chromatin modification that has been linked with diverse epigenetic functions. Several enzymes target H4K20 methylation, consistent with distinct mono-, di-, and trimethylation states controlling different biological outputs. To analyze the roles of H4K20 methylation states, we generated conditional null alleles for the two Suv4-20h ...
28-May-2008
www.molbiolcell.org , online article
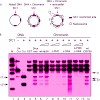
Heterochromatic chromosomal regions undergo large-scale reorganization and progressively aggregate, forming chromocenters. These are dynamic structures that rapidly adapt to various stimuli that influence gene expression patterns, cell cycle progression, and differentiation. Np95-ICBP90 (m- and h-UHRF1) is a histone-binding protein expressed only in proliferating ...
19-May-2008
BMC Genomics, online article
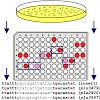
Photorhabdus luminescens is a Gram-negative luminescent enterobacterium and a symbiote to soil nematodes belonging to the species Heterorhabditis bacteriophora. P.luminescens is simultaneously highly pathogenic to insects. This bacterium exhibits a complex life cycle, including one symbiotic stage characterized by colonization of the upper nematode gut, and a ...
09-May-2008
Traffic, online article
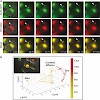
Intracellular mRNA localization is a common mechanism to achieve asymmetric distributions of proteins. Previous studies have revealed that in a number of cell types, differentmRNA species are localized by the same transport machinery. However, it has been unclear if these individual mRNA species are specifically sorted into separate or common ribonucleoprotein ...
08-May-2008

In higher eukaryotes, an unusual C-terminal domain (CTD) is crucial to the function of RNA polymerase II in transcription. The CTD consists of multiple heptapeptide repeats; differences in the number of repeats between organisms and their degree of conservation have intrigued researchers for two decades. Here, we review the evolution of the CTD at the molecular ...
27-Apr-2008

Fluorescent proteins (FP) are widely used as in vivo reporter molecules and are available in multiple colors spanning almost the entire visible light spectrum. Genetically fused to any protein target, FPs offer a powerful tool to study protein localization and dynamics. After the isolation of the prototypical green fluorescent protein (GFP) from the jellyfish ...
24-Apr-2008
Microb Cell Fact, online article
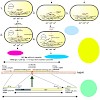
Introducing point mutations into bacterial chromosomes is important for further progress in studies relying on functional genomics, systems- and synthetic biology, and for metabolic engineering. For many investigations, chromosomal systems are required rather than artificial plasmid based systems. Here we describe the introduction of a single point mutation into ...
16-Apr-2008
European Journal of Pharmacology, online article
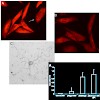
Antibodies against the neurite outgrowth inhibitor Nogo-A enhance axonal regeneration following spinal cord injury. However, antibodies directed against myelin components can also enhance CNS inflammation. The present study was designed to assess the efficacy of DNA vaccination for generating antibodies against Nogo-A and to study their pathogenic potential in a ...
01-Apr-2008
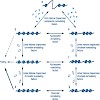
Chromatin serves to package, protect and organize the complex eukaryotic genomes to assure their stable inheritance over many cell generations. At the same time, chromatin must be dynamic to allow continued use of DNA during a cell’s lifetime. One important principle that endows chromatin with flexibility involves ATPdependent ‘remodeling’ factors, which alter ...
19-Mar-2008
Heinrich Leonhardt

CIPSM-Researchers Heinrich Leonhardt and Ulrich Rothbauer win the Binder-Innovation-Award for their work on the usage of fluorescent nano-antibodies to detect biological structures and processes in living cells. From left to right: Prof. Vestweber (President of the German Association of Cellbiology), Prof. Baumeister (MPI Martinsried), Dr. Ankerhold (Carl ...
04-Mar-2008
Current Opinion in Genetics & Development, 2008, 18, 175-80 published on 04.03.2008
Current Opinion in Genetics & Development, online article
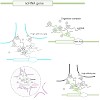
The combination of chromatin structure and the organization of chromosomes in eukaryotic nuclei affects many genome functions. Distinct functional states of genes ranging from ‘highly active’ to ‘silenced’ correlate with particular nucleosome arrangements, histone variants, histone modifications, and interactions of non-histone regulators. Transcription factors ...
08-Feb-2008
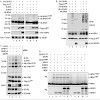
The ubiquitin-like SUMO system functions by a cyclic process of modification and demodification, and recent data suggest that the nucleolus is a site of sumoylation–desumoylation cycles.For example, the tumour suppressor ARF stimulates sumoylation of nucleolar proteins. Here, we show that the nucleolar SUMOspecific protease SENP3 is associated with nucleophosmin ...
06-Feb-2008

The linker histone H1 binds to the DNA in between adjacent nucleosomes and contributes to chromatin organization and transcriptional control. It is known that H1 carries diverse posttranslational modifications (PTMs), including phosphorylation, lysine methylation and ADP-ribosylation. Their biological functions, however, remain largely unclear. This is in part ...
01-Feb-2008
Expert Reviews, online article
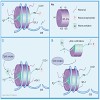
Many phenotypic changes of eukaryotic cells due to changes in gene expression depend on alterations in chromatin structure. Processes involved in the alteration of chromatin are diverse and include post-translational modifications of histone proteins, incorporation of specific histone variants, methylation of DNA and ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling. ...










